444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Naval remote weapons stations (RWS) are advanced weapon systems designed for remote operation and control from within a naval vessel. These systems enable the deployment of a variety of weapon systems, including machine guns, automatic cannons, and guided missiles, for ship self-defense, maritime security, and naval warfare missions. Naval RWS offer enhanced accuracy, firepower, and situational awareness while minimizing crew exposure to combat risks and improving operational efficiency.
Meaning
Naval remote weapons stations (RWS) represent a critical component of modern naval warfare systems, providing ships with the capability to deploy and control weapons remotely from a protected position within the vessel. These systems integrate sensors, fire control systems, and weapon platforms to enable precise targeting, engagement, and neutralization of threats in maritime environments. Naval RWS enhance ship self-defense capabilities, increase operational flexibility, and reduce crew workload during combat operations.
Executive Summary
The naval remote weapons station market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing focus on naval modernization, maritime security, and littoral warfare capabilities. Key naval RWS manufacturers are investing in research and development initiatives to enhance system performance, modularity, and interoperability with existing shipborne sensors and combat systems. Moreover, advancements in sensor technology, electro-optics, and network-centric warfare are driving innovation and expanding the capabilities of naval RWS for anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine warfare missions.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The naval remote weapons station market is characterized by dynamic trends, technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and competitive dynamics. Understanding these dynamics is essential for stakeholders to identify opportunities, address challenges, and formulate effective strategies for sustained growth and competitiveness.
Regional Analysis
The naval remote weapons station market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as defense budgets, naval modernization priorities, geopolitical dynamics, and maritime security challenges. Key regions driving market growth include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
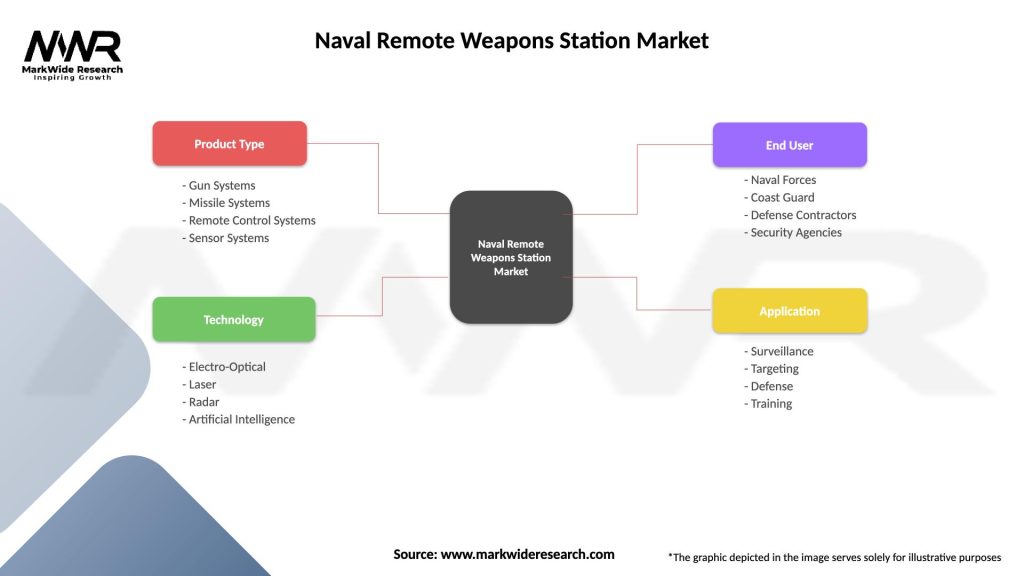
Segmentation
The naval remote weapons station market can be segmented based on various parameters, including:
Segmentation facilitates a deeper understanding of market dynamics and enables companies to tailor their strategies to target specific segments and customer needs.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the naval remote weapons station market:
Understanding these factors enables companies to leverage strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats to maintain a competitive edge in the naval remote weapons station market.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had mixed effects on the naval remote weapons station market. While the initial phase of the pandemic led to disruptions in supply chains, manufacturing operations, and project timelines, the subsequent recovery phase saw increased investments in defense spending, naval modernization programs, and maritime security initiatives. Key impacts of COVID-19 on the market include:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The naval remote weapons station market is poised for significant growth and innovation driven by increasing maritime threats, naval modernization programs, and technological advancements. Integration with unmanned systems, network-centric warfare solutions, and advanced sensor technologies will enhance the capabilities and effectiveness of naval RWS for future maritime operations. However, companies must address challenges such as cost constraints, technological complexity, and cybersecurity risks to capitalize on growth opportunities and maintain market leadership.
Conclusion
The naval remote weapons station market represents a critical component of modern naval warfare systems, providing ships with enhanced ship self-defense capabilities, situational awareness, and operational flexibility. With advancements in technology, integration with unmanned systems, and focus on maritime security, naval RWS are poised to play a pivotal role in future naval operations. By investing in innovation, strengthening partnerships, and addressing market challenges, companies can capitalize on growth opportunities and contribute to maritime security and defense worldwide.
What is Naval Remote Weapons Station?
A Naval Remote Weapons Station is a system that allows for the remote operation of weaponry on naval vessels, enhancing operational efficiency and safety. These systems are designed to provide precise targeting and engagement capabilities while minimizing the risk to personnel.
What are the key players in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market?
Key players in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market include companies such as Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, and BAE Systems, which are known for their advanced defense technologies and weapon systems, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market?
The growth of the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market is driven by increasing defense budgets, the rising need for enhanced naval capabilities, and advancements in remote weapon technologies. Additionally, geopolitical tensions are prompting nations to invest in modernizing their naval fleets.
What challenges does the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market face?
Challenges in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market include high development costs, the complexity of integrating new technologies with existing systems, and regulatory hurdles related to defense procurement. These factors can hinder the timely deployment of new systems.
What opportunities exist in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market?
Opportunities in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market include the development of next-generation systems that incorporate artificial intelligence and automation. Additionally, increasing collaboration between defense contractors and governments can lead to innovative solutions and enhanced capabilities.
What trends are shaping the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market?
Trends in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market include the growing emphasis on unmanned systems, advancements in sensor technologies, and the integration of cyber capabilities for enhanced security. These trends are reshaping how naval operations are conducted and weapon systems are deployed.
Naval Remote Weapons Station Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Gun Systems, Missile Systems, Remote Control Systems, Sensor Systems |
| Technology | Electro-Optical, Laser, Radar, Artificial Intelligence |
| End User | Naval Forces, Coast Guard, Defense Contractors, Security Agencies |
| Application | Surveillance, Targeting, Defense, Training |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Naval Remote Weapons Station Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at