444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Nigeria geospatial analytics market represents a rapidly expanding sector within the country’s technology landscape, driven by increasing government digitization initiatives and growing private sector adoption of location-based intelligence solutions. Geospatial analytics encompasses the collection, processing, and analysis of geographic and location-based data to derive actionable insights for various applications including urban planning, agriculture, oil and gas exploration, telecommunications, and environmental monitoring.
Nigeria’s strategic position as Africa’s largest economy and most populous nation creates substantial demand for geospatial solutions across multiple industries. The market is experiencing robust growth with a projected compound annual growth rate of 12.8% CAGR over the forecast period, reflecting the increasing recognition of spatial data’s value in decision-making processes. Government initiatives such as the National Geospatial Data Infrastructure (NGDI) and smart city projects are accelerating market adoption.
Key market segments include geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, global positioning systems (GPS), and location-based services (LBS). The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with geospatial technologies is creating new opportunities for advanced analytics and predictive modeling. Private sector adoption is particularly strong in sectors such as banking, insurance, retail, and logistics, where location intelligence drives operational efficiency and customer insights.
The Nigeria geospatial analytics market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of technologies, services, and solutions that enable the collection, processing, visualization, and analysis of geographic and spatial data within Nigeria’s economic and governmental framework. This market encompasses hardware components such as GPS devices and satellite imagery systems, software platforms for data processing and visualization, and professional services including consulting, implementation, and maintenance.
Geospatial analytics combines traditional geographic information systems with advanced analytical capabilities, enabling organizations to understand spatial relationships, patterns, and trends in their data. The technology integrates multiple data sources including satellite imagery, aerial photography, sensor networks, and mobile device location data to create comprehensive spatial intelligence solutions.
Market participants include technology vendors, system integrators, data providers, consulting firms, and end-user organizations across government and private sectors. The ecosystem supports applications ranging from basic mapping and navigation to complex spatial modeling and predictive analytics for strategic planning and operational optimization.
Nigeria’s geospatial analytics market is positioned for significant expansion, driven by digital transformation initiatives across government and private sectors. The market benefits from increasing awareness of spatial data’s strategic value and growing investment in smart infrastructure projects. Government support through policy frameworks and funding programs is accelerating market development and technology adoption.
Key growth drivers include urbanization challenges requiring spatial planning solutions, agricultural modernization needs, oil and gas exploration activities, and telecommunications network optimization requirements. The market is witnessing 65% adoption rate among large enterprises, while small and medium enterprises are increasingly recognizing the value proposition of geospatial solutions.
Technological advancement in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and mobile technologies is expanding market accessibility and reducing implementation barriers. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors with geospatial platforms is creating new data sources and analytical capabilities. Market consolidation trends are evident as larger technology providers acquire specialized geospatial companies to enhance their solution portfolios.
Challenges include limited technical expertise, infrastructure constraints, and data quality issues. However, increasing educational programs and international partnerships are addressing skill gaps while infrastructure investments improve connectivity and data accessibility.
Government digitization initiatives represent the primary market driver, with federal and state governments implementing comprehensive digital transformation programs requiring spatial data management and analysis capabilities. The National Digital Economy Policy specifically emphasizes geospatial technology adoption for improved governance and service delivery. Smart city projects across major urban centers are creating substantial demand for integrated geospatial solutions.
Infrastructure development programs including transportation networks, power grid expansion, and telecommunications infrastructure require extensive spatial planning and monitoring capabilities. The Economic Recovery and Growth Plan allocates significant resources to infrastructure projects that rely heavily on geospatial analytics for planning, implementation, and maintenance phases.
Agricultural modernization needs are driving adoption of precision farming technologies, satellite-based crop monitoring, and GPS-guided equipment. Nigeria’s position as Africa’s largest agricultural producer creates substantial market opportunities for geospatial solutions supporting food security and agricultural productivity improvements.
Oil and gas exploration activities continue to generate demand for advanced geospatial technologies including seismic data analysis, pipeline monitoring, and environmental impact assessment. The sector’s regulatory requirements for environmental compliance and safety monitoring further drive technology adoption.
