444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The mRNA therapeutics contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) market represents a rapidly evolving sector within the biopharmaceutical industry, driven by the revolutionary success of mRNA-based vaccines and the expanding potential of mRNA therapeutics. This specialized market encompasses organizations that provide comprehensive development, manufacturing, and regulatory support services for mRNA-based therapeutic products, including vaccines, protein replacement therapies, and gene editing applications.
Market dynamics indicate unprecedented growth following the global deployment of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, which demonstrated the viability and scalability of mRNA technology platforms. The market is experiencing robust expansion with a projected CAGR of 15.8% through the forecast period, reflecting increasing demand for specialized manufacturing capabilities and expertise in mRNA production processes.
Key market characteristics include the complex nature of mRNA manufacturing, which requires specialized facilities, advanced cold chain logistics, and sophisticated quality control systems. The market serves pharmaceutical companies ranging from established biotechnology firms to emerging startups developing novel mRNA therapeutics for various therapeutic areas including oncology, rare diseases, and infectious diseases.
Geographic distribution shows strong concentration in North America and Europe, with approximately 68% market share attributed to these regions due to their advanced biomanufacturing infrastructure and regulatory frameworks. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific are gaining momentum as companies seek cost-effective manufacturing solutions and regional market access.
The mRNA therapeutics CDMO market refers to the specialized segment of contract manufacturing organizations that provide comprehensive development, production, and regulatory support services specifically for messenger RNA-based therapeutic products and vaccines.
Contract development and manufacturing organizations in this space offer end-to-end services including process development, analytical method development, clinical and commercial manufacturing, regulatory support, and supply chain management. These organizations possess specialized expertise in mRNA synthesis, lipid nanoparticle formulation, purification processes, and the stringent quality control requirements specific to mRNA therapeutics.
Core service offerings encompass various stages of mRNA therapeutic development, from early-stage research support through commercial-scale manufacturing. This includes plasmid DNA production, in vitro transcription, purification and quality control, lipid nanoparticle encapsulation, fill-finish operations, and comprehensive analytical testing services.
Strategic importance of these organizations has grown significantly as pharmaceutical companies recognize the complexity and capital-intensive nature of mRNA manufacturing. Many companies prefer to partner with specialized CDMOs rather than invest in developing internal capabilities, particularly for early-stage development and clinical trial material production.
The mRNA therapeutics CDMO market has emerged as a critical component of the broader biopharmaceutical manufacturing ecosystem, catalyzed by the unprecedented success of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines and the expanding pipeline of mRNA therapeutic candidates across multiple therapeutic areas.
Market growth drivers include increasing investment in mRNA research and development, growing number of mRNA therapeutic programs entering clinical trials, and the complex manufacturing requirements that favor outsourcing to specialized providers. The market benefits from approximately 42% of pharmaceutical companies indicating plans to increase their use of CDMO services for mRNA programs over the next five years.
Technological advancements in mRNA synthesis, purification methods, and lipid nanoparticle formulation continue to drive market evolution. Key players are investing heavily in expanding manufacturing capacity and developing next-generation production technologies to meet growing demand and improve cost-effectiveness.
Competitive landscape features a mix of established CDMO providers expanding into mRNA capabilities and specialized pure-play mRNA manufacturers. Market consolidation is occurring through strategic acquisitions and partnerships as companies seek to build comprehensive service offerings and global manufacturing networks.
Future outlook remains highly positive, with expanding applications beyond vaccines into therapeutic areas such as oncology, rare diseases, and protein replacement therapy driving sustained demand for specialized manufacturing services.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical factors shaping the mRNA therapeutics CDMO landscape:
Market maturation is evident in the evolution from emergency pandemic response manufacturing to sustainable commercial production capabilities, with CDMOs investing in permanent infrastructure and workforce development to support long-term market growth.
Primary growth drivers propelling the mRNA therapeutics CDMO market include several interconnected factors that create sustained demand for specialized manufacturing services.
