444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Myanmar plastic market represents a rapidly evolving sector within Southeast Asia’s industrial landscape, characterized by substantial growth potential and increasing domestic demand. Myanmar’s plastic industry has experienced remarkable transformation following economic liberalization, with local manufacturers and international investors recognizing the country’s strategic position as a manufacturing hub. The market encompasses diverse applications including packaging, construction, automotive components, and consumer goods, driven by urbanization and industrial development.
Market dynamics indicate robust expansion across multiple segments, with the packaging sector leading consumption patterns. The country’s growing middle class and increasing consumer spending have created significant demand for plastic products, particularly in food packaging and household items. Manufacturing capabilities have expanded considerably, with both domestic and foreign companies establishing production facilities to serve local and regional markets.
Regional positioning within ASEAN has enhanced Myanmar’s attractiveness as a plastic manufacturing destination, benefiting from competitive labor costs and improving infrastructure. The market demonstrates strong growth momentum, with industry analysts projecting continued expansion driven by construction activities, agricultural modernization, and export-oriented manufacturing. Investment flows into the sector have increased substantially, supporting technology upgrades and capacity expansion initiatives.
The Myanmar plastic market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing production, distribution, and consumption of plastic materials and products within Myanmar’s borders. This market includes raw material processing, manufacturing of finished plastic goods, import and export activities, and the entire value chain from petrochemical feedstock to end-user applications.
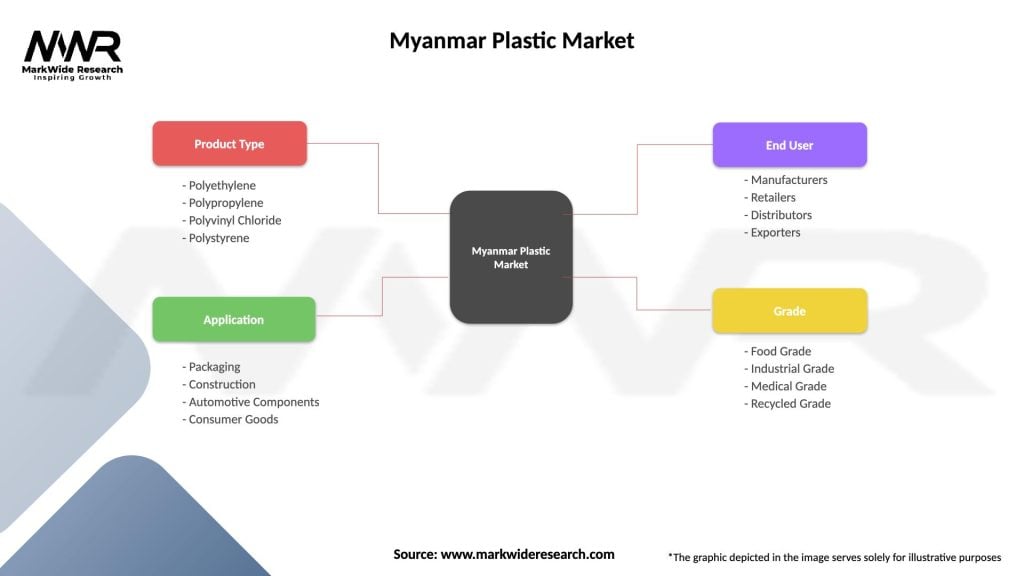
Market scope covers various plastic types including polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, and engineering plastics used across industries such as packaging, construction, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. The market represents both domestic consumption patterns and export-oriented production capabilities, reflecting Myanmar’s integration into regional and global supply chains.
Industry definition encompasses upstream activities like polymer production and compounding, midstream processing including injection molding and extrusion, and downstream applications across diverse end-use sectors. The market’s significance extends beyond economic value to include employment generation, technology transfer, and industrial development contributions to Myanmar’s broader economic transformation.
Myanmar’s plastic market demonstrates exceptional growth potential, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing consumer demand across multiple sectors. The market has evolved from primarily import-dependent to developing significant domestic manufacturing capabilities, supported by favorable government policies and international investment.
Key growth drivers include expanding construction activities, agricultural modernization requiring plastic applications, and growing packaging demand from food and beverage industries. The market benefits from Myanmar’s strategic location within ASEAN, providing access to regional markets and supply chains. Manufacturing expansion has been particularly notable in the packaging and construction materials segments.
