444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Netherlands commercial greenhouse market stands as a global benchmark for advanced horticultural technology and sustainable agricultural practices. This sophisticated sector encompasses controlled environment agriculture facilities designed for commercial crop production, featuring state-of-the-art climate control systems, automated irrigation, and precision growing technologies. The Dutch greenhouse industry has evolved into a highly efficient ecosystem that maximizes crop yields while minimizing resource consumption through innovative growing methodologies.
Market dynamics in the Netherlands reflect a strong emphasis on technological advancement and environmental sustainability. The sector demonstrates remarkable growth potential, with expansion driven by increasing demand for year-round fresh produce, export opportunities, and the adoption of smart farming technologies. Dutch commercial greenhouses are renowned for their exceptional productivity levels, achieving yields up to 500 times higher per square meter compared to traditional open-field agriculture.
Technological integration remains a cornerstone of the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market, with facilities incorporating advanced climate control systems, LED lighting solutions, and automated crop management platforms. The market benefits from strong government support for sustainable agriculture initiatives and substantial investments in research and development. Energy efficiency improvements of approximately 35-40% have been achieved through innovative heating systems and renewable energy integration, positioning Dutch greenhouses as leaders in sustainable horticultural production.
The Netherlands commercial greenhouse market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of controlled environment agricultural facilities designed for large-scale commercial crop production within the Netherlands. These sophisticated structures utilize advanced technologies including climate control systems, automated irrigation, precision lighting, and integrated crop management platforms to optimize growing conditions and maximize agricultural productivity throughout the year.
Commercial greenhouses in the Netherlands represent highly engineered agricultural environments that enable precise control over temperature, humidity, light exposure, nutrient delivery, and atmospheric composition. These facilities are specifically designed to support intensive horticultural production while minimizing environmental impact through efficient resource utilization and sustainable growing practices.
The market encompasses various greenhouse types including glass houses, polycarbonate structures, and high-tech growing facilities equipped with hydroponic and aeroponic systems. Dutch commercial greenhouses are characterized by their integration of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things sensors, and automated harvesting systems that collectively enhance operational efficiency and crop quality.
The Netherlands commercial greenhouse market represents a pinnacle of agricultural innovation, combining advanced technology with sustainable farming practices to achieve exceptional productivity levels. This dynamic sector serves as a global model for efficient food production, demonstrating how controlled environment agriculture can address growing food security challenges while maintaining environmental responsibility.
Key market characteristics include widespread adoption of smart farming technologies, strong focus on energy efficiency, and robust export capabilities that position Dutch greenhouse products in international markets. The sector benefits from favorable government policies supporting sustainable agriculture, substantial research and development investments, and a well-established supply chain infrastructure that facilitates efficient operations.
Growth drivers encompass increasing consumer demand for fresh, locally-grown produce, expanding export opportunities to European and global markets, and continuous technological advancement in greenhouse automation systems. The market demonstrates resilience through its ability to adapt to changing climate conditions and evolving consumer preferences while maintaining high standards of product quality and environmental stewardship.
Strategic positioning of the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market emphasizes innovation leadership, with approximately 60-65% of facilities incorporating advanced automation technologies. The sector’s commitment to sustainability is evident through significant investments in renewable energy systems and circular economy principles that minimize waste and optimize resource utilization.

Market intelligence reveals several critical insights that define the Netherlands commercial greenhouse landscape. The sector demonstrates exceptional technological sophistication, with Dutch greenhouse facilities achieving some of the highest productivity rates globally through innovative growing methodologies and precision agriculture techniques.
Primary growth drivers propelling the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market include escalating global demand for fresh, high-quality produce available year-round. Consumer preferences increasingly favor locally-grown, pesticide-free vegetables and fruits, creating substantial market opportunities for Dutch greenhouse operators who can deliver consistent quality regardless of seasonal variations.