Urbanization pressures in major cities are creating urgent needs for spatial planning tools, traffic management systems, and infrastructure optimization solutions. The rapid population growth in urban areas requires sophisticated geospatial analytics for sustainable development planning.
Limited technical expertise represents a significant market constraint, with shortage of qualified GIS professionals and spatial analysts limiting implementation capabilities across organizations. The specialized nature of geospatial technologies requires extensive training and certification programs that are currently underdeveloped in Nigeria’s educational system.
Infrastructure limitations including inconsistent internet connectivity and power supply challenges affect the deployment and operation of cloud-based geospatial solutions. Rural areas particularly face connectivity constraints that limit the effectiveness of real-time spatial data collection and analysis systems.
High implementation costs for comprehensive geospatial solutions create barriers for small and medium enterprises, limiting market penetration beyond large organizations and government agencies. The initial investment requirements for hardware, software, and training often exceed budget capabilities of smaller organizations.
Data quality and availability issues constrain the effectiveness of geospatial analytics, with inconsistent data standards, limited historical datasets, and challenges in data integration across different sources and formats. The lack of standardized spatial data infrastructure affects interoperability and analytical accuracy.
Regulatory uncertainties regarding data privacy, cross-border data transfer, and spatial data sharing create compliance challenges for organizations implementing geospatial solutions. The evolving regulatory landscape requires ongoing adaptation of systems and processes.
Smart city development projects across Nigeria present substantial opportunities for geospatial technology providers, with multiple state governments planning comprehensive urban digitization initiatives. These projects require integrated spatial data platforms supporting traffic management, utility monitoring, and citizen services delivery.
Agricultural technology advancement opportunities include precision farming solutions, crop yield optimization systems, and supply chain management platforms utilizing spatial analytics. The growing focus on food security and agricultural productivity creates demand for innovative geospatial applications in farming and agribusiness sectors.
Financial services integration presents emerging opportunities as banks and insurance companies recognize the value of location intelligence for risk assessment, branch optimization, and customer analytics. The expanding fintech sector is particularly interested in geospatial solutions for mobile banking and payment services.
Environmental monitoring applications are gaining importance due to climate change concerns and regulatory requirements for environmental impact assessment. Opportunities exist for solutions supporting deforestation monitoring, water resource management, and pollution tracking systems.
Telecommunications network optimization creates opportunities for geospatial solutions supporting 5G network deployment, coverage optimization, and infrastructure planning. The ongoing telecommunications infrastructure expansion requires sophisticated spatial analysis capabilities.
Market dynamics in Nigeria’s geospatial analytics sector are characterized by rapid technological evolution and increasing integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. The convergence of geospatial analytics with big data platforms is creating new analytical capabilities and market opportunities.
Competitive landscape shifts are evident as international technology providers establish local partnerships and subsidiaries to better serve the Nigerian market. Local system integrators are developing specialized expertise in geospatial solutions to compete with international vendors. MarkWide Research analysis indicates increasing collaboration between local and international players to address market-specific requirements.
Technology adoption patterns show preference for cloud-based solutions among new implementations, with 70% adoption rate for SaaS platforms compared to traditional on-premise deployments. Mobile-first approaches are becoming standard as organizations leverage smartphone capabilities for data collection and field operations.
Investment trends indicate growing venture capital interest in Nigerian geospatial technology startups, particularly those developing solutions for agriculture, logistics, and urban planning applications. Government funding programs are supporting research and development initiatives in spatial technologies.
Regulatory developments are creating more structured frameworks for geospatial data management and sharing, improving market confidence and enabling larger-scale implementations. The establishment of national spatial data standards is facilitating interoperability and system integration.
Primary research methodology encompasses comprehensive interviews with key market participants including technology vendors, system integrators, government officials, and end-user organizations across various sectors. Structured questionnaires and in-depth discussions provide insights into market trends, challenges, and growth opportunities.
Secondary research sources include government publications, industry reports, academic studies, and technology vendor documentation. Analysis of public procurement data, project announcements, and regulatory filings provides quantitative insights into market size and growth patterns.
