444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The North America floating offshore wind power market represents a transformative segment of the renewable energy sector, experiencing unprecedented growth as the region seeks to harness vast offshore wind resources in deeper waters. Floating offshore wind technology enables wind energy generation in water depths exceeding 60 meters, where traditional fixed-bottom foundations become economically unfeasible. This innovative approach opens access to approximately 85% of offshore wind resources that were previously unreachable, significantly expanding the potential for clean energy generation across North American coastlines.
Market dynamics indicate robust expansion driven by technological advancements, supportive government policies, and increasing corporate commitments to renewable energy. The region’s extensive coastlines, particularly along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts, offer exceptional wind resources with capacity factors often exceeding 45% in optimal locations. California, Maine, and Hawaii have emerged as pioneering states, implementing comprehensive floating offshore wind development programs that serve as models for broader regional adoption.
Investment momentum continues accelerating as major energy companies, utilities, and technology developers recognize the substantial potential of floating wind platforms. The technology’s ability to access stronger, more consistent winds in deeper waters translates to higher energy yields and improved project economics. Recent developments demonstrate growing confidence in commercial viability, with multiple demonstration projects transitioning toward full-scale commercial deployment phases.
The North America floating offshore wind power market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the development, manufacturing, installation, and operation of floating wind turbine platforms in North American waters. Floating offshore wind systems utilize specialized floating foundations that are moored to the seabed, enabling wind energy generation in water depths typically ranging from 60 to 200 meters or deeper.
This market encompasses various stakeholder categories including technology developers, turbine manufacturers, floating platform designers, installation contractors, utility companies, and supporting service providers. The technology represents a significant evolution from traditional fixed-bottom offshore wind installations, offering access to previously untapped wind resources in deeper waters where wind speeds are typically higher and more consistent.
Key components of floating offshore wind systems include the wind turbine generator, floating platform structure, mooring system, dynamic cables, and onshore transmission infrastructure. The market covers multiple floating platform technologies, including semi-submersible, spar-buoy, and tension leg platform designs, each optimized for specific water depths, environmental conditions, and project requirements.
North America’s floating offshore wind power market stands at a pivotal juncture, transitioning from demonstration phases toward commercial-scale deployment. The market benefits from exceptional wind resources, supportive regulatory frameworks, and increasing recognition of floating wind technology’s potential to significantly contribute to regional decarbonization goals. California leads North American development efforts, with ambitious targets driving substantial investment in floating wind infrastructure and supply chain development.
Technology maturation has reached critical milestones, with multiple floating platform designs proving commercial viability through successful demonstration projects. Cost reduction trajectories indicate improving project economics, supported by economies of scale, manufacturing optimization, and supply chain development. Federal and state policies provide strong foundation for market growth, including lease area designations, streamlined permitting processes, and financial incentives supporting early-stage development.
Market challenges include high capital requirements, complex installation logistics, and the need for specialized port infrastructure. However, these obstacles are being systematically addressed through industry collaboration, technology innovation, and strategic infrastructure investments. Supply chain development represents a critical success factor, with regional manufacturing capabilities expanding to support growing project pipelines and reduce dependence on international suppliers.
Strategic market insights reveal several fundamental trends shaping the North American floating offshore wind landscape:
Primary market drivers propelling North American floating offshore wind development encompass technological, economic, and policy factors that create compelling conditions for market expansion. Renewable energy mandates across multiple states establish clear demand signals, with coastal states particularly relying on offshore wind to meet ambitious clean energy targets. These policy commitments provide long-term market visibility essential for major capital investments in floating wind infrastructure.
Technological advancement serves as a fundamental driver, with floating platform designs achieving commercial readiness through successful demonstration projects and operational experience. Cost reduction trends make floating wind increasingly competitive with other renewable energy sources, particularly when considering the superior capacity factors achievable in deeper waters. Advanced materials, improved manufacturing processes, and optimized installation techniques continue driving down project costs while enhancing performance reliability.