Expanding therapeutic applications represent the most significant driver, with mRNA technology platforms being developed for cancer immunotherapy, rare genetic diseases, protein replacement therapy, and infectious disease prevention. The versatility of mRNA technology enables rapid development of new therapeutic candidates, creating continuous demand for manufacturing services.
Investment surge in mRNA research and development has reached unprecedented levels, with pharmaceutical companies and investors recognizing the transformative potential of mRNA therapeutics. This increased funding translates directly into demand for CDMO services as companies advance programs through clinical development.
Manufacturing complexity inherent in mRNA production drives outsourcing decisions, as the specialized equipment, expertise, and regulatory knowledge required for successful mRNA manufacturing represents significant barriers to internal development. Approximately 78% of emerging biotechnology companies prefer outsourcing mRNA manufacturing rather than building internal capabilities.
Regulatory pathway clarity has improved significantly following successful mRNA vaccine approvals, providing pharmaceutical companies with greater confidence in pursuing mRNA therapeutic development. Clear regulatory guidelines and precedents reduce development risks and encourage investment in mRNA programs.
Global market access requirements drive demand for CDMOs with international manufacturing capabilities and regulatory expertise across multiple jurisdictions. Companies seeking worldwide commercialization require partners capable of supporting global supply chains and regulatory submissions.
Significant market restraints challenge the growth and development of the mRNA therapeutics CDMO sector, requiring strategic approaches to overcome these limitations.
High capital requirements for establishing mRNA manufacturing capabilities create barriers to market entry and expansion. The specialized equipment, facility requirements, and quality systems necessary for mRNA production require substantial upfront investment, limiting the number of potential market participants.
Technical complexity of mRNA manufacturing processes presents ongoing challenges for CDMOs seeking to achieve consistent quality and yield optimization. The sensitivity of mRNA molecules to degradation and the complexity of lipid nanoparticle formulation require sophisticated technical expertise and process control capabilities.
Regulatory uncertainty in some therapeutic areas and geographic regions creates hesitation among pharmaceutical companies considering mRNA therapeutic development. Evolving regulatory requirements and varying international standards can complicate development timelines and increase costs.
Skilled workforce shortage represents a critical constraint, as the specialized knowledge required for mRNA manufacturing is limited. Competition for experienced personnel drives up labor costs and can limit expansion capabilities for CDMO providers.
Supply chain vulnerabilities for critical raw materials, particularly specialized lipids and nucleotides, can impact manufacturing reliability and cost predictability. Limited supplier bases for key components create potential bottlenecks in production scaling.
Intellectual property considerations may limit CDMO flexibility in process optimization and technology implementation, as many fundamental mRNA technologies are protected by extensive patent portfolios held by pharmaceutical companies and technology developers.
Substantial market opportunities exist for CDMOs positioned to capitalize on the expanding mRNA therapeutics landscape and evolving industry needs.
Emerging therapeutic areas present significant growth opportunities as mRNA technology platforms expand beyond vaccines into oncology, rare diseases, and regenerative medicine. Each new therapeutic application creates demand for specialized development and manufacturing services tailored to specific product requirements.
Geographic expansion opportunities exist in emerging markets where local manufacturing capabilities can provide cost advantages and regulatory benefits. Establishing regional manufacturing hubs can serve growing pharmaceutical markets while reducing supply chain complexity and costs.
Technology advancement opportunities include developing next-generation manufacturing processes, automation systems, and analytical methods that improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. CDMOs investing in innovation can differentiate themselves and capture premium pricing.
Vertical integration opportunities allow CDMOs to expand service offerings across the entire mRNA therapeutic value chain, from raw material production through final product distribution. Comprehensive service capabilities can strengthen client relationships and improve profit margins.
Partnership development with pharmaceutical companies, technology providers, and academic institutions can create new revenue streams and access to innovative technologies. Strategic alliances can accelerate capability development and market penetration.
Personalized medicine applications represent emerging opportunities as mRNA technology enables patient-specific therapeutic development. Specialized manufacturing capabilities for small-batch, personalized products can command premium pricing and create competitive advantages.
