444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Nuclear Waste Disposal System market involves technologies and solutions designed for the safe and effective management of radioactive waste generated from nuclear power plants, medical facilities, research institutions, and industrial processes. These systems encompass various methods such as deep geological repositories, interim storage facilities, and advanced treatment technologies aimed at minimizing environmental impact and ensuring long-term containment of radioactive materials.
Meaning
Nuclear Waste Disposal Systems are critical infrastructure designed to handle radioactive waste materials generated from nuclear activities. These systems include storage, treatment, and disposal solutions that adhere to stringent safety, regulatory, and environmental standards. The primary goal is to isolate and contain radioactive waste to prevent environmental contamination and safeguard public health over extended periods, spanning thousands of years.
Executive Summary
The Nuclear Waste Disposal System market is driven by increasing nuclear power generation, decommissioning activities, and regulatory mandates for safe waste management. Key market players focus on developing robust disposal technologies, site characterization methodologies, and public engagement strategies. With global expansion in nuclear energy usage and growing emphasis on sustainable waste management practices, the market presents opportunities for innovation and investment in advanced disposal solutions.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market:
Market Restraints
Despite growth prospects, the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market faces challenges:
Market Opportunities
The Nuclear Waste Disposal System market offers opportunities for innovation and growth:
Market Dynamics
The Nuclear Waste Disposal System market dynamics are shaped by technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, public perception, and geopolitical factors. Continuous innovation in disposal technologies, safety protocols, and environmental stewardship drives market competitiveness and operational efficiency. Strategic partnerships, joint ventures, and international cooperation facilitate knowledge exchange, regulatory harmonization, and market expansion opportunities across global regions.
Regional Analysis
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market due to established nuclear power infrastructure, regulatory compliance frameworks, and investments in waste management technologies. Asia-Pacific exhibits significant growth potential driven by expanding nuclear energy capacities, infrastructure development, and increasing focus on sustainable development practices. Emerging markets in Latin America, Middle East & Africa are poised for market growth with rising energy demands, infrastructure investments, and regulatory developments in nuclear waste management.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
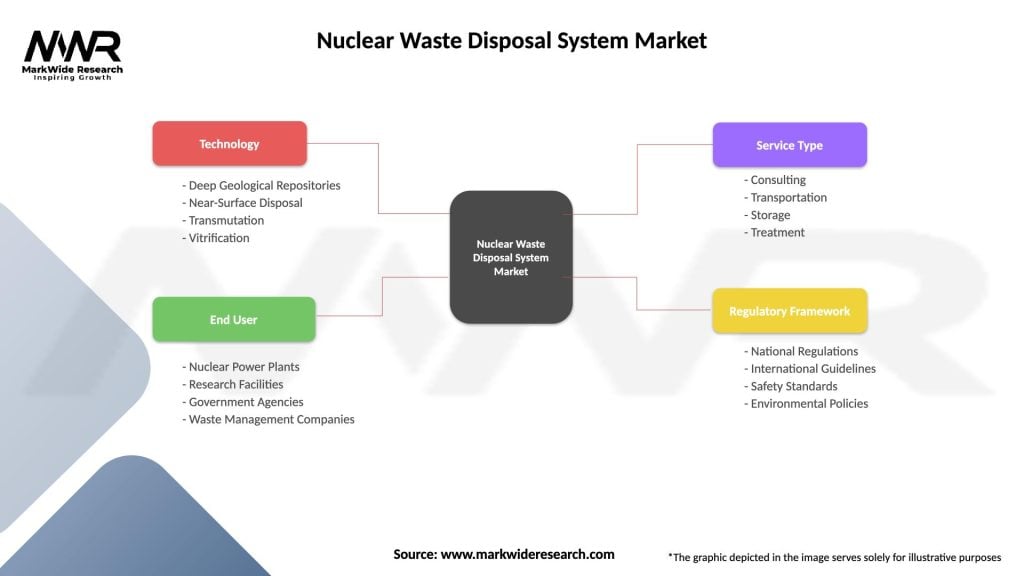
Segmentation
The Nuclear Waste Disposal System market can be segmented based on:
Category-wise Insights
Each category of Nuclear Waste Disposal Systems offers unique solutions tailored to specific waste types and disposal requirements:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Industry participants benefit from Nuclear Waste Disposal Systems in various ways:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths: Technological expertise, regulatory compliance, and long-term environmental stewardship ensuring safe and effective radioactive waste management.