Resource accessibility represents a unique advantage, as floating technology unlocks wind resources in areas with exceptional wind quality but unsuitable seabed conditions for fixed foundations. Environmental benefits include reduced visual impact from shore, minimal seabed disturbance, and the ability to locate projects in areas with less conflict with other ocean uses. Corporate renewable energy procurement provides additional demand drivers, with major corporations seeking large-scale clean energy sources to meet sustainability commitments.
Grid modernization initiatives create synergistic opportunities, as utilities invest in transmission infrastructure capable of handling variable renewable energy sources. Economic development potential drives state and local government support, with floating wind projects creating substantial employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and ongoing operations and maintenance activities.
Significant market restraints continue challenging floating offshore wind development in North America, requiring strategic solutions to enable widespread commercial deployment. High capital costs remain the primary barrier, with floating wind projects requiring substantial upfront investments in specialized equipment, installation vessels, and supporting infrastructure. Current project costs exceed those of fixed-bottom offshore wind, though cost reduction trajectories indicate improving economics over time.
Technical complexity presents ongoing challenges, particularly regarding dynamic cable systems, mooring design optimization, and long-term platform durability in harsh marine environments. Limited installation capacity constrains project development timelines, as specialized vessels and equipment required for floating platform installation remain scarce and expensive. The industry faces a chicken-and-egg scenario where limited project volumes don’t justify major investments in installation infrastructure.
Regulatory uncertainty in some jurisdictions creates development risks, despite generally supportive policy environments. Permitting complexity involves multiple federal and state agencies, potentially extending project development timelines and increasing costs. Grid connection challenges arise from the need to transmit power from remote offshore locations to onshore demand centers, requiring significant transmission infrastructure investments.
Supply chain limitations include insufficient domestic manufacturing capacity for key components, creating dependence on international suppliers and potential supply chain vulnerabilities. Skilled workforce availability represents another constraint, as the industry requires specialized expertise in marine operations, floating platform design, and offshore installation techniques. Financial market familiarity with floating wind technology remains limited, potentially affecting project financing availability and terms.
Substantial market opportunities position North America’s floating offshore wind sector for transformative growth, driven by unique geographic advantages and supportive market conditions. Vast untapped resources along the Pacific Coast offer exceptional development potential, with water depths and wind conditions ideally suited for floating wind technology. California’s ambitious targets create immediate market opportunities, with the state planning multiple gigawatts of floating wind capacity to support its carbon neutrality goals.
Technology export potential represents a significant opportunity, as North American companies developing floating wind expertise can compete in global markets experiencing similar resource constraints. Supply chain development offers opportunities for manufacturing job creation and economic development in coastal communities, particularly in regions with existing maritime industrial capabilities. Port infrastructure development creates additional economic opportunities while building essential capabilities for floating wind deployment.
Hybrid project opportunities combine floating wind with energy storage, hydrogen production, or aquaculture operations, creating additional revenue streams and improving project economics. Research and development initiatives supported by federal funding create opportunities for technology advancement and cost reduction. International collaboration enables knowledge sharing and technology transfer with leading floating wind markets in Europe and Asia.
Grid modernization synergies create opportunities for integrated planning that optimizes both renewable energy integration and transmission system reliability. Environmental co-benefits including marine habitat enhancement and carbon sequestration research offer additional value propositions. Energy independence benefits align with national security priorities, creating potential for additional policy support and funding opportunities.
Complex market dynamics shape the North American floating offshore wind landscape, reflecting the interplay between technological innovation, policy support, economic factors, and industry development. Technology maturation cycles influence market timing, with demonstration projects providing crucial operational data that validates commercial viability and attracts investment capital. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that successful demonstration projects significantly accelerate subsequent commercial development phases.
Competitive dynamics involve both collaboration and competition among industry participants, with technology developers, utilities, and investors forming strategic partnerships while competing for prime development sites and market share. Supply chain evolution creates dynamic relationships between component manufacturers, platform developers, and project developers, with vertical integration strategies emerging as companies seek to control critical value chain elements.
