444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
New Zealand’s sustainable tourism market has gained significant attention in recent years. With its breathtaking landscapes, pristine natural beauty, and commitment to environmental preservation, New Zealand has positioned itself as a leading destination for eco-conscious travelers. Sustainable tourism refers to a responsible approach to travel and tourism that aims to minimize negative impacts on the environment, preserve local culture and heritage, and support the well-being of local communities.
Meaning
Sustainable tourism in New Zealand is characterized by the integration of environmental, social, and economic factors to ensure long-term viability and minimal ecological footprint. It involves practices such as reducing carbon emissions, conserving water resources, promoting local employment and entrepreneurship, and supporting indigenous communities. The focus is on creating a positive experience for travelers while maintaining the integrity of the natural and cultural assets that make New Zealand a unique destination.
Executive Summary
New Zealand’s sustainable tourism market has experienced robust growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness among travelers about the importance of responsible travel practices. The country’s commitment to sustainability, coupled with its stunning natural landscapes, has positioned it as a premier destination for eco-conscious tourists. This executive summary provides key insights into the market, including drivers, restraints, opportunities, and trends, along with an analysis of the market’s dynamics, competitive landscape, and regional outlook.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The New Zealand sustainable tourism market is dynamic and influenced by various factors. Key dynamics include government policies and support, changing consumer preferences, industry collaboration, and emerging trends in the global travel and tourism sector. The market is driven by a growing demand for sustainable experiences, supported by the country’s unique natural attractions and strong commitment to sustainability. However, challenges such as infrastructure limitations, seasonal variations, and competing interests pose restraints to the market’s growth. Despite these challenges, there are significant opportunities for investment and innovation in sustainable accommodation, nature-based experiences, indigenous tourism, and education and awareness initiatives.
Regional Analysis
New Zealand’s sustainable tourism market exhibits regional variations due to differences in natural landscapes, cultural heritage, and local initiatives. The country can be divided into several regions, each offering unique opportunities for sustainable tourism development. The following regions are particularly noteworthy:
Regional analysis allows stakeholders to identify specific areas for sustainable tourism development and tailor strategies to maximize the potential of each region.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in New Zealand Sustainable Tourism Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
The New Zealand sustainable tourism market can be segmented based on various factors:
Segmentation helps businesses and industry stakeholders to better understand their target audience, tailor marketing strategies, and develop sustainable tourism products and services that meet specific market demands.
Category-wise Insights
By focusing on these categories, industry participants can develop sustainable tourism offerings that align with market demands and contribute to the preservation of New Zealand’s natural and cultural heritage.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Industry participants and stakeholders in the New Zealand sustainable tourism market can enjoy several benefits, including:
By recognizing and embracing these benefits, industry participants and stakeholders can contribute to the growth and sustainability of the New Zealand tourism industry.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the New Zealand sustainable tourism market, as it has the global tourism industry as a whole. Travel restrictions, lockdowns, and reduced international travel have resulted in a decline in tourist arrivals and revenue for businesses reliant on tourism. However, the pandemic has also provided an opportunity for reflection and innovation. Many businesses have used this time to reassess their operations, adopt sustainable practices, and invest in infrastructure improvements. The crisis has highlighted the importance of resilience, adaptability, and community engagement in the face of unprecedented challenges. As travel resumes and borders reopen, the focus on sustainable tourism is expected to rebound, with travelers seeking meaningful and responsible experiences.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the New Zealand sustainable tourism market appears promising, despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. The country’s commitment to sustainability, coupled with its stunning natural landscapes, positions it well to attract eco-conscious travelers. As travel resumes, the demand for sustainable tourism experiences is expected to increase. Industry participants and stakeholders are likely to invest in infrastructure improvements, adopt innovative technologies, and collaborate to promote responsible travel practices. The integration of indigenous perspectives and the development of community-led initiatives will further enhance the authenticity and sustainability of tourism experiences in New Zealand.