Complex market dynamics shape the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the mRNA therapeutics CDMO sector, influenced by technological, regulatory, and commercial factors.
Supply-demand imbalance currently favors CDMO providers, with manufacturing capacity constraints creating pricing power and strong negotiating positions. However, this dynamic is expected to evolve as new capacity comes online and competition intensifies.
Technology evolution drives continuous change in manufacturing processes and capabilities, requiring CDMOs to maintain substantial R&D investments to remain competitive. Process improvements can deliver 25-40% efficiency gains in manufacturing throughput and cost reduction.
Client relationship dynamics are shifting toward longer-term strategic partnerships rather than transactional arrangements. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly value reliable, high-quality manufacturing partners capable of supporting programs from development through commercialization.
Regulatory dynamics continue evolving as agencies gain experience with mRNA therapeutics and develop more specific guidance documents. CDMOs must maintain current regulatory expertise and adapt quality systems to meet changing requirements.
Competitive dynamics include both horizontal competition among CDMOs and vertical competition from pharmaceutical companies developing internal capabilities. Market leaders are establishing competitive moats through scale, technology, and client relationships.
Investment dynamics show continued strong capital flows into mRNA therapeutic development and manufacturing infrastructure, with private equity and strategic investors recognizing the long-term growth potential of the sector.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing the mRNA therapeutics CDMO market incorporates multiple data sources and analytical approaches to ensure accuracy and completeness of market insights.
Primary research activities include extensive interviews with industry executives, CDMO management teams, pharmaceutical company decision-makers, and regulatory experts. These discussions provide firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities from key stakeholders across the value chain.
Secondary research sources encompass industry reports, regulatory filings, company financial statements, patent databases, clinical trial registries, and academic publications. This comprehensive data collection ensures broad market coverage and validation of primary research findings.
Quantitative analysis methods include market sizing calculations, growth rate projections, competitive positioning analysis, and statistical correlation studies. Advanced analytical techniques help identify market patterns and forecast future trends with greater accuracy.
Qualitative assessment approaches involve expert opinion synthesis, scenario planning, and strategic impact analysis. These methods provide context for quantitative findings and help identify emerging trends and potential market disruptions.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources, expert review panels, and sensitivity analysis to ensure research reliability and accuracy. Rigorous validation helps eliminate bias and improves confidence in market projections and strategic recommendations.
Continuous monitoring systems track market developments, regulatory changes, and competitive activities to maintain current market intelligence and identify emerging trends that may impact market dynamics and growth projections.
North America dominates the mRNA therapeutics CDMO market, accounting for approximately 45% market share due to its advanced biopharmaceutical infrastructure, regulatory expertise, and concentration of mRNA therapeutic developers. The region benefits from established CDMO providers, significant investment in manufacturing capacity expansion, and supportive regulatory frameworks.
United States leadership stems from the presence of major pharmaceutical companies developing mRNA therapeutics, substantial government investment in pandemic preparedness, and a mature contract manufacturing ecosystem. Key manufacturing hubs in Massachusetts, North Carolina, and California provide geographic diversification and specialized capabilities.
European market represents approximately 23% market share, with strong growth driven by increasing mRNA therapeutic development activities and regulatory harmonization across EU member states. Germany, Switzerland, and Belgium serve as key manufacturing centers with established biopharmaceutical clusters and skilled workforces.
Asia-Pacific region shows rapid growth potential with an estimated 18% market share, led by expanding pharmaceutical markets in China, Japan, and South Korea. The region offers cost-effective manufacturing solutions and growing domestic demand for mRNA therapeutics, attracting international CDMO investment.
Emerging markets in Latin America, Middle East, and Africa represent smaller but growing opportunities as local pharmaceutical industries develop and regulatory frameworks mature. These regions offer potential for regional manufacturing hubs serving local and export markets.
Geographic diversification strategies are becoming increasingly important as pharmaceutical companies seek supply chain resilience and regulatory risk mitigation through multi-regional manufacturing networks and strategic partnerships with local CDMO providers.