Policy dynamics create both opportunities and uncertainties, as supportive policies drive market development while regulatory changes can significantly impact project economics and timelines. Market consolidation trends reflect the capital-intensive nature of floating wind development, with larger companies acquiring smaller technology developers and development assets. International market influences affect North American development through technology transfer, supply chain competition, and investment flows.
Environmental considerations increasingly influence project development approaches, with stakeholder engagement and environmental impact minimization becoming critical success factors. Grid integration dynamics require coordination between wind developers, transmission operators, and grid planners to ensure optimal system integration and reliability.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing the North American floating offshore wind power market incorporates multiple data sources and analytical approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, technology developers, utility representatives, government officials, and academic researchers actively involved in floating wind development. These interviews provide insights into market trends, technological challenges, policy impacts, and future development prospects.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government reports, industry publications, academic studies, patent filings, and company financial disclosures. Technical literature review covers floating platform design innovations, installation methodologies, operational performance data, and cost analysis studies. Policy analysis examines federal and state legislation, regulatory frameworks, permitting processes, and incentive programs affecting market development.
Market modeling utilizes quantitative analysis of project pipelines, capacity additions, investment flows, and cost trends to identify market patterns and growth trajectories. Competitive intelligence involves systematic tracking of company strategies, technology developments, partnership announcements, and project milestones. Stakeholder mapping identifies key market participants and their roles in the value chain, from technology developers to end users.
Data validation processes ensure information accuracy through cross-referencing multiple sources, expert review, and consistency checking. Scenario analysis explores different market development pathways based on varying assumptions about technology advancement, policy support, and economic conditions. Regional analysis examines state-specific market conditions, resource potential, and development strategies to provide localized insights.
Regional market analysis reveals distinct development patterns and opportunities across North American coastal areas, with each region offering unique advantages and facing specific challenges. West Coast markets lead floating wind development, driven by exceptional wind resources, deep water close to shore, and supportive state policies. California dominates regional activity, with the state accounting for approximately 75% of planned floating wind capacity in North America through 2030.
Pacific Northwest offers substantial long-term potential, with Oregon and Washington developing floating wind strategies to complement existing renewable energy portfolios. The region benefits from existing maritime industrial infrastructure and skilled workforce capabilities that support floating wind development. Deep water access within reasonable distances from shore creates favorable project economics compared to other coastal regions.
East Coast markets present different opportunities and challenges, with Maine emerging as the leading Atlantic floating wind market. The state’s demonstration projects provide valuable operational experience while building local supply chain capabilities. Mid-Atlantic states focus primarily on fixed-bottom offshore wind but maintain interest in floating technology for deeper water areas beyond current lease zones.
Gulf Coast represents an emerging opportunity, with Louisiana and Texas exploring floating wind potential to complement existing offshore energy infrastructure. The region’s extensive offshore experience and port capabilities provide advantages for floating wind development, though hurricane risks require specialized design considerations. Hawaii pursues floating wind as a key component of its renewable energy transition, with island geography creating unique market dynamics and opportunities for innovative project structures.
The competitive landscape for North American floating offshore wind encompasses diverse participants ranging from established energy companies to innovative technology startups, creating a dynamic ecosystem of collaboration and competition. Major market participants include both international companies with global floating wind experience and domestic players developing North American-specific capabilities.
Competitive strategies focus on technology differentiation, supply chain development, strategic partnerships, and project pipeline building. Vertical integration trends see companies expanding across the value chain to control critical capabilities and improve project economics.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct categories within the North American floating offshore wind market, each characterized by specific technology requirements, development timelines, and market dynamics. By Platform Technology, the market divides into three primary categories reflecting different engineering approaches and application suitability.
By Technology:
By Water Depth:
By Application:
Semi-submersible platforms demonstrate clear market leadership through proven performance in demonstration projects and favorable installation characteristics. Technology advantages include excellent stability in various sea states, modular construction enabling onshore assembly, and compatibility with standard installation vessels. Cost optimization benefits from simplified installation procedures and reduced specialized equipment requirements compared to alternative platform designs.