Technological advancement serves as a fundamental driver, with continuous innovation in climate control systems, LED lighting technology, and automated crop management platforms enhancing operational efficiency and crop yields. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms enables predictive analytics for optimal growing conditions, reducing resource consumption while maximizing productivity.
Export market expansion provides significant growth momentum, as Dutch greenhouse products gain recognition for superior quality in international markets. The strategic geographic location of the Netherlands facilitates efficient distribution throughout Europe and beyond, while established trade relationships support market penetration and expansion opportunities.
Government support initiatives accelerate market development through favorable policies, research funding, and sustainability incentives. Public-private partnerships foster innovation and technology transfer, while regulatory frameworks encourage environmentally responsible farming practices that align with broader sustainability objectives.
Climate change adaptation drives demand for controlled environment agriculture as traditional farming faces increasing challenges from weather variability. Commercial greenhouses offer reliable production capabilities that ensure food security while reducing agricultural vulnerability to climate-related disruptions.
Capital intensity represents a significant market restraint, as establishing modern commercial greenhouse facilities requires substantial upfront investments in infrastructure, technology, and equipment. The high initial costs can limit market entry for smaller operators and may constrain expansion plans for existing facilities seeking to upgrade or expand their operations.
Energy costs pose ongoing operational challenges, particularly for heating and lighting systems essential for year-round production. Despite improvements in energy efficiency, commercial greenhouses remain energy-intensive operations, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in energy prices and potentially impacting profitability margins.
Skilled labor shortage affects the sector’s ability to fully leverage advanced technologies and maintain optimal operational standards. The specialized nature of modern greenhouse operations requires workers with technical expertise in automation systems, crop management, and precision agriculture techniques, creating recruitment and retention challenges.
Regulatory complexity can impede market development through stringent environmental regulations, food safety requirements, and international trade standards. While these regulations ensure quality and safety, compliance costs and administrative burdens may limit operational flexibility and increase business complexity.
Market saturation concerns in certain crop segments may limit growth opportunities, particularly for traditional greenhouse crops where supply may exceed demand in specific markets. This situation requires diversification strategies and exploration of new crop varieties or market segments to maintain growth momentum.
Emerging crop diversification presents substantial opportunities for Netherlands commercial greenhouse operators to expand beyond traditional vegetables and explore high-value crops such as medicinal plants, exotic fruits, and specialty herbs. These niche markets often command premium prices and offer differentiation opportunities in competitive agricultural markets.
Vertical farming integration offers potential for maximizing space utilization and increasing production capacity within existing greenhouse facilities. The combination of traditional greenhouse growing with vertical farming techniques can significantly enhance productivity per square meter while maintaining quality standards.
International expansion opportunities exist through technology transfer, consulting services, and direct investment in greenhouse projects worldwide. Dutch expertise in greenhouse design, operation, and management is highly valued globally, creating opportunities for knowledge export and international partnerships.
Circular economy initiatives provide opportunities for waste reduction, resource optimization, and additional revenue streams through byproduct utilization. Implementing closed-loop systems for water, nutrients, and energy can reduce operational costs while enhancing environmental sustainability credentials.
Digital agriculture advancement opens possibilities for enhanced data analytics, predictive modeling, and precision farming techniques. The integration of blockchain technology, IoT sensors, and artificial intelligence can further optimize operations and create new value propositions for customers and stakeholders.
Market dynamics in the Netherlands commercial greenhouse sector reflect a complex interplay of technological innovation, environmental sustainability, and economic competitiveness. The sector demonstrates remarkable adaptability to changing market conditions while maintaining its position as a global leader in controlled environment agriculture.
Supply chain integration plays a crucial role in market dynamics, with greenhouse operators developing sophisticated relationships with suppliers, distributors, and retailers. This integration enables efficient resource utilization, quality assurance, and market responsiveness that supports competitive positioning in both domestic and international markets.
Innovation cycles drive continuous market evolution, with research institutions, technology providers, and commercial operators collaborating to develop next-generation greenhouse solutions. According to MarkWide Research analysis, approximately 25-30% of greenhouse operators invest significantly in new technologies annually, demonstrating the sector’s commitment to continuous improvement.