Market challenges include infrastructure limitations, skilled labor shortages, and regulatory uncertainties that occasionally impact investment decisions. However, ongoing infrastructure development and economic reforms continue to address these constraints. Future prospects remain highly positive, with industry experts anticipating sustained growth driven by domestic consumption and export opportunities.
Investment trends show increasing foreign direct investment in plastic manufacturing facilities, technology transfer agreements, and joint ventures between international companies and local partners. The market’s evolution reflects Myanmar’s broader economic development trajectory and integration into global manufacturing networks.
Market segmentation reveals diverse applications with packaging representing the largest consumption category, followed by construction materials and consumer goods. The following key insights characterize the Myanmar plastic market:
Economic liberalization has created favorable conditions for plastic market expansion, with improved business environment and investment incentives attracting domestic and foreign capital. The removal of trade barriers and simplification of business registration processes have facilitated market entry and expansion for plastic manufacturers.
Urbanization trends significantly drive plastic consumption, as growing urban populations demand packaged goods, modern construction materials, and consumer products. Urban development projects require substantial plastic inputs for infrastructure, housing, and commercial construction, creating sustained demand growth.
Industrial development across sectors including textiles, electronics, and automotive creates derived demand for plastic components and materials. Manufacturing expansion in export-oriented industries particularly drives demand for high-quality plastic inputs and packaging solutions. Infrastructure investment in roads, bridges, and utilities incorporates significant plastic materials usage.
Consumer behavior changes toward modern retail and packaged goods consumption patterns support plastic market growth. Rising disposable incomes and changing lifestyle preferences increase demand for convenience products and modern packaging solutions. Agricultural modernization drives adoption of plastic applications including irrigation systems, greenhouse materials, and crop protection solutions.
Regional integration within ASEAN provides market access opportunities and supply chain efficiencies, encouraging investment in plastic manufacturing capabilities. Trade facilitation measures and economic cooperation agreements enhance Myanmar’s attractiveness as a regional manufacturing hub.
Infrastructure limitations pose significant challenges to plastic market development, including inadequate power supply, transportation networks, and industrial facilities. Unreliable electricity supply affects manufacturing operations and increases production costs, while poor road conditions impact distribution efficiency and market reach.
Skilled labor shortage constrains industry expansion, as plastic manufacturing requires technical expertise in processing, quality control, and equipment maintenance. Limited technical education and training programs create workforce development challenges, affecting productivity and technology adoption rates.
Raw material dependency on imports creates vulnerability to price volatility and supply disruptions. Limited domestic petrochemical production capacity necessitates reliance on imported polymers and additives, affecting cost competitiveness and supply chain stability. Currency fluctuations impact import costs and profit margins for manufacturers.
Regulatory uncertainties occasionally create investment hesitation, as evolving policies and administrative procedures can affect business planning and operations. Environmental regulations and waste management requirements add compliance costs and operational complexity for plastic manufacturers.
Competition from established markets in neighboring countries with more developed infrastructure and manufacturing capabilities creates competitive pressure. Technology gaps compared to regional competitors affect product quality and production efficiency, limiting market positioning opportunities.
Export market potential presents significant opportunities as Myanmar develops manufacturing capabilities for regional and global markets. The country’s competitive labor costs and strategic location provide advantages for export-oriented plastic manufacturing, particularly for ASEAN markets and beyond.
Infrastructure development projects create substantial demand for plastic materials including pipes, fittings, insulation, and construction components. Government infrastructure investment programs and private development projects offer sustained market opportunities for plastic suppliers and manufacturers.
Agricultural sector modernization opens new application areas for plastic products including greenhouse films, irrigation systems, mulch films, and storage solutions. Growing agricultural productivity focus and mechanization trends drive demand for specialized plastic applications. Aquaculture expansion requires plastic components for pond liners, nets, and processing equipment.
Technology transfer opportunities through joint ventures and foreign investment enable capability development and market expansion. International partnerships provide access to advanced manufacturing technologies, quality systems, and global market networks. Recycling and sustainability initiatives create new business opportunities in waste management and circular economy applications.
E-commerce growth drives packaging demand as online retail expands, requiring protective packaging, shipping materials, and logistics solutions. Healthcare sector development creates opportunities for medical-grade plastics and pharmaceutical packaging applications.