Spar-buoy platforms offer unique advantages for larger turbine applications, with superior motion characteristics enabling optimal turbine performance in challenging conditions. Market positioning focuses on projects requiring maximum energy yield and minimal turbine wear, particularly in areas with severe weather conditions. Development challenges include requirements for deeper water installation and specialized heavy-lift capabilities that may limit near-term deployment opportunities.
Tension leg platforms provide innovative solutions for specific market segments, offering reduced material requirements and compact designs suitable for areas with space constraints. Technical advantages include minimal platform motion and efficient use of materials, potentially enabling cost advantages in appropriate applications. Market limitations arise from specific seabed requirements and limited operational experience compared to alternative platform technologies.
Utility-scale applications drive primary market demand, with projects typically ranging from 200MW to over 1GW capacity to achieve optimal economies of scale. Industrial applications represent emerging opportunities, particularly for hydrogen production facilities requiring large-scale renewable energy inputs. Hybrid systems offer innovative approaches to improve project economics through multiple revenue streams and optimized ocean space utilization.
Industry participants across the floating offshore wind value chain realize substantial benefits from market development, creating compelling incentives for continued investment and participation. Technology developers benefit from expanding market opportunities that justify continued research and development investments while providing pathways to commercial scale and profitability. Revenue diversification opportunities enable companies to expand beyond traditional markets and develop new capabilities.
Utility companies gain access to high-quality renewable energy resources that support decarbonization goals while providing predictable long-term energy costs. Capacity factor advantages of floating wind in optimal locations can exceed 50% annually, providing superior energy yield compared to onshore alternatives. Grid stability benefits emerge from offshore wind’s complementary generation patterns with solar and onshore wind resources.
Manufacturing companies benefit from supply chain development opportunities, with floating wind requiring specialized components and services that create new market segments. Port communities realize economic development benefits through infrastructure investments, job creation, and increased maritime activity. Coastal states achieve energy independence benefits while meeting renewable energy mandates and supporting economic development objectives.
Environmental stakeholders benefit from reduced carbon emissions and minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuel alternatives. Investors gain access to long-term, stable returns supported by power purchase agreements and government policy support. Research institutions benefit from funding opportunities and collaboration with industry partners on technology advancement initiatives.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Transformative market trends are reshaping the North American floating offshore wind landscape, driven by technological innovation, policy evolution, and changing industry dynamics. Platform standardization emerges as a critical trend, with successful designs being replicated across multiple projects to achieve economies of scale and reduce development risks. Modular manufacturing approaches enable cost reduction through standardized components and optimized production processes.
Supply chain localization accelerates as project pipelines justify domestic manufacturing investments, reducing dependence on international suppliers while supporting local economic development. Port infrastructure specialization creates dedicated facilities for floating wind assembly and deployment, optimizing logistics and reducing project costs. Installation vessel development addresses current capacity constraints through purpose-built vessels and innovative installation techniques.
Hybrid project integration combines floating wind with complementary technologies, including energy storage systems, hydrogen production facilities, and aquaculture operations. Digital technology adoption enhances project development through advanced modeling, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Environmental co-benefits receive increasing attention, with projects designed to provide marine habitat enhancement and carbon sequestration benefits.
Financial innovation develops new funding mechanisms and risk management approaches tailored to floating wind project characteristics. Grid integration advancement addresses transmission challenges through innovative cable technologies and grid planning approaches. International collaboration facilitates technology transfer and knowledge sharing between North American and global floating wind markets.
Recent industry developments demonstrate accelerating momentum in North American floating offshore wind markets, with multiple milestone achievements validating commercial viability and attracting increased investment. California’s lease auctions represent landmark events, with successful bidding processes demonstrating strong industry interest and commitment to floating wind development. Winning bid amounts exceeded expectations, indicating confidence in technology and market potential.
