444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market refers to the process of dismantling and disposing of offshore oil and gas facilities in the North Sea region. As oil and gas fields in the North Sea reach maturity, there is a growing need to decommission these aging facilities in a safe and environmentally responsible manner. The market for offshore decommissioning services has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing number of decommissioning projects and the stringent regulations imposed by regulatory bodies.
Meaning
Offshore decommissioning involves the safe removal of offshore platforms, wells, pipelines, and other infrastructure that are no longer economically viable or environmentally sustainable. This process includes plugging and abandonment of wells, removal of platforms and subsea structures, and the disposal or recycling of decommissioned materials. The aim of decommissioning is to restore the marine ecosystem and minimize the potential risks associated with abandoned infrastructure.
Executive Summary
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market has experienced substantial growth in recent years, primarily due to the maturing oil and gas fields in the region. The decommissioning process presents significant challenges in terms of technical complexity, regulatory compliance, and cost management. However, it also offers lucrative opportunities for service providers and stakeholders involved in the decommissioning value chain. The market is characterized by the presence of established players and increasing collaboration between industry participants to leverage their expertise and resources.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
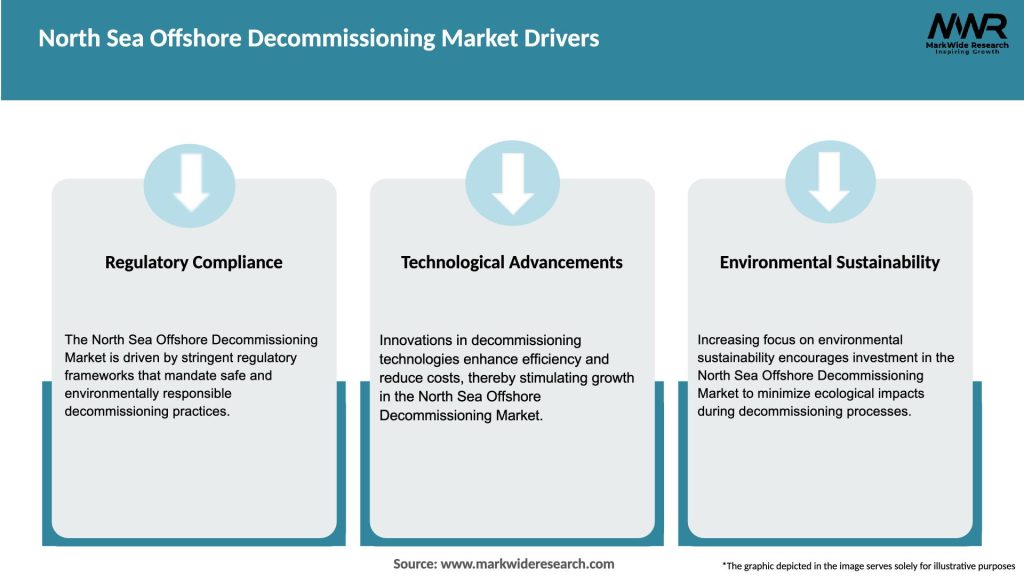
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market is characterized by dynamic factors that influence its growth and evolution. The market dynamics are shaped by various trends, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, industry collaborations, and the evolving energy landscape. The interplay of these factors creates both challenges and opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders involved in offshore decommissioning activities.