The competitive landscape features a diverse mix of established contract manufacturing organizations expanding into mRNA capabilities and specialized pure-play mRNA manufacturers, creating a dynamic and rapidly evolving market structure.
Market leaders include several key players positioned across different segments of the mRNA CDMO value chain:
Competitive strategies focus on capacity expansion, technology advancement, geographic diversification, and strategic partnerships to build comprehensive service offerings and competitive advantages in this rapidly growing market.
Market consolidation is occurring through acquisitions, joint ventures, and strategic alliances as companies seek to build scale, acquire specialized capabilities, and establish global manufacturing networks to serve international pharmaceutical clients.
Market segmentation reveals distinct categories based on service type, therapeutic application, development stage, and end-user characteristics, each presenting unique growth opportunities and competitive dynamics.
By Service Type:
By Therapeutic Application:
By Development Stage:
Clinical manufacturing services represent the largest and fastest-growing segment, driven by the expanding pipeline of mRNA therapeutics entering clinical development. This category benefits from approximately 35% annual growth as pharmaceutical companies advance programs through clinical trials and require specialized GMP manufacturing capabilities.
Process development services show strong demand as companies seek to optimize manufacturing processes for cost-effectiveness and scalability. Early-stage process optimization can deliver significant long-term value, with successful optimization programs achieving 30-50% cost reduction in commercial manufacturing.
Vaccine manufacturing remains a cornerstone category following COVID-19 vaccine success, with sustained demand for pandemic preparedness and seasonal vaccine production. This segment provides stable revenue streams and demonstrates the commercial viability of mRNA manufacturing at scale.
Oncology applications represent the highest growth potential category, with personalized cancer vaccines and immunotherapy approaches driving innovation in manufacturing processes. The complexity of personalized medicine applications creates opportunities for premium pricing and specialized service offerings.
Analytical services are becoming increasingly sophisticated as regulatory requirements evolve and product complexity increases. Advanced analytical capabilities serve as competitive differentiators and support higher-value service offerings across all therapeutic categories.
Regulatory support services gain importance as companies navigate complex international regulatory landscapes and seek to accelerate approval timelines. Expert regulatory guidance can significantly impact program success and time-to-market for mRNA therapeutics.
Pharmaceutical companies benefit significantly from partnering with specialized mRNA CDMOs, gaining access to advanced manufacturing capabilities without substantial capital investment. Key advantages include reduced time-to-market, risk mitigation, and access to specialized expertise that would be costly and time-consuming to develop internally.
Cost optimization benefits include avoiding large upfront capital expenditures for manufacturing facilities and equipment, while leveraging CDMO economies of scale and operational efficiency. Companies can achieve 40-60% cost savings compared to building internal manufacturing capabilities, particularly for early-stage programs.
Risk mitigation advantages encompass regulatory compliance assurance, quality system reliability, and supply chain resilience through geographic diversification. CDMOs provide established quality systems and regulatory expertise that reduce program risks and improve success probability.
Speed-to-market benefits result from immediate access to manufacturing capacity and expertise, eliminating the time required to build internal capabilities. This acceleration can provide competitive advantages in rapidly evolving therapeutic areas and improve patient access to innovative treatments.
CDMO providers benefit from strong market demand, premium pricing opportunities, and long-term client relationships that provide revenue stability and growth visibility. The specialized nature of mRNA manufacturing creates barriers to competition and supports sustainable competitive advantages.
Investors and stakeholders benefit from exposure to high-growth market segments with strong fundamentals and expanding applications. The mRNA therapeutics CDMO market offers attractive investment opportunities with multiple value creation drivers and defensive characteristics.
Patients and healthcare systems ultimately benefit from improved access to innovative mRNA therapeutics through efficient manufacturing and supply chain management that supports global product availability and cost-effectiveness.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Automation and digitalization represent major trends transforming mRNA manufacturing processes, with CDMOs investing in advanced automation systems, process analytical technology, and digital quality management systems. These investments can improve manufacturing efficiency by 25-35% while reducing human error and enhancing product consistency.