Demonstration project successes provide crucial operational data and performance validation, with multiple platforms achieving target performance metrics and demonstrating long-term reliability. Maine’s demonstration projects have operated successfully for multiple years, providing valuable insights into North American operating conditions and maintenance requirements. Technology partnerships between international developers and domestic companies facilitate knowledge transfer and capability building.
Manufacturing announcements indicate growing supply chain commitment, with multiple companies announcing North American production facilities for floating wind components. Port development initiatives create specialized infrastructure for floating wind assembly and deployment, with several coastal states investing in dedicated facilities. Workforce development programs address skill requirements through partnerships between industry, educational institutions, and government agencies.
Policy milestones include federal lease area designations, state procurement targets, and streamlined permitting processes that reduce development barriers. Research funding from federal agencies supports continued technology advancement and cost reduction initiatives. International agreements facilitate collaboration with leading floating wind markets in Europe and Asia.
Strategic recommendations for market participants emphasize the importance of early positioning in this rapidly evolving market while managing development risks and capital requirements. Technology developers should focus on platform standardization and cost optimization while building strategic partnerships with utilities and investors. Demonstration project participation provides valuable operational experience and credibility essential for commercial-scale development.
Utility companies should develop floating wind expertise through pilot projects and strategic partnerships, positioning for larger-scale procurement as technology costs decline. Supply chain participants should evaluate opportunities for domestic manufacturing capabilities, particularly in regions with planned project clusters. Early market entry provides competitive advantages through learning curve benefits and relationship building.
Investors should consider floating wind’s long-term potential while carefully evaluating near-term risks and development timelines. Portfolio diversification across multiple technologies and regions reduces concentration risks while capturing market upside. Policy risk assessment remains critical given the importance of government support for early market development.
Policymakers should maintain consistent support frameworks while addressing infrastructure and workforce development needs. Regional coordination can optimize resource allocation and avoid duplicative efforts across state boundaries. MWR analysis suggests that sustained policy support through initial commercial deployment phases will be crucial for long-term market success.
The future outlook for North America’s floating offshore wind market indicates substantial growth potential driven by technology maturation, cost reduction, and expanding policy support. Market expansion is expected to accelerate significantly through the late 2020s as demonstration projects transition to commercial scale and supply chains develop adequate capacity. Cost reduction trajectories suggest floating wind will achieve competitiveness with fixed-bottom offshore wind by the early 2030s, opening broader market opportunities.
Technology advancement will continue driving performance improvements and cost reductions, with larger turbines, optimized platform designs, and improved installation techniques enhancing project economics. Supply chain maturation will reduce costs and improve project timelines as domestic manufacturing capabilities expand and specialized infrastructure develops. Grid integration solutions will evolve to accommodate large-scale floating wind deployment while maintaining system reliability.
Regional market development will expand beyond current focus areas, with Gulf Coast and additional East Coast markets emerging as significant opportunities. International market integration will facilitate technology transfer and supply chain optimization across global floating wind markets. Hybrid project development will create new market segments and revenue opportunities, particularly in hydrogen production and energy storage applications.
Long-term projections indicate floating wind could represent a substantial portion of North American offshore wind capacity by 2040, with growth rates potentially exceeding 25% annually during peak deployment periods. MarkWide Research forecasts suggest that successful early deployment will establish North America as a major global floating wind market, with potential for technology export and international market leadership.
North America’s floating offshore wind power market represents a transformative opportunity in the renewable energy sector, offering access to vast untapped wind resources while supporting regional decarbonization goals and economic development objectives. Technology maturation has reached critical milestones, with multiple platform designs proving commercial viability and operational reliability through successful demonstration projects.
Market fundamentals remain strong, supported by exceptional wind resources, supportive policy frameworks, and growing industry commitment to floating wind development. Regional leadership from California, Maine, and other coastal states provides momentum for broader market development while creating opportunities for supply chain growth and workforce development. Investment momentum continues building as major energy companies and financial institutions recognize the long-term potential of floating wind technology.