Supply chain evolution reflects Myanmar’s transition from import-dependent to increasingly self-sufficient plastic production. Domestic manufacturing capacity has expanded significantly, with new facilities established across various plastic processing segments. Raw material sourcing strategies balance import requirements with developing local capabilities.
Demand patterns show strong correlation with economic growth and urbanization rates, with packaging and construction applications leading consumption growth. Seasonal variations affect certain segments, particularly agricultural applications and construction materials. Price dynamics reflect global polymer markets while incorporating local factors including transportation costs and currency fluctuations.
Competitive landscape includes both domestic manufacturers and international companies establishing local operations. Market consolidation trends show larger companies acquiring smaller operations and expanding production capacity. Technology adoption varies across market segments, with export-oriented manufacturers typically implementing more advanced processing technologies.
Regulatory environment continues evolving with increasing focus on environmental standards and product quality requirements. Government policies support industrial development while addressing sustainability concerns through waste management and recycling initiatives. Investment flows demonstrate confidence in long-term market prospects despite short-term challenges.
Market analysis employs comprehensive research methodologies combining primary and secondary data sources to provide accurate market insights. Primary research includes direct interviews with industry stakeholders, manufacturers, distributors, and end-users across Myanmar’s plastic value chain.
Data collection encompasses production statistics, import/export data, consumption patterns, and pricing information from government agencies, industry associations, and commercial databases. MarkWide Research utilizes established networks within Myanmar’s industrial sector to gather current market intelligence and validate findings.
Secondary research incorporates government publications, industry reports, trade statistics, and economic indicators to establish market context and trends. Cross-referencing multiple sources ensures data accuracy and reliability for market analysis and projections.
Market segmentation analysis examines consumption patterns across applications, product types, and regional distributions. Manufacturing capacity assessments include facility surveys and production capability evaluations. Competitive analysis covers market share assessments, company profiles, and strategic positioning evaluation.
Validation processes include expert consultations, industry feedback, and statistical verification to ensure research accuracy and relevance. Market projections incorporate economic indicators, policy developments, and industry trends to provide reliable forecasting.
Yangon region dominates Myanmar’s plastic market, accounting for approximately 45% of total consumption and hosting the majority of manufacturing facilities. The region benefits from port access, industrial infrastructure, and proximity to major consumer markets. Manufacturing concentration in Yangon includes packaging, consumer goods, and export-oriented production facilities.
Mandalay region represents the second-largest market, with growing industrial development and strategic location for serving northern Myanmar and cross-border trade. The region shows particular strength in construction materials and agricultural applications, supported by regional development initiatives.
Coastal regions including Ayeyarwady and Mon states demonstrate growing plastic consumption driven by aquaculture, agriculture, and port-related activities. These areas show increasing adoption of plastic applications in fishing, agriculture, and small-scale manufacturing. Border regions benefit from cross-border trade opportunities and regional economic cooperation.
Rural areas represent emerging markets with growing plastic adoption in agriculture, construction, and consumer goods. Infrastructure development and rural electrification programs support market expansion in these regions. Regional distribution networks continue expanding to serve growing demand across Myanmar’s diverse geographic areas.
Urban centers beyond Yangon and Mandalay show increasing plastic consumption as economic development spreads across the country. Regional manufacturing capabilities are developing to serve local markets and reduce transportation costs.
Market structure includes both established domestic companies and international manufacturers establishing local operations. The competitive environment reflects Myanmar’s economic opening and integration into regional supply chains.
Competitive strategies focus on capacity expansion, technology upgrades, and market diversification. Companies increasingly emphasize quality improvements and export market development. Market consolidation trends show larger companies acquiring smaller operations and expanding production capacity.
Innovation focus includes product development, process improvements, and sustainability initiatives. Companies invest in modern equipment and technical capabilities to enhance competitiveness and market positioning.
By Product Type:
By Application:
By End-User Industry:
Packaging Category represents the largest market segment, driven by food and beverage industry growth and changing consumer preferences. Flexible packaging shows particularly strong growth, with increasing demand for convenience foods and modern retail formats. Rigid packaging applications include containers, bottles, and industrial packaging solutions.
Construction Category demonstrates robust growth supported by infrastructure development and urbanization. Pipe and fittings represent major applications, with increasing adoption of plastic alternatives to traditional materials. Insulation materials and building components show growing market penetration.