Market segmentation analysis utilizes both top-down and bottom-up approaches to validate market sizing and growth projections. Cross-validation of data sources ensures accuracy and reliability of market estimates and forecasts.
Expert validation processes involve consultation with industry specialists, academic researchers, and technology consultants to verify findings and validate market assumptions. Regular feedback sessions with market participants ensure ongoing accuracy of market intelligence.
Data collection frameworks incorporate both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to provide comprehensive market understanding. Continuous monitoring of market developments ensures timely updates to market intelligence and forecasts.
Lagos State dominates the Nigerian geospatial analytics market with approximately 35% market share, driven by its position as the commercial capital and concentration of technology companies, financial institutions, and government agencies. The state’s smart city initiatives and infrastructure development projects create substantial demand for spatial analytics solutions.
Federal Capital Territory (Abuja) represents the second-largest market segment with 25% market share, primarily driven by federal government agencies and international organizations requiring geospatial solutions for policy development and program implementation. The concentration of diplomatic missions and development organizations creates additional market demand.
Rivers State accounts for 15% market share, with demand primarily driven by oil and gas industry activities requiring exploration, production, and environmental monitoring solutions. The state’s industrial base and port facilities create additional opportunities for logistics and supply chain optimization applications.
Kano State represents 10% market share with growing demand from agricultural applications and urban planning initiatives. The state’s position as a major agricultural hub creates opportunities for precision farming and crop monitoring solutions.
Other states collectively account for 15% market share, with emerging opportunities in states implementing digital transformation programs and infrastructure development projects. Rural areas present growing opportunities for agricultural and environmental monitoring applications.
International technology providers maintain strong market positions through partnerships with local system integrators and direct sales operations. These companies leverage global expertise and comprehensive solution portfolios to serve large government and enterprise clients.
Local system integrators play crucial roles in market development through customized solution development, implementation services, and ongoing support. These companies provide market-specific expertise and local language support essential for successful deployments.
Emerging technology startups are developing innovative solutions addressing specific Nigerian market needs, particularly in agriculture, logistics, and mobile applications. These companies often focus on cost-effective solutions suitable for small and medium enterprises.
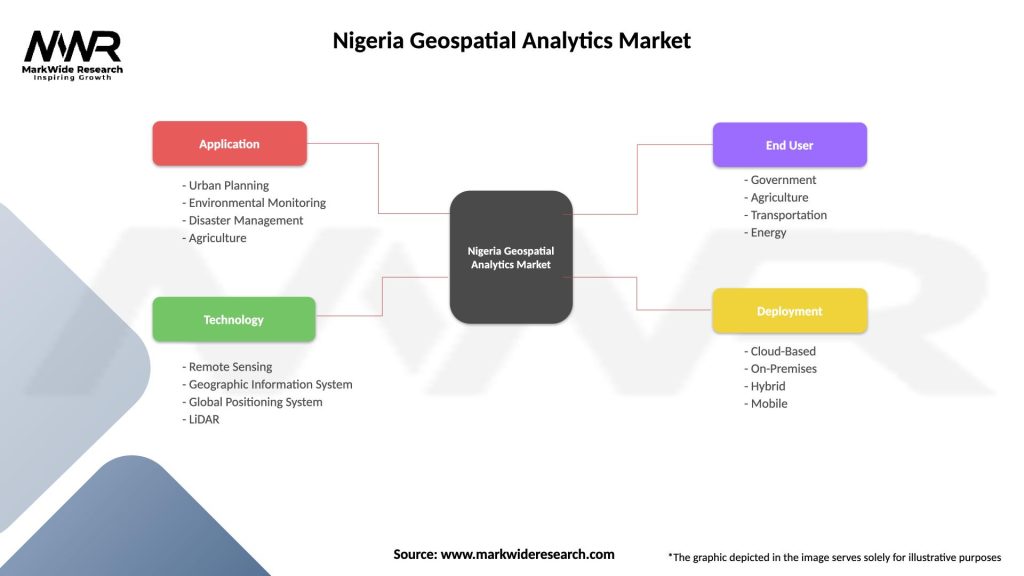
By Technology:
By Application:
By Deployment Model:
Government sector applications dominate market demand with comprehensive requirements for spatial data management, urban planning, and infrastructure monitoring. Federal agencies are implementing national geospatial data infrastructure while state governments focus on smart city initiatives and service delivery optimization.