Success factors for market development include continued technology advancement, supply chain localization, workforce development, and sustained policy support through initial commercial deployment phases. Industry collaboration between technology developers, utilities, manufacturers, and government agencies will be essential for addressing development challenges and optimizing market growth. The North America floating offshore wind power market is positioned to become a cornerstone of the region’s clean energy future, offering substantial benefits for industry participants, communities, and the environment while contributing to global leadership in renewable energy innovation.
What is Floating Offshore Wind Power?
Floating Offshore Wind Power refers to wind energy systems that are installed on floating platforms in deep waters, allowing for the harnessing of wind energy in locations where traditional fixed-bottom turbines are not feasible. This technology enables access to stronger and more consistent wind resources, contributing to renewable energy generation.
What are the key companies in the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market?
Key companies in the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market include Ørsted, Equinor, and Dominion Energy, which are actively involved in developing and operating floating wind projects. These companies are focusing on innovative technologies and partnerships to enhance their market presence, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market?
The growth of the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, advancements in floating wind technology, and supportive government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Additionally, the need for energy security and diversification of energy sources plays a significant role.
What challenges does the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market face?
The North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market faces challenges such as high initial capital costs, regulatory hurdles, and environmental concerns related to marine ecosystems. Additionally, the lack of established supply chains for floating wind technology can hinder project development.
What opportunities exist in the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market?
Opportunities in the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market include the potential for large-scale offshore wind farms, technological innovations in turbine design, and increasing investments from both public and private sectors. The growing focus on sustainability and energy transition also presents avenues for expansion.
What trends are shaping the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market?
Trends shaping the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market include the integration of digital technologies for monitoring and maintenance, collaboration between energy companies and technology providers, and a shift towards hybrid energy systems that combine wind with other renewable sources. These trends are enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
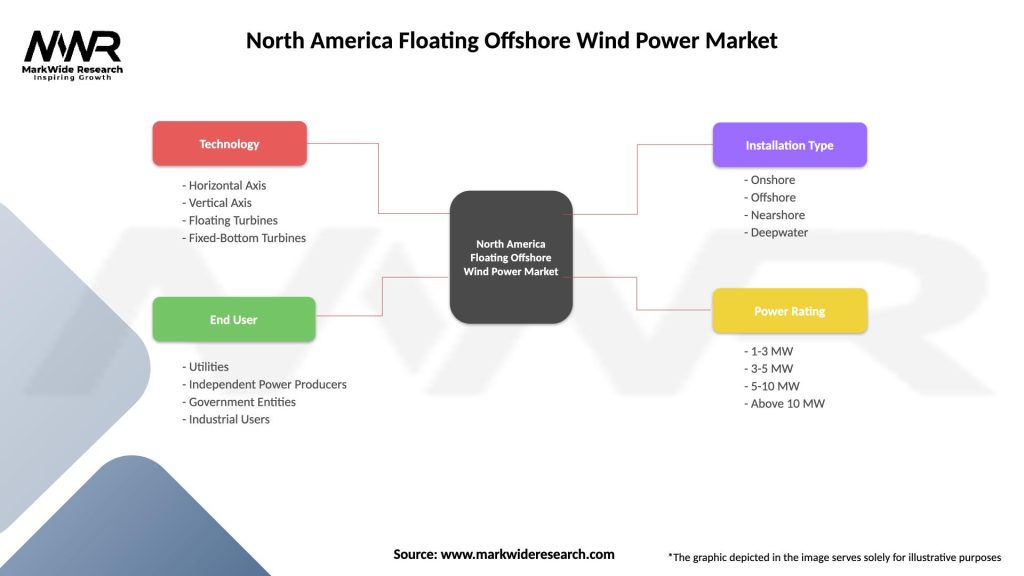
| Technology | Horizontal Axis, Vertical Axis, Floating Turbines, Fixed-Bottom Turbines |
| End User | Utilities, Independent Power Producers, Government Entities, Industrial Users |
| Installation Type | Onshore, Offshore, Nearshore, Deepwater |
| Power Rating | 1-3 MW, 3-5 MW, 5-10 MW, Above 10 MW |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the North America Floating Offshore Wind Power Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at