Competitive pressures encourage operational efficiency improvements and differentiation strategies among market participants. The focus on sustainability, quality, and technological advancement creates a dynamic environment where successful operators must continuously innovate to maintain market position and profitability.
Market consolidation trends reflect economies of scale advantages and the need for substantial capital investments in modern greenhouse technologies. Larger operators can leverage their resources more effectively while smaller facilities may seek partnerships or specialization strategies to remain competitive.
Comprehensive market analysis for the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings. The research approach combines quantitative data analysis with qualitative insights gathered from industry stakeholders, technology providers, and market participants.
Primary research activities include structured interviews with greenhouse operators, equipment manufacturers, research institutions, and government agencies involved in agricultural policy development. These interactions provide valuable insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities that shape the commercial greenhouse landscape.
Secondary research sources encompass industry reports, government statistics, academic publications, and trade association data that provide comprehensive market context and historical trends. This information supports trend analysis and market projection development while ensuring research findings align with established industry knowledge.
Data validation processes involve cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting follow-up interviews with key stakeholders, and applying statistical analysis techniques to ensure data accuracy and reliability. The methodology emphasizes transparency and objectivity in data collection and analysis procedures.
Market modeling techniques utilize advanced analytical tools to project market trends, assess growth potential, and evaluate scenario-based outcomes. These models incorporate various factors including technological advancement rates, policy changes, and economic conditions that influence market development.
Regional distribution within the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market reveals distinct geographic concentrations that reflect optimal growing conditions, infrastructure availability, and historical development patterns. The Westland region maintains its position as the primary greenhouse cluster, accounting for approximately 40-45% of total greenhouse area and serving as the heart of Dutch horticultural innovation.
North Holland represents another significant greenhouse concentration, particularly around the Aalsmeer and surrounding areas, where flower production and high-tech vegetable growing facilities operate in close proximity to major distribution hubs and transportation infrastructure. This region benefits from excellent logistics connectivity and proximity to international markets.
South Holland encompasses diverse greenhouse operations ranging from traditional glass houses to cutting-edge research facilities that develop and test new growing technologies. The region’s strong research infrastructure supports innovation and technology transfer throughout the commercial greenhouse sector.
Limburg province has emerged as a growing greenhouse region, particularly for tomato and cucumber production, leveraging favorable climate conditions and available land for expansion. The area demonstrates significant growth potential with modern facilities incorporating the latest sustainable technologies.
Regional specialization patterns reflect local advantages and market focus areas, with certain regions concentrating on specific crops or production methods. This specialization enables knowledge clustering and efficiency gains through shared infrastructure and expertise development.
The competitive landscape of the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market features a diverse mix of operators ranging from family-owned businesses to large-scale commercial enterprises. Market leadership is determined by factors including production capacity, technological sophistication, product quality, and market reach.
Competitive strategies emphasize technological differentiation, sustainability leadership, and market specialization. Successful operators leverage advanced automation systems, energy-efficient technologies, and premium product positioning to maintain competitive advantages in increasingly sophisticated markets.
Innovation partnerships between commercial operators, research institutions, and technology providers foster collaborative development of next-generation greenhouse solutions. These partnerships accelerate technology adoption and enable rapid implementation of innovative growing techniques across the sector.