Agricultural technology adoption is accelerating with increasing awareness of precision farming benefits and government support for agricultural modernization. Smallholder farmers are beginning to adopt mobile-based geospatial solutions for crop monitoring and market access.
Oil and gas industry applications remain significant market drivers with ongoing exploration activities and regulatory requirements for environmental monitoring. The sector’s technical sophistication creates demand for advanced analytical capabilities and real-time monitoring systems.
Financial services integration is emerging as banks and insurance companies recognize location intelligence value for risk assessment, branch optimization, and customer analytics. Mobile banking applications increasingly incorporate geospatial capabilities for service delivery.
Telecommunications applications are growing with 5G network deployment requirements and ongoing infrastructure expansion. Network optimization and coverage planning create substantial demand for spatial analysis tools.
Technology vendors benefit from expanding market opportunities driven by government digitization initiatives and private sector digital transformation programs. The growing awareness of geospatial analytics value creates demand for comprehensive solution portfolios and professional services.
System integrators gain opportunities to develop specialized expertise in geospatial solutions while building long-term client relationships through implementation and support services. Local market knowledge provides competitive advantages over international competitors.
Government agencies achieve improved decision-making capabilities through spatial data analysis, enhanced service delivery through location-based applications, and better resource allocation through spatial planning tools. Transparency and accountability improvements result from spatial data visualization and analysis.
Private sector organizations realize operational efficiency improvements through location intelligence, enhanced customer insights through spatial analytics, and competitive advantages through innovative geospatial applications. Risk management capabilities improve through spatial risk assessment tools.
End users and citizens benefit from improved government services, enhanced mobile applications with location-based features, and better infrastructure planning resulting in improved quality of life. Agricultural communities gain access to precision farming technologies improving productivity and income.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Cloud-first adoption strategies are becoming standard as organizations recognize the benefits of reduced infrastructure requirements, scalable computing resources, and lower total cost of ownership. Software-as-a-Service platforms are gaining preference over traditional on-premise deployments.
Artificial intelligence integration with geospatial analytics is creating new capabilities for automated pattern recognition, predictive modeling, and intelligent decision support. Machine learning algorithms are enhancing spatial data analysis and visualization capabilities.
Mobile-first development approaches are prioritizing smartphone and tablet applications for field data collection, real-time monitoring, and location-based services. Progressive web applications are enabling offline capabilities and improved user experiences.
Internet of Things convergence with geospatial platforms is creating new data sources and real-time monitoring capabilities. Sensor networks are providing continuous spatial data streams for environmental monitoring and infrastructure management.
Open source technology adoption is increasing as organizations seek cost-effective alternatives to proprietary solutions. Open geospatial standards and APIs are facilitating system integration and interoperability.
Data democratization initiatives are making spatial data more accessible to non-technical users through intuitive interfaces and self-service analytics capabilities. MWR analysis indicates growing demand for user-friendly geospatial tools across organizations.
Government policy initiatives including the National Digital Economy Policy and National Broadband Plan are creating supportive frameworks for geospatial technology adoption. The establishment of the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA) guidelines for spatial data management is standardizing implementation approaches.
International partnerships between Nigerian organizations and global technology providers are facilitating knowledge transfer and capacity building. Development agencies are supporting geospatial technology projects through funding and technical assistance programs.
Educational program development in universities and technical institutions is addressing the skills gap through specialized geospatial technology curricula and certification programs. Industry partnerships are providing practical training opportunities and internship programs.
Infrastructure investments in broadband connectivity and data centers are improving the foundation for cloud-based geospatial solutions. The ongoing expansion of fiber optic networks is enabling real-time spatial data processing and analysis capabilities.
Startup ecosystem growth is fostering innovation in geospatial applications with venture capital funding supporting technology development and market entry. Incubation programs are supporting entrepreneurs developing location-based solutions for Nigerian market needs.