Continuous manufacturing adoption is gaining momentum as companies seek to improve process efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs. Continuous processes offer advantages in scalability, quality control, and resource utilization compared to traditional batch manufacturing approaches.
Personalized medicine applications are driving demand for flexible manufacturing platforms capable of producing small batches of patient-specific therapeutics. This trend requires specialized capabilities and creates opportunities for premium pricing and differentiated service offerings.
Sustainability initiatives are becoming increasingly important as pharmaceutical companies focus on environmental responsibility and regulatory agencies emphasize green manufacturing practices. CDMOs are investing in energy-efficient processes, waste reduction, and sustainable raw material sourcing.
Global supply chain diversification continues as companies seek to reduce geographic concentration risks and improve supply chain resilience. Multi-regional manufacturing strategies are becoming standard for commercial products and large clinical programs.
Technology platform standardization is emerging as CDMOs develop scalable, standardized processes that can be applied across multiple mRNA therapeutic programs. Standardization improves efficiency and reduces development timelines while maintaining product quality.
Strategic partnership evolution shows movement toward deeper, longer-term relationships between pharmaceutical companies and CDMOs, with risk-sharing arrangements and joint investment in manufacturing capabilities becoming more common.
Capacity expansion initiatives dominate recent industry developments, with major CDMOs announcing substantial investments in new manufacturing facilities and equipment to meet growing demand. These expansions represent multi-billion dollar commitments to mRNA manufacturing infrastructure globally.
Technology acquisitions and licensing agreements are accelerating as CDMOs seek to acquire specialized capabilities and intellectual property. Recent transactions focus on lipid nanoparticle technologies, purification methods, and analytical capabilities critical for mRNA manufacturing.
Regulatory milestone achievements include successful inspections and approvals for mRNA manufacturing facilities, establishing precedents for quality standards and regulatory expectations. These milestones provide confidence for continued investment and expansion in the sector.
Partnership announcements between pharmaceutical companies and CDMOs continue at a rapid pace, with long-term supply agreements and strategic alliances providing revenue visibility and capacity allocation for both parties. According to MarkWide Research analysis, partnership activity has increased by 85% compared to pre-pandemic levels.
Innovation breakthroughs in manufacturing processes, including novel purification techniques and improved lipid nanoparticle formulations, are enhancing product quality and reducing production costs. These advances support the commercial viability of mRNA therapeutics across broader therapeutic applications.
Geographic expansion activities include establishment of manufacturing facilities in emerging markets and development of regional supply chains to serve local pharmaceutical markets and reduce supply chain complexity.
Workforce development programs are being implemented to address skilled labor shortages, with CDMOs partnering with academic institutions and government agencies to develop specialized training programs for mRNA manufacturing personnel.
Strategic positioning recommendations for CDMO providers emphasize the importance of developing comprehensive service offerings that span the entire mRNA therapeutic development lifecycle, from early-stage process development through commercial manufacturing and supply chain management.
Investment priorities should focus on advanced manufacturing technologies, automation systems, and analytical capabilities that provide competitive advantages and operational efficiency. CDMOs investing in next-generation technologies can achieve 20-30% operational cost advantages over competitors using traditional manufacturing approaches.
Geographic diversification strategies are essential for managing supply chain risks and accessing global markets. MarkWide Research recommends establishing manufacturing presence in at least two major geographic regions to provide supply chain resilience and regulatory flexibility.
Partnership development should prioritize long-term strategic relationships with pharmaceutical companies over transactional arrangements. Successful partnerships provide revenue stability, capacity utilization, and opportunities for joint technology development and investment.
Talent acquisition and retention strategies must address the critical shortage of experienced mRNA manufacturing personnel through competitive compensation, professional development programs, and partnerships with academic institutions for workforce development.
Quality system excellence remains paramount for success in this highly regulated industry. CDMOs should invest in robust quality management systems, advanced analytical capabilities, and regulatory expertise to maintain competitive positioning and client confidence.
