444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The newborn screening program market encompasses a range of services, technologies, and products aimed at identifying newborn babies at risk of certain genetic, metabolic, and congenital disorders shortly after birth. Newborn screening programs are crucial for early detection and intervention, enabling timely medical treatment and management of these conditions. This market is driven by the growing awareness of the benefits of newborn screening, advancements in screening technologies, and government initiatives to expand screening programs worldwide.
Meaning
Newborn screening programs involve the systematic testing of newborn infants for a panel of genetic, metabolic, and congenital disorders. These screenings typically occur within the first few days of life and involve collecting a small blood sample from the baby’s heel. The sample is then analyzed in a laboratory to detect markers or abnormalities associated with various conditions. Early identification through newborn screening allows healthcare providers to initiate prompt interventions, such as dietary modifications, medication, or specialized care, to improve outcomes for affected infants.
Executive Summary
The newborn screening program market is experiencing steady growth, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, advancements in screening technologies, and the expanding coverage of newborn screening programs globally. The market offers opportunities for stakeholders involved in screening test development, laboratory services, equipment manufacturing, and policy advocacy. However, challenges such as funding constraints, infrastructure limitations, and ethical considerations need to be addressed to ensure the effective implementation and sustainability of newborn screening programs.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The newborn screening program market is influenced by dynamic factors such as healthcare policies, regulatory frameworks, technological innovation, and public awareness campaigns. Stakeholders must collaborate across sectors and disciplines to address challenges, leverage opportunities, and ensure the equitable delivery of newborn screening services to all infants, regardless of geographic location or socioeconomic status.
Regional Analysis
The implementation and structure of newborn screening programs vary by region, reflecting differences in healthcare systems, disease prevalence, regulatory requirements, and resource availability. High-income countries often have well-established, comprehensive newborn screening programs covering a wide range of conditions, while low- and middle-income countries may face challenges related to funding, infrastructure, and access to screening services.
Competitive Landscape
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
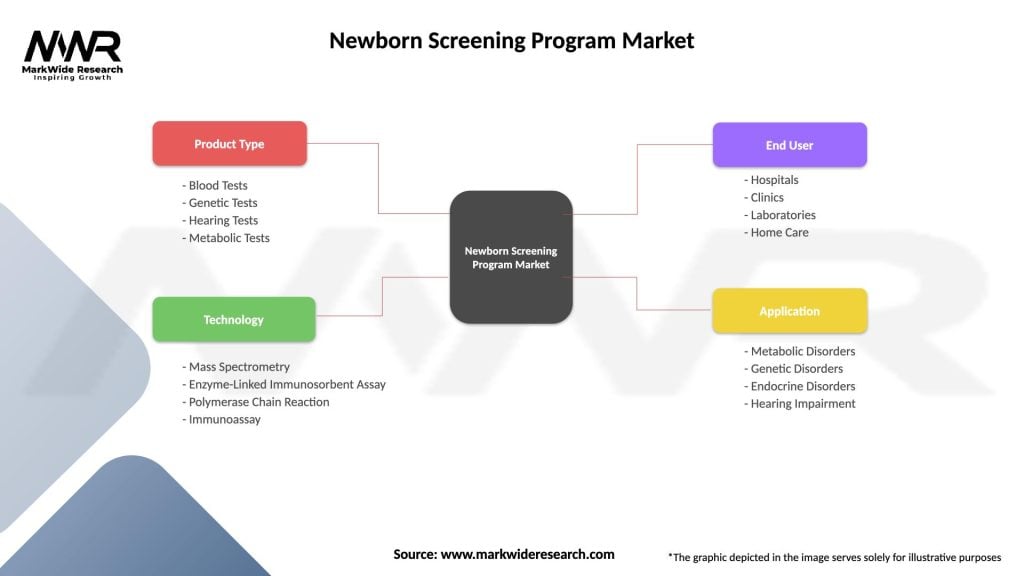
Segmentation
The newborn screening program market can be segmented based on various parameters, including:
Category-wise Insight
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of newborn screening as an essential public health intervention. While the pandemic posed challenges to screening programs due to disruptions in healthcare services and resource reallocation, it also underscored the need for resilient and adaptable screening systems capable of responding to emergencies and ensuring the continuity of essential services.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the newborn screening program market is promising, driven by advancements in screening technologies, expanding screening panels, and increasing recognition of the benefits of early detection and intervention. Continued investment in research, innovation, and healthcare infrastructure is essential for realizing the full potential of newborn screening in improving infant health outcomes and reducing the burden of genetic and metabolic disorders globally.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the newborn screening program market plays a critical role in public health by identifying infants at risk of genetic, metabolic, and congenital disorders and enabling early intervention and treatment. Despite challenges such as resource constraints and ethical considerations, the market offers significant opportunities for stakeholders to innovate, collaborate, and drive positive health outcomes for newborns worldwide. By leveraging advances in technology, expanding screening programs, and prioritizing public health initiatives, stakeholders can contribute to the success and sustainability of newborn screening efforts and improve infant health and well-being.
What is Newborn Screening Program?
Newborn Screening Program refers to a public health initiative aimed at identifying certain genetic, metabolic, hormonal, and functional conditions in newborns shortly after birth. This early detection allows for timely intervention and treatment, significantly improving health outcomes for affected infants.
What are the key players in the Newborn Screening Program Market?
Key players in the Newborn Screening Program Market include companies such as PerkinElmer, Inc., Natus Medical Incorporated, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. These companies are involved in developing screening technologies and tests that help in the early detection of various conditions in newborns, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Newborn Screening Program Market?
The main drivers of the Newborn Screening Program Market include increasing awareness of genetic disorders, advancements in screening technologies, and government initiatives promoting early detection. These factors contribute to the growing adoption of screening programs across various healthcare settings.
What challenges does the Newborn Screening Program Market face?
Challenges in the Newborn Screening Program Market include the high costs associated with comprehensive screening tests and the need for standardized protocols across different regions. Additionally, there may be limitations in the availability of follow-up care for identified conditions.
What opportunities exist in the Newborn Screening Program Market?
Opportunities in the Newborn Screening Program Market include the potential for expanding screening panels to include more conditions and the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence for data analysis. These advancements can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of screening processes.
What trends are shaping the Newborn Screening Program Market?
Trends shaping the Newborn Screening Program Market include the increasing implementation of genetic testing and personalized medicine approaches. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on public health policies that support universal screening for newborns, ensuring broader access to essential health services.
Newborn Screening Program Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Blood Tests, Genetic Tests, Hearing Tests, Metabolic Tests |
| Technology | Mass Spectrometry, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, Polymerase Chain Reaction, Immunoassay |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Laboratories, Home Care |
| Application | Metabolic Disorders, Genetic Disorders, Endocrine Disorders, Hearing Impairment |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at