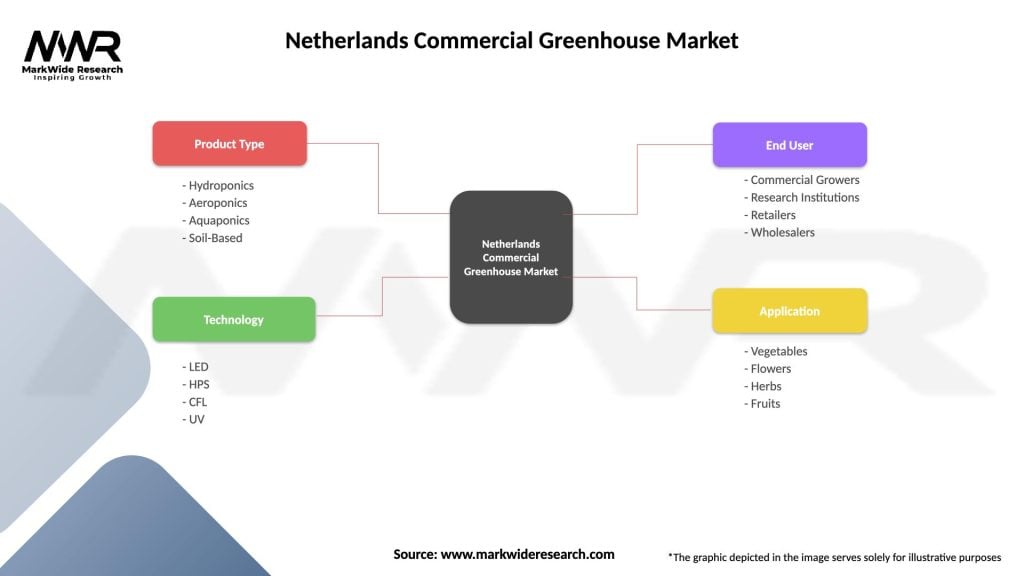
Market segmentation of the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market reveals distinct categories based on crop types, technology levels, and operational scales. This segmentation provides insights into market dynamics and growth opportunities across different greenhouse applications and production methods.
By Crop Type:
By Technology Level:
By Production Method:
Vegetable production dominates the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market, with tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers representing the largest production volumes and economic value. These crops benefit from well-established growing protocols, efficient supply chains, and strong market demand both domestically and internationally.
Tomato cultivation showcases the pinnacle of Dutch greenhouse technology, with yields reaching exceptional levels through precise climate control, optimized nutrition programs, and advanced crop management techniques. Modern tomato greenhouses achieve productivity levels exceeding 500 tons per hectare annually, demonstrating the effectiveness of controlled environment agriculture.
Floriculture operations maintain the Netherlands’ reputation as a global flower production and distribution center. Commercial flower greenhouses utilize sophisticated environmental controls to produce high-quality cut flowers and potted plants that meet exacting international standards for appearance, longevity, and consistency.
Specialty crop production represents a growing market segment, with greenhouse operators exploring high-value crops such as medicinal plants, exotic vegetables, and gourmet herbs. These niche markets often command premium prices and offer differentiation opportunities for innovative growers.
Leafy greens cultivation has expanded significantly, driven by consumer demand for fresh, locally-grown salads and vegetables. Advanced hydroponic and aeroponic systems enable rapid crop cycles and consistent quality that meets retail and foodservice requirements.
Greenhouse operators benefit from enhanced productivity, improved crop quality, and reduced production risks through controlled environment agriculture. Advanced greenhouse technologies enable year-round production, optimal resource utilization, and consistent yields that support stable business operations and profitability.
Technology providers gain access to a sophisticated market that values innovation and is willing to invest in advanced solutions. The Netherlands commercial greenhouse sector serves as a testing ground for new technologies and provides valuable feedback for product development and improvement.
Research institutions benefit from close collaboration with commercial operators, enabling practical application of research findings and accelerated technology transfer. This partnership approach ensures research relevance and supports continuous innovation in greenhouse production methods.
Consumers receive access to high-quality, fresh produce available year-round, often with reduced pesticide use and enhanced nutritional value. Local greenhouse production reduces transportation distances and environmental impact while ensuring product freshness and quality.
Government stakeholders achieve agricultural policy objectives including food security, environmental sustainability, and economic development through a thriving commercial greenhouse sector that demonstrates responsible resource utilization and innovation leadership.
