444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
Nanopatterning is a cutting-edge technology that involves the manipulation of materials and surfaces at the nanoscale level, enabling the creation of intricate patterns and structures with remarkable precision. This emerging field has gained significant attention in various industries, including electronics, biotechnology, healthcare, and optics. Nanopatterning techniques offer unprecedented control over the properties of materials, opening up a world of possibilities for next-generation devices and applications.
Meaning
Nanopatterning refers to the process of creating patterns or structures on a nanometer scale, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers. It involves techniques such as lithography, self-assembly, and nanomolding, which allow the precise positioning and arrangement of nanoparticles or molecules to achieve desired functionalities. By manipulating materials at such a small scale, scientists and engineers can unlock unique properties and tailor them to specific applications.
Executive Summary
The nanopatterning market has been witnessing remarkable growth in recent years, driven by advancements in nanotechnology and increasing demand for high-performance devices and materials. This market’s value is expected to reach billions of dollars in the coming years, presenting lucrative opportunities for both established players and new entrants.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The nanopatterning market is driven by a combination of technological advancements, increasing demand from various industries, and a favorable regulatory environment. The constant evolution of nanofabrication techniques and the development of new materials are pushing the boundaries of what is possible at the nanoscale. As industries across the globe recognize the potential benefits of nanopatterning, investments and collaborations are increasing, driving the market forward.
Regional Analysis
The nanopatterning market is geographically diverse, with key regions including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the rest of the world. North America holds a significant market share due to its well-established nanotechnology infrastructure and presence of key players. Europe is also a prominent region, with a strong focus on research and development activities. The Asia Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth, driven by the increasing adoption of nanopatterning in electronics and healthcare industries, as well as growing investments in nanotechnology by countries like China and Japan.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Nanopatterning market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
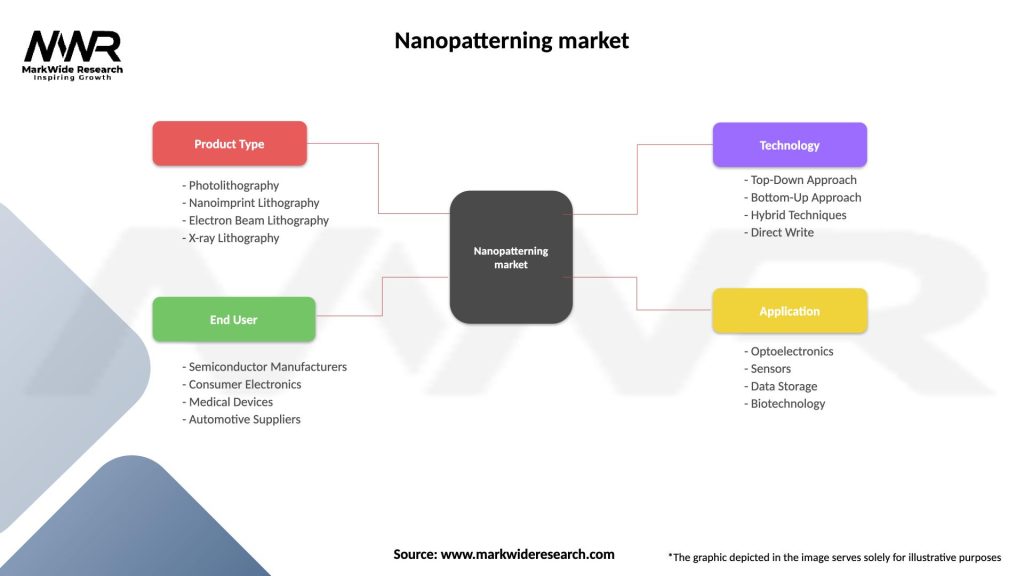
The nanopatterning market can be segmented based on technology, application, and end-use industry.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative effects on the nanopatterning market. On the positive side, there has been an increased focus on healthcare-related applications of nanopatterning, including the development of diagnostics, antiviral coatings, and drug delivery systems. However, supply chain disruptions and reduced research activities during lockdowns have impacted the market’s growth to some extent.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the nanopatterning market looks promising, with significant growth expected in the coming years. Technological advancements, increasing investments in nanotechnology research, and expanding application areas will drive the market’s growth. The development of scalable and cost-effective nanopatterning processes, along with the establishment of regulatory frameworks, will further boost the adoption of nanopatterning technologies across industries.
Conclusion
Nanopatterning is revolutionizing industries by enabling precise control over materials and surfaces at the nanoscale level. The market is driven by the demand for high-performance electronics, advancements in nanofabrication techniques, and growing applications in biotechnology, healthcare, and energy. While there are challenges to overcome, such as complex manufacturing processes and scalability issues, the nanopatterning market presents immense opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. By leveraging technological advancements, collaborating with research institutions, and focusing on scalability and cost-effectiveness, companies can position themselves at the forefront of this transformative market. As nanotechnology continues to evolve, nanopatterning will play a vital role in shaping the future of various industries, paving the way for advanced devices, materials, and applications.
What is Nanopatterning?
Nanopatterning refers to the process of creating nanoscale patterns on surfaces, which can be used in various applications such as electronics, photonics, and biotechnology. This technique enables the fabrication of devices with enhanced performance and functionality at the nanoscale.
What are the key companies in the Nanopatterning market?
Key companies in the Nanopatterning market include ASML, Canon, and Heidelberg Instruments, which are known for their advanced lithography and patterning technologies. These companies play a significant role in driving innovation and competition in the field, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Nanopatterning market?
The Nanopatterning market is driven by the increasing demand for miniaturized electronic devices, advancements in nanotechnology, and the growing applications in sectors such as healthcare and renewable energy. These factors contribute to the expansion of the market and its technological advancements.
What challenges does the Nanopatterning market face?
The Nanopatterning market faces challenges such as high production costs, complexity in manufacturing processes, and the need for precision in patterning techniques. These challenges can hinder the widespread adoption of nanopatterning technologies in various industries.
What opportunities exist in the future of the Nanopatterning market?
The future of the Nanopatterning market presents opportunities in emerging fields like quantum computing, advanced materials, and personalized medicine. As research progresses, new applications and technologies are likely to emerge, driving further growth in the market.
What trends are shaping the Nanopatterning market?
Current trends in the Nanopatterning market include the development of more efficient patterning techniques, integration with other nanofabrication methods, and the increasing focus on sustainable practices. These trends are influencing how companies approach nanopatterning and its applications.
Nanopatterning market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Photolithography, Nanoimprint Lithography, Electron Beam Lithography, X-ray Lithography |
| End User | Semiconductor Manufacturers, Consumer Electronics, Medical Devices, Automotive Suppliers |
| Technology | Top-Down Approach, Bottom-Up Approach, Hybrid Techniques, Direct Write |
| Application | Optoelectronics, Sensors, Data Storage, Biotechnology |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Nanopatterning market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at