Technology vendors should prioritize local partnership development to understand market-specific requirements and build sustainable business relationships. Investment in local technical support capabilities and training programs will differentiate providers in the competitive landscape.
Government agencies should develop comprehensive spatial data strategies including standardization frameworks, sharing protocols, and interoperability requirements. Coordination between federal and state initiatives will maximize technology investments and avoid duplication.
Private sector organizations should start with pilot implementations to demonstrate value and build internal expertise before scaling geospatial solutions. Focus on applications with clear return on investment and measurable business impact.
Educational institutions should develop specialized geospatial technology programs to address the growing demand for qualified professionals. Industry partnerships will ensure curriculum relevance and provide practical training opportunities.
Investment considerations should focus on solutions addressing specific Nigerian market needs rather than generic global applications. MarkWide Research recommends prioritizing mobile-first solutions and cost-effective deployment models suitable for local market conditions.
Market growth trajectory indicates continued expansion driven by government digitization initiatives, private sector digital transformation, and increasing awareness of spatial data value. The integration of emerging technologies will create new application areas and market opportunities.
Technology evolution will focus on artificial intelligence integration, real-time analytics capabilities, and improved user interfaces for non-technical users. Cloud-native solutions will become standard with enhanced security and compliance features.
Sector-specific applications will develop with specialized solutions for agriculture, oil and gas, telecommunications, and financial services. Vertical market expertise will become increasingly important for solution providers.
Skills development programs will expand through university partnerships, professional certification programs, and industry training initiatives. The availability of qualified professionals will improve market adoption rates and implementation success.
Regional expansion beyond major urban centers will create new market opportunities as infrastructure improvements and government programs reach rural areas. Agricultural and environmental monitoring applications will drive rural market development.
Nigeria’s geospatial analytics market presents substantial growth opportunities driven by government digitization initiatives, private sector digital transformation needs, and increasing recognition of spatial data’s strategic value. The market’s projected 12.8% CAGR reflects strong fundamentals and supportive policy environment.
Key success factors for market participants include developing local partnerships, investing in technical expertise, and focusing on solutions addressing specific Nigerian market requirements. The integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and Internet of Things will create new competitive advantages and application opportunities.
Market challenges including skills gaps, infrastructure constraints, and implementation costs are being addressed through government programs, educational initiatives, and technology advancement. The growing ecosystem of local system integrators and international partnerships is improving market accessibility and solution quality.
Future market development will be characterized by increased cloud adoption, mobile-first approaches, and sector-specific solution development. Organizations that invest early in geospatial capabilities will gain competitive advantages in their respective markets while contributing to Nigeria’s digital transformation objectives.
What is Geospatial Analytics?
Geospatial Analytics refers to the collection, analysis, and visualization of data related to geographic locations. It is used in various applications such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and transportation management.
What are the key players in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market?
Key players in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market include Esri, Trimble, and Hexagon, which provide advanced geospatial solutions and technologies for various sectors, including agriculture, mining, and urban development, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market?
The Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for location-based services, the growth of smart city initiatives, and advancements in satellite imagery and GIS technologies.
What challenges does the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market face?
Challenges in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market include data privacy concerns, the high cost of technology implementation, and a lack of skilled professionals in geospatial data analysis.
What opportunities exist in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market?
Opportunities in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market include the expansion of mobile geospatial applications, the integration of AI and machine learning in data analysis, and the increasing use of geospatial data in disaster management and response.
What trends are shaping the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market?
Trends in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market include the rise of cloud-based geospatial solutions, the growing importance of real-time data analytics, and the increasing collaboration between public and private sectors to enhance geospatial infrastructure.
Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Application | Urban Planning, Environmental Monitoring, Disaster Management, Agriculture |
| Technology | Remote Sensing, Geographic Information System, Global Positioning System, LiDAR |
| End User | Government, Agriculture, Transportation, Energy |
| Deployment | Cloud-Based, On-Premises, Hybrid, Mobile |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Nigeria Geospatial Analytics Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at