Supply chain partners benefit from reliable, consistent product supply that enables efficient logistics operations and inventory management. The predictable production schedules of commercial greenhouses support supply chain optimization and reduce market volatility.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Automation advancement represents a dominant trend in the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market, with operators increasingly adopting robotic systems for planting, harvesting, and crop maintenance activities. These automated solutions address labor shortages while improving operational efficiency and consistency in crop management practices.
Sustainable energy integration continues gaining momentum as greenhouse operators implement renewable energy systems, waste heat recovery, and energy storage solutions. MWR data indicates that approximately 55-60% of modern facilities now incorporate some form of renewable energy technology, reflecting the sector’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
Data-driven agriculture emerges as a transformative trend, with greenhouse operators leveraging sensors, analytics, and artificial intelligence to optimize growing conditions and predict crop performance. This precision agriculture approach enables fine-tuned resource management and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Vertical growing systems gain adoption as operators seek to maximize production capacity within existing facilities. These systems enable higher plant densities and improved space utilization while maintaining quality standards and operational efficiency.
Consumer-direct marketing expands as greenhouse operators develop direct relationships with consumers through online platforms, farm stores, and subscription services. This trend enables premium pricing and enhanced customer engagement while reducing dependence on traditional distribution channels.
Circular economy practices become increasingly prevalent, with greenhouse operators implementing closed-loop systems for water, nutrients, and organic waste. These initiatives reduce environmental impact while creating potential cost savings and additional revenue opportunities.
Recent industry developments highlight the dynamic nature of the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market and its continuous evolution toward greater efficiency and sustainability. Major investments in research and development have yielded breakthrough technologies that enhance productivity while reducing environmental impact.
LED lighting advancement has revolutionized greenhouse operations, with new generation systems providing optimal light spectra for different crops while significantly reducing energy consumption. These developments enable year-round production with improved crop quality and reduced operational costs.
Climate control innovations include advanced ventilation systems, precision humidity management, and integrated environmental monitoring that optimize growing conditions while minimizing energy usage. These technologies contribute to improved crop yields and resource efficiency.
Automation breakthroughs encompass robotic harvesting systems, automated seeding and transplanting equipment, and intelligent crop monitoring platforms that reduce labor requirements while maintaining high quality standards. These developments address workforce challenges while improving operational consistency.
Sustainability initiatives include implementation of circular water systems, organic waste processing facilities, and renewable energy integration projects that demonstrate the sector’s commitment to environmental stewardship and resource conservation.
Market expansion projects involve development of new greenhouse facilities, modernization of existing operations, and international collaboration initiatives that extend Dutch greenhouse expertise to global markets through technology transfer and consulting services.
Strategic recommendations for Netherlands commercial greenhouse market participants emphasize the importance of continued technology adoption and sustainability leadership to maintain competitive advantages in evolving agricultural markets. Operators should prioritize investments in automation systems and energy-efficient technologies that reduce operational costs while improving productivity.
Diversification strategies should focus on high-value specialty crops and emerging market segments that offer premium pricing opportunities and reduced competition from traditional agricultural producers. Exploring medicinal plants, exotic vegetables, and gourmet herbs can provide differentiation and enhanced profitability.
International expansion opportunities merit serious consideration, particularly through technology licensing, consulting services, and joint venture partnerships in developing markets. Dutch greenhouse expertise commands premium value globally and can generate substantial revenue streams beyond domestic operations.
Sustainability investments should accelerate, with focus on renewable energy systems, circular economy practices, and carbon footprint reduction initiatives. These investments not only reduce operational costs but also enhance market positioning and access to environmentally conscious consumers.
Workforce development requires immediate attention through training programs, educational partnerships, and technology adoption that reduces dependence on manual labor. Addressing skill gaps ensures operational continuity and enables full utilization of advanced greenhouse technologies.
Supply chain optimization should emphasize direct market relationships, value-added processing capabilities, and logistics efficiency improvements that enhance profitability and market responsiveness. Building stronger connections with end consumers can reduce intermediary costs and improve market positioning.