Regional Analysis
The North Sea region encompasses various countries, including the United Kingdom, Norway, the Netherlands, Denmark, and Germany. Each country has its regulatory framework and decommissioning requirements, which influence the regional dynamics of the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market. The UK and Norway are the key players in the market, accounting for a significant share of decommissioning activities. These countries have well-established regulatory bodies and support infrastructure for decommissioning operations.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
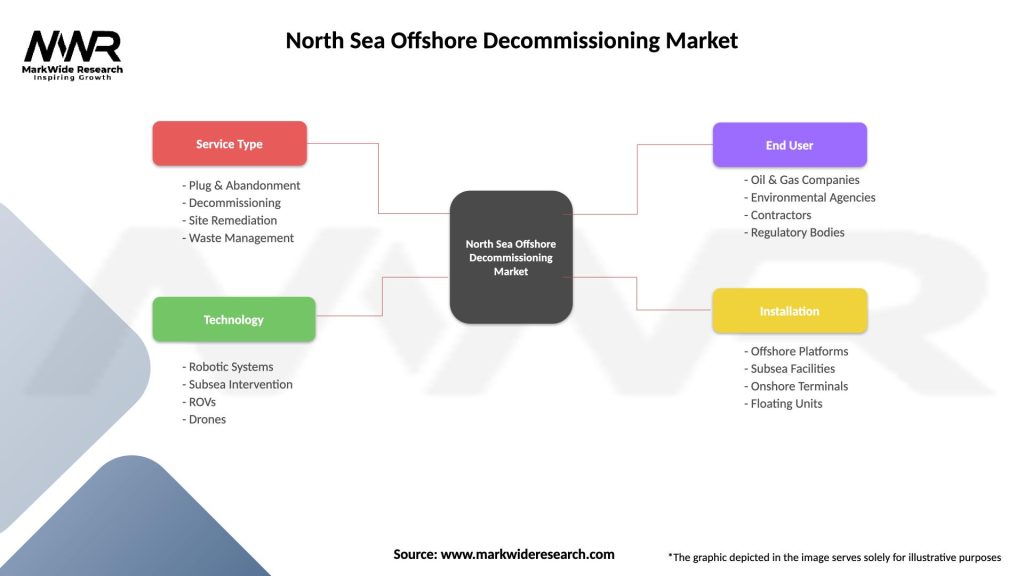
Segmentation
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market can be segmented based on various parameters, including the type of offshore facility, decommissioning stage, service type, and geography. The type of offshore facility includes platforms, wells, pipelines, and subsea structures. The decommissioning stage refers to the different phases of the decommissioning process, such as planning, well plugging and abandonment, platform removal, and site remediation. Service types include engineering and project management, well services, platform removal, and waste disposal.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had an impact on the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market, causing disruptions and delays in decommissioning activities. The pandemic led to workforce restrictions, supply chain disruptions, and a decline in oil prices, which affected the financial viability of decommissioning projects. However, the long-term demand for decommissioning services remains strong, and the industry has adapted to the challenges by implementing safety protocols, remote work practices, and technological solutions.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years as more offshore facilities reach the end of their operational life. The market will be driven by the increasing number of decommissioning projects, the need for environmental sustainability, and the development of advanced technologies and methodologies. Collaboration between industry players, international cooperation, and regulatory support will play crucial roles in shaping the future of the market.
Conclusion
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market presents both challenges and opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. Decommissioning aging offshore infrastructure is essential to ensure environmental sustainability and mitigate potential risks. The market is driven by factors such as aging infrastructure, environmental concerns, regulatory compliance, and technological advancements. Collaboration, innovation, and a focus on environmental stewardship will be key to navigating the evolving market landscape and achieving successful decommissioning outcomes in the North Sea region.
What is North Sea Offshore Decommissioning?
North Sea Offshore Decommissioning refers to the process of safely dismantling and removing offshore oil and gas infrastructure in the North Sea, including platforms, pipelines, and subsea installations. This process is essential for environmental protection and compliance with regulatory standards.
What are the key players in the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market?
Key players in the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market include companies like Petrofac, Wood Group, and Aker Solutions, which specialize in decommissioning services and project management. These companies are involved in various aspects of decommissioning, from planning to execution, among others.
What are the main drivers of the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market?
The main drivers of the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market include the aging of offshore infrastructure, increasing regulatory pressures for environmental compliance, and the shift towards sustainable energy practices. Additionally, the need for safe disposal of hazardous materials is a significant factor.
What challenges does the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market face?
The North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market faces challenges such as high operational costs, complex regulatory frameworks, and environmental concerns related to decommissioning activities. Additionally, the availability of skilled labor and technology can impact project timelines.
What opportunities exist in the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market?
Opportunities in the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market include advancements in decommissioning technologies, increased investment in renewable energy projects, and the potential for repurposing decommissioned sites for new energy initiatives. These factors can lead to innovative solutions and partnerships.
What trends are shaping the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market?
Trends shaping the North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market include the adoption of digital technologies for project management, increased focus on sustainability and environmental impact assessments, and collaborative approaches among stakeholders. These trends aim to enhance efficiency and reduce costs in decommissioning projects.
North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Plug & Abandonment, Decommissioning, Site Remediation, Waste Management |
| Technology | Robotic Systems, Subsea Intervention, ROVs, Drones |
| End User | Oil & Gas Companies, Environmental Agencies, Contractors, Regulatory Bodies |
| Installation | Offshore Platforms, Subsea Facilities, Onshore Terminals, Floating Units |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in North Sea Offshore Decommissioning Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at