Weaknesses: High capital costs, regulatory complexities, public opposition, and technical challenges in developing and implementing disposal technologies.
Opportunities: Innovation in disposal technologies, international collaboration, market expansion in emerging economies, and public engagement strategies fostering acceptance.
Threats: Regulatory changes, political uncertainties, public resistance, and economic factors impacting market dynamics, project timelines, and profitability.
Market Key Trends
Key trends shaping the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market include:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has influenced the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market in several ways:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market dynamics and industry trends, analysts recommend the following strategies for Nuclear Waste Disposal System stakeholders:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market is optimistic, driven by technological advancements, regulatory enhancements, and increasing global emphasis on sustainable development goals. As countries expand nuclear energy capacities, decommission aging facilities, and invest in waste management infrastructure, demand for advanced disposal technologies, regulatory compliance solutions, and public engagement strategies will grow. Stakeholders that prioritize innovation, sustainability, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder engagement are well-positioned to capitalize on market opportunities, drive industry transformation, and lead in safe and effective nuclear waste management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Nuclear Waste Disposal System market plays a crucial role in managing radioactive waste from nuclear activities while ensuring environmental protection, public safety, and regulatory compliance. Despite challenges such as regulatory complexities, public opposition, and technical uncertainties, the market offers opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and sustainable development. By focusing on technological innovation, regulatory compliance, public engagement, and sustainability initiatives, industry stakeholders can navigate market dynamics, capitalize on growth opportunities, and advance safe and effective nuclear waste disposal practices globally.
What is Nuclear Waste Disposal System?
Nuclear Waste Disposal System refers to the methods and technologies used to safely manage and dispose of radioactive waste generated from nuclear power plants and other nuclear applications. This includes various strategies such as deep geological repositories, interim storage facilities, and advanced containment systems.
What are the key players in the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market?
Key players in the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market include companies like Areva, Waste Control Specialists, and Holtec International, which specialize in nuclear waste management and disposal solutions. These companies are involved in developing technologies and facilities for safe waste handling, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market?
The main drivers of the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market include the increasing demand for nuclear energy, the need for effective waste management solutions, and stringent regulatory requirements for radioactive waste disposal. Additionally, advancements in disposal technologies are also contributing to market growth.
What challenges does the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market face?
The Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market faces challenges such as public opposition to nuclear waste facilities, high costs associated with waste disposal, and the long-term environmental impacts of radioactive waste. These factors can hinder the development and implementation of disposal solutions.
What opportunities exist in the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market?
Opportunities in the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market include the development of innovative disposal technologies, partnerships between governments and private companies, and the potential for international collaboration on waste management solutions. These factors can enhance the effectiveness and safety of nuclear waste disposal.
What trends are shaping the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market?
Trends shaping the Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market include the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental protection, advancements in waste recycling technologies, and the exploration of alternative disposal methods such as deep borehole disposal. These trends are influencing how nuclear waste is managed and disposed of.
Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Deep Geological Repositories, Near-Surface Disposal, Transmutation, Vitrification |
| End User | Nuclear Power Plants, Research Facilities, Government Agencies, Waste Management Companies |
| Service Type | Consulting, Transportation, Storage, Treatment |
| Regulatory Framework | National Regulations, International Guidelines, Safety Standards, Environmental Policies |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Nuclear Waste Disposal System Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at