Agricultural Category exhibits significant potential as farming practices modernize and productivity requirements increase. Greenhouse applications show rapid adoption, with farmers recognizing benefits of controlled environment agriculture. Irrigation systems and crop protection materials represent growing application areas.
Consumer Goods Category reflects rising living standards and changing lifestyle preferences. Household products show steady growth with urbanization and income improvements. Electronics and appliance applications increase with technology adoption and consumer electronics market expansion.
Industrial Category encompasses diverse applications across manufacturing sectors. Automotive applications grow with vehicle production increases and lightweighting trends. Electronics and electrical applications expand with industrial development and infrastructure modernization.
Manufacturers benefit from growing domestic demand, competitive production costs, and export market opportunities. Cost advantages include lower labor costs compared to developed markets and improving infrastructure supporting efficient operations. Access to ASEAN markets provides expansion opportunities beyond domestic consumption.
Investors gain exposure to high-growth market with substantial development potential and government support for industrial development. Strategic positioning in Myanmar provides early-mover advantages in an emerging market with significant upside potential. Joint venture opportunities enable technology transfer and market access.
End-users benefit from improving product quality, competitive pricing, and local supply chain advantages. Supply security improves with domestic manufacturing development, reducing dependency on imports and transportation risks. Technical support and customization capabilities enhance user experience.
Government stakeholders benefit from industrial development, employment generation, and export revenue contributions. Economic diversification reduces dependency on traditional sectors and enhances industrial capabilities. Technology transfer and skill development support broader economic development objectives.
Local communities benefit from employment opportunities, skill development, and economic activity generation. Infrastructure development associated with industrial projects improves regional connectivity and services. Environmental benefits include reduced transportation requirements and local recycling initiatives.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainability Focus emerges as a major trend, with increasing attention to recycling initiatives, biodegradable alternatives, and circular economy principles. Companies invest in waste management capabilities and sustainable product development to address environmental concerns and regulatory requirements.
Technology Modernization accelerates across the industry, with manufacturers upgrading equipment and processes to improve efficiency and product quality. Automation adoption increases to address labor shortages and enhance productivity. Digital technologies including IoT and data analytics gain traction for process optimization.
Export Orientation grows as manufacturers develop capabilities for regional and global markets. Quality certifications and international standards compliance become priorities for export market access. Supply chain integration with regional networks enhances competitiveness and market reach.
Product Innovation focuses on specialized applications and value-added products to differentiate from commodity competition. Customization capabilities develop to serve specific industry requirements and customer needs. Research and development investments increase to support innovation initiatives.
Market Consolidation continues with larger companies acquiring smaller operations and expanding capacity. Vertical integration strategies emerge as companies seek to control supply chains and improve margins. Strategic partnerships and joint ventures facilitate technology transfer and market expansion.
Manufacturing Expansion includes several major facility developments and capacity additions across different plastic processing segments. New production lines and technology upgrades enhance manufacturing capabilities and product quality standards. Foreign Investment projects bring advanced technologies and international expertise to the market.
Infrastructure Projects support industry development through improved power supply, transportation networks, and industrial zones. Government initiatives include policy reforms, investment incentives, and regulatory improvements to support industrial growth. Special economic zones provide enhanced facilities and services for manufacturers.
Technology Transfer agreements between international companies and local partners facilitate knowledge sharing and capability development. MWR analysis indicates increasing collaboration between foreign technology providers and domestic manufacturers to develop local expertise and production capabilities.
Sustainability Initiatives include recycling facility development, waste management programs, and sustainable product development projects. Industry associations promote best practices and coordinate sustainability efforts across the sector. Environmental compliance programs address regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
Market Access improvements through trade facilitation measures and regional economic integration enhance export opportunities. Quality certification programs help manufacturers meet international standards and access global markets. Supply chain development initiatives improve efficiency and competitiveness.
Investment Strategy should focus on segments with strong growth potential and competitive advantages, particularly packaging, construction materials, and export-oriented manufacturing. Technology adoption remains critical for competitiveness, requiring investment in modern equipment and process improvements.
Market Entry strategies should consider joint ventures with local partners to navigate regulatory requirements and market dynamics effectively. Capacity planning should align with demand growth projections while maintaining flexibility for market changes. Geographic diversification across Myanmar’s regions can reduce concentration risks.
