444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market represents a promising sector within the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, offering innovative solutions for treating genetic disorders and chronic diseases. Unlike viral vectors, non-viral vectors provide a safer and more versatile approach to gene delivery, opening up new avenues for therapeutic interventions. This market is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing the efficacy and safety of non-viral gene therapy platforms.
Meaning
Non-viral vectors gene therapy involves the delivery of therapeutic genes into target cells using non-viral vectors, such as liposomes, nanoparticles, and polymers. Unlike viral vectors, which carry the risk of immunogenicity and insertional mutagenesis, non-viral vectors offer a safer alternative for gene delivery. This technology holds promise for the treatment of various genetic disorders, cancers, and infectious diseases by enabling precise targeting and controlled gene expression.
Executive Summary
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market has witnessed significant growth driven by advancements in gene editing technologies, increasing investment in research and development, and rising demand for personalized medicine. Key stakeholders are leveraging non-viral vectors to develop innovative gene therapies with improved safety profiles and therapeutic outcomes. However, challenges such as delivery efficiency, scalability, and regulatory hurdles remain areas of focus for industry players.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by scientific advancements, technological innovation, regulatory considerations, and market dynamics. As research progresses and clinical data accumulates, the market is poised for growth and expansion, driven by the increasing recognition of gene therapy as a viable treatment modality for a diverse range of diseases.
Regional Analysis
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as research infrastructure, healthcare expenditure, regulatory frameworks, and market demand. Key regions include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa, each offering unique opportunities and challenges for market participants.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
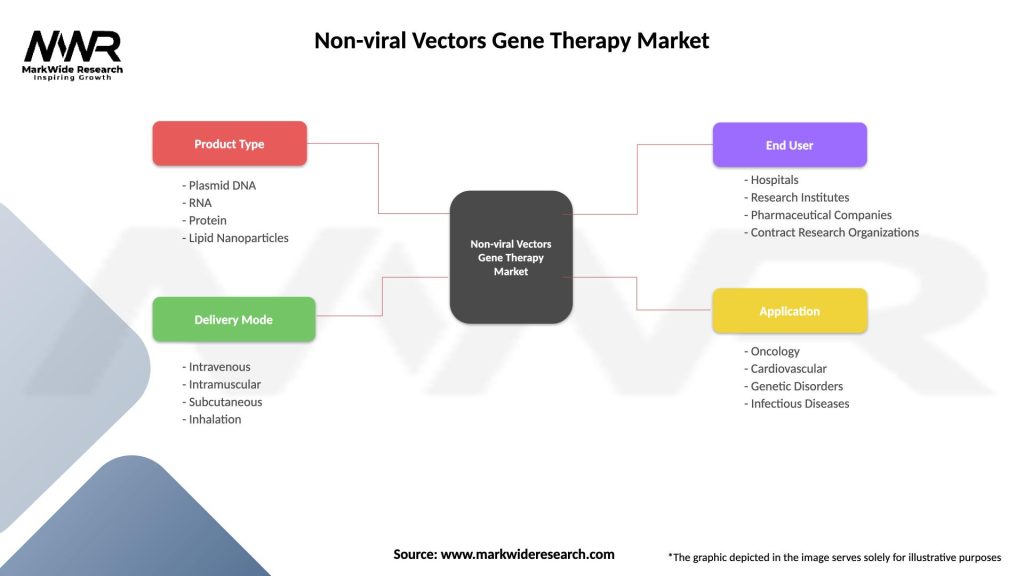
Segmentation
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market can be segmented based on factors such as vector type, application, disease indication, and end-user. This segmentation provides insights into market dynamics and helps stakeholders identify target markets, tailor their strategies, and address specific customer needs.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the non-viral vectors gene therapy market. While it has accelerated research and development efforts in some areas, it has also disrupted clinical trials and supply chains, leading to delays in product development and commercialization. However, the pandemic has underscored the importance of innovative gene therapy approaches in addressing global health challenges and may drive increased investment in the field.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market is poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years, driven by advancements in delivery technologies, expanding therapeutic applications, and increasing investment in research and development. Despite challenges and uncertainties, the market holds immense potential to revolutionize the treatment of genetic disorders, cancer, and other diseases, paving the way for personalized and targeted therapies.
Conclusion
The non-viral vectors gene therapy market represents a rapidly evolving sector within the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, offering promising solutions for addressing unmet medical needs and advancing personalized medicine. While challenges remain, including delivery efficiency, regulatory complexities, and competitive pressures, ongoing innovation and collaboration are driving progress and shaping the future of gene therapy. By harnessing the potential of non-viral vectors and embracing emerging technologies, stakeholders can accelerate the development and commercialization of safe, effective, and accessible gene therapies for patients worldwide.
What is Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy?
Non-viral vectors gene therapy refers to methods of delivering genetic material into cells without the use of viral carriers. This approach often utilizes techniques such as liposomes, nanoparticles, and electroporation to facilitate gene transfer for therapeutic purposes.
What are the key companies in the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market?
Key companies in the non-viral vectors gene therapy market include Cellectis, Synlogic, and Moderna, which are involved in developing innovative therapies and technologies. These companies focus on various applications, including cancer treatment and genetic disorders, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market?
The growth of the non-viral vectors gene therapy market is driven by increasing investments in gene therapy research, advancements in delivery technologies, and a rising prevalence of genetic disorders. Additionally, the growing acceptance of personalized medicine is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market face?
Challenges in the non-viral vectors gene therapy market include issues related to the efficiency of gene delivery, potential immune responses, and regulatory hurdles. These factors can hinder the development and commercialization of new therapies.
What opportunities exist in the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market?
Opportunities in the non-viral vectors gene therapy market include the potential for developing novel therapies for rare diseases and the integration of advanced technologies like CRISPR. The increasing collaboration between biotech firms and research institutions also presents significant growth prospects.
What trends are shaping the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market?
Current trends in the non-viral vectors gene therapy market include the rise of mRNA-based therapies and the use of artificial intelligence in drug development. Additionally, there is a growing focus on improving delivery mechanisms to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Plasmid DNA, RNA, Protein, Lipid Nanoparticles |
| Delivery Mode | Intravenous, Intramuscular, Subcutaneous, Inhalation |
| End User | Hospitals, Research Institutes, Pharmaceutical Companies, Contract Research Organizations |
| Application | Oncology, Cardiovascular, Genetic Disorders, Infectious Diseases |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Non-viral Vectors Gene Therapy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at