Conclusion
New Zealand’s sustainable tourism market offers significant opportunities for businesses and stakeholders to contribute to environmental conservation, support local communities, and provide meaningful experiences for travelers. With its pristine natural landscapes, government support, and growing consumer demand for responsible travel, New Zealand has established itself as a leading sustainable tourism destination. By embracing sustainable practices, collaborating with stakeholders, and investing in infrastructure and education, the industry can continue to thrive while preserving the natural and cultural heritage that makes New Zealand a truly unique and sustainable tourism destination.
What is Sustainable Tourism?
Sustainable tourism refers to travel practices that minimize negative impacts on the environment and local cultures while promoting conservation and economic benefits. It encompasses eco-friendly accommodations, responsible travel behaviors, and community engagement.
What are the key players in the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market?
Key players in the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market include companies like EcoTravel, Pure New Zealand, and Sustainable Travel International, which focus on eco-friendly travel experiences and conservation efforts among others.
What are the growth factors driving the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market?
The New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market is driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues, a growing demand for eco-friendly travel options, and government initiatives promoting sustainable practices in tourism.
What challenges does the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market face?
Challenges in the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market include balancing tourism growth with environmental conservation, managing the impact of climate change on natural attractions, and ensuring that local communities benefit from tourism activities.
What opportunities exist in the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market?
Opportunities in the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market include the development of new eco-tourism experiences, investment in sustainable infrastructure, and partnerships with local communities to enhance cultural tourism offerings.
What trends are shaping the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market?
Trends in the New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market include the rise of regenerative tourism, increased use of technology for sustainable travel solutions, and a focus on authentic cultural experiences that engage travelers with local communities.
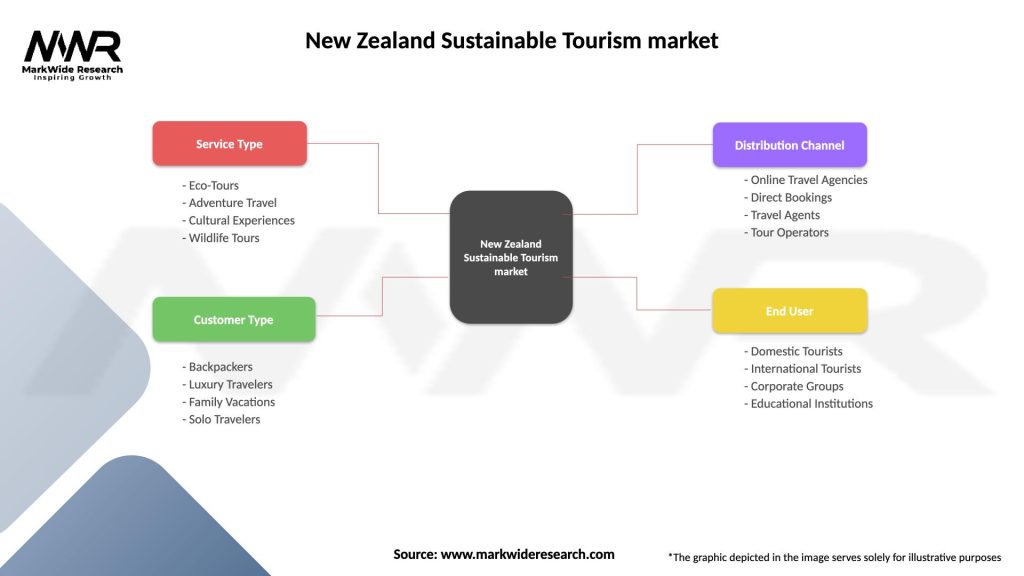
New Zealand Sustainable Tourism market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Eco-Tours, Adventure Travel, Cultural Experiences, Wildlife Tours |
| Customer Type | Backpackers, Luxury Travelers, Family Vacations, Solo Travelers |
| Distribution Channel | Online Travel Agencies, Direct Bookings, Travel Agents, Tour Operators |
| End User | Domestic Tourists, International Tourists, Corporate Groups, Educational Institutions |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in New Zealand Sustainable Tourism Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at