Future prospects for the Netherlands commercial greenhouse market remain exceptionally positive, driven by continued technological advancement, growing demand for sustainable food production, and expanding international opportunities. The sector is positioned to maintain its global leadership role while adapting to evolving market conditions and consumer preferences.
Technology evolution will accelerate with artificial intelligence integration, advanced robotics deployment, and precision agriculture systems becoming standard features in commercial greenhouse operations. These developments promise further productivity improvements and operational efficiency gains that strengthen competitive positioning.
Market expansion opportunities include both domestic growth through facility modernization and international development through technology export and consulting services. The global recognition of Dutch greenhouse expertise creates substantial opportunities for knowledge transfer and partnership development worldwide.
Sustainability leadership will intensify as greenhouse operators implement increasingly sophisticated environmental management systems and circular economy practices. According to MarkWide Research projections, sustainability-focused operations are expected to achieve efficiency improvements of 20-25% over the next five years through advanced resource management techniques.
Innovation acceleration will continue through strengthened research partnerships, increased investment in technology development, and collaborative projects that advance greenhouse production capabilities. The sector’s commitment to continuous improvement ensures ongoing competitiveness and market leadership.
Market resilience will be enhanced through diversification strategies, risk management improvements, and adaptive capacity development that enables successful navigation of changing market conditions and external challenges while maintaining growth momentum and profitability.
The Netherlands commercial greenhouse market represents a pinnacle of agricultural innovation and sustainable food production, demonstrating how advanced technology and environmental stewardship can coexist to create exceptional value for producers, consumers, and society. This dynamic sector continues to set global standards for controlled environment agriculture while adapting to evolving market demands and technological possibilities.
Market fundamentals remain strong, supported by continuous innovation, robust export capabilities, and unwavering commitment to sustainability that positions Dutch greenhouse operations as global leaders in efficient food production. The sector’s ability to achieve remarkable productivity levels while minimizing environmental impact provides a compelling model for agricultural development worldwide.
Strategic positioning for future success requires continued investment in technology advancement, workforce development, and market diversification that leverages existing strengths while exploring new opportunities. The integration of artificial intelligence, automation systems, and sustainable practices will define competitive advantages in increasingly sophisticated agricultural markets.
Long-term prospects indicate sustained growth potential through domestic market expansion, international technology transfer, and continuous innovation that maintains the Netherlands’ position as the global center of excellence for commercial greenhouse production. The sector’s commitment to research, development, and sustainable practices ensures continued leadership in controlled environment agriculture for years to come.
What is Commercial Greenhouse?
Commercial Greenhouse refers to structures designed for the cultivation of plants, vegetables, and flowers in a controlled environment. These greenhouses utilize advanced technologies to optimize growth conditions, including temperature, humidity, and light, enhancing productivity and sustainability.
What are the key players in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market?
Key players in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market include companies like Ridder, Kubo Group, and Van der Hoeven Horticultural Projects. These companies are known for their innovative greenhouse designs and technologies that support efficient agricultural practices, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market?
The Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for locally grown produce, advancements in greenhouse technology, and the need for sustainable agricultural practices. Additionally, the rise in urban farming initiatives contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market face?
Challenges in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market include high initial investment costs, regulatory compliance related to environmental standards, and competition from alternative farming methods. These factors can hinder the expansion of greenhouse operations.
What opportunities exist in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market?
Opportunities in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market include the integration of smart farming technologies, expansion into new crop varieties, and the potential for vertical farming solutions. These innovations can enhance productivity and sustainability in greenhouse operations.
What trends are shaping the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market?
Trends in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market include the adoption of automation and AI technologies, increased focus on energy-efficient systems, and the growing popularity of organic and sustainable farming practices. These trends are transforming how greenhouses operate and produce food.
Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Hydroponics, Aeroponics, Aquaponics, Soil-Based |
| Technology | LED, HPS, CFL, UV |
| End User | Commercial Growers, Research Institutions, Retailers, Wholesalers |
| Application | Vegetables, Flowers, Herbs, Fruits |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Netherlands Commercial Greenhouse Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at