Supply Chain optimization should balance import requirements with domestic sourcing opportunities as local capabilities develop. Quality systems implementation becomes essential for market positioning and export market access. Sustainability initiatives should be integrated into business strategies to address regulatory and market requirements.
Human Resource development requires investment in training programs and technical capability building to address skill shortages. Government relations management remains important given evolving regulatory environment and policy developments. Risk management strategies should address currency, political, and operational risks.
Innovation focus should emphasize product development, process improvements, and customer-specific solutions to differentiate from commodity competition. Market intelligence capabilities should be developed to track trends, competition, and opportunities in this dynamic market environment.
Growth trajectory remains highly positive, with industry analysts projecting sustained expansion driven by domestic consumption growth and export market development. MarkWide Research forecasts continued strong performance across multiple segments, with packaging and construction materials leading growth momentum.
Manufacturing capabilities are expected to expand significantly, with new facilities and technology upgrades enhancing production capacity and product quality. Export potential shows particular promise, with Myanmar positioned to serve growing regional markets and global supply chains. Competitive advantages in labor costs and strategic location support export development.
Infrastructure development will continue supporting market growth through improved power supply, transportation networks, and industrial facilities. Government policies are expected to maintain support for industrial development while addressing sustainability and environmental concerns. Regulatory framework evolution should provide greater clarity and stability for investors.
Technology advancement will accelerate as companies invest in modernization and automation to improve efficiency and competitiveness. Sustainability focus will intensify, with recycling capabilities and sustainable product development becoming increasingly important. Market consolidation trends are likely to continue, creating larger, more capable industry players.
Regional integration within ASEAN will enhance market access and supply chain opportunities, supporting export-oriented manufacturing development. Long-term prospects remain highly favorable, with Myanmar’s plastic market positioned for sustained growth and development over the coming decade.
The Myanmar plastic market represents a compelling growth opportunity within Southeast Asia’s industrial landscape, characterized by strong domestic demand, competitive advantages, and significant export potential. Despite infrastructure and regulatory challenges, the market demonstrates robust fundamentals supported by economic development, urbanization, and industrial modernization trends.
Market dynamics favor continued expansion across multiple segments, with packaging, construction, and agricultural applications leading growth momentum. The combination of competitive labor costs, strategic location, and government support creates favorable conditions for both domestic and international investors seeking exposure to this emerging market.
Future success will depend on addressing infrastructure limitations, developing technical capabilities, and maintaining competitive positioning as the market matures. Companies that invest in technology, quality systems, and sustainability initiatives are best positioned to capitalize on Myanmar’s plastic market opportunities and contribute to the country’s industrial development trajectory.
What is Plastic?
Plastic refers to a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that are used in various applications, including packaging, construction, and consumer goods. In Myanmar, the plastic industry is growing, driven by increasing demand for packaging and durable goods.
What are the key players in the Myanmar Plastic Market?
Key players in the Myanmar Plastic Market include companies like Myanmar Plastic Industries, Aung Myin Hmu, and Shwe Pyi Tan, which are involved in manufacturing and distributing various plastic products. These companies contribute significantly to the local economy and meet the rising demand for plastic goods among others.
What are the growth factors for the Myanmar Plastic Market?
The growth of the Myanmar Plastic Market is driven by factors such as urbanization, increased consumer spending, and the expansion of the packaging industry. Additionally, the rise in e-commerce and food delivery services is boosting demand for plastic packaging solutions.
What challenges does the Myanmar Plastic Market face?
The Myanmar Plastic Market faces challenges such as environmental concerns regarding plastic waste and limited recycling infrastructure. Additionally, regulatory issues and competition from alternative materials can hinder market growth.
What opportunities exist in the Myanmar Plastic Market?
Opportunities in the Myanmar Plastic Market include the development of biodegradable plastics and innovations in recycling technologies. As sustainability becomes a priority, companies that invest in eco-friendly solutions may gain a competitive edge.
What trends are shaping the Myanmar Plastic Market?
Trends in the Myanmar Plastic Market include a shift towards sustainable packaging solutions and increased use of recycled materials. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies are enabling the production of higher-quality plastic products.
Myanmar Plastic Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Polyvinyl Chloride, Polystyrene |
| Application | Packaging, Construction, Automotive Components, Consumer Goods |
| End User | Manufacturers, Retailers, Distributors, Exporters |
| Grade | Food Grade, Industrial Grade, Medical Grade, Recycled Grade |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Myanmar Plastic Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at