Innovation investment in process development, analytical methods, and manufacturing technologies is essential for maintaining competitive advantages and supporting client success in bringing innovative mRNA therapeutics to market.
Long-term market prospects remain highly positive for the mRNA therapeutics CDMO sector, driven by expanding therapeutic applications, growing pharmaceutical investment, and increasing acceptance of mRNA technology platforms across multiple disease areas.
Therapeutic expansion beyond vaccines into oncology, rare diseases, and protein replacement therapy will drive sustained demand growth over the next decade. The versatility of mRNA technology platforms enables rapid development of new therapeutic candidates, creating continuous opportunities for CDMO providers.
Technology advancement will continue improving manufacturing efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling new therapeutic applications. Process innovations and automation technologies are expected to deliver 40-50% cost reductions in mRNA manufacturing over the next five to seven years.
Market maturation will bring increased competition and pricing pressure, but also greater market size and stability as mRNA therapeutics become mainstream pharmaceutical products. Early market leaders with strong competitive positions are expected to maintain advantages through scale and expertise.
Global expansion will accelerate as pharmaceutical companies seek worldwide market access and CDMOs develop international manufacturing networks. Emerging markets represent significant growth opportunities as local pharmaceutical industries mature and regulatory frameworks develop.
Regulatory evolution will continue providing greater clarity and standardization for mRNA therapeutic development and manufacturing, reducing development risks and encouraging continued investment in the sector.
Investment outlook remains strong with continued capital flows into mRNA manufacturing infrastructure and technology development. The combination of proven technology platforms, expanding applications, and strong market fundamentals supports sustained investor interest and market growth.
The mRNA therapeutics CDMO market represents one of the most dynamic and promising sectors within the biopharmaceutical industry, driven by revolutionary advances in mRNA technology and expanding therapeutic applications beyond the initial vaccine successes that established the platform’s viability.
Market fundamentals remain exceptionally strong, with growing pharmaceutical investment, expanding clinical pipelines, and increasing recognition of mRNA technology’s versatility across multiple therapeutic areas. The specialized nature of mRNA manufacturing creates sustainable competitive advantages for established CDMO providers while presenting significant barriers to new market entrants.
Strategic opportunities abound for companies positioned to capitalize on this growth through capacity expansion, technology advancement, geographic diversification, and strategic partnerships with pharmaceutical companies developing innovative mRNA therapeutics. The market’s evolution from emergency pandemic response to sustainable commercial manufacturing creates long-term value creation opportunities.
Future success in this market will depend on CDMOs’ ability to maintain technological leadership, develop comprehensive service offerings, build global manufacturing networks, and establish strong client relationships that provide revenue stability and growth visibility. Companies investing in advanced manufacturing capabilities, quality systems, and specialized expertise are well-positioned to capture the significant opportunities presented by the expanding mRNA therapeutics CDMO market over the coming decade.
What is MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization?
MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization refers to companies that specialize in the development and manufacturing of mRNA-based therapeutics. These organizations provide services such as formulation development, process optimization, and large-scale production to support the growing demand for mRNA therapies.
What are the key players in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market?
Key players in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market include companies like Moderna, BioNTech, and Lonza, which are known for their expertise in mRNA technology and manufacturing capabilities, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market?
The growth of the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market is driven by increasing investments in mRNA research, the rising prevalence of infectious diseases, and the expanding applications of mRNA in cancer therapies and personalized medicine.
What challenges does the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market face?
Challenges in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market include the complexity of mRNA production processes, regulatory hurdles, and the need for specialized infrastructure and skilled workforce to ensure quality and compliance.
What opportunities exist in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market?
Opportunities in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market include the potential for collaboration with biotech firms, advancements in mRNA delivery systems, and the growing interest in mRNA vaccines beyond infectious diseases, such as in oncology.
What trends are shaping the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market?
Trends in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market include the increasing focus on rapid response capabilities for emerging health threats, the integration of automation in manufacturing processes, and the exploration of novel mRNA applications in gene editing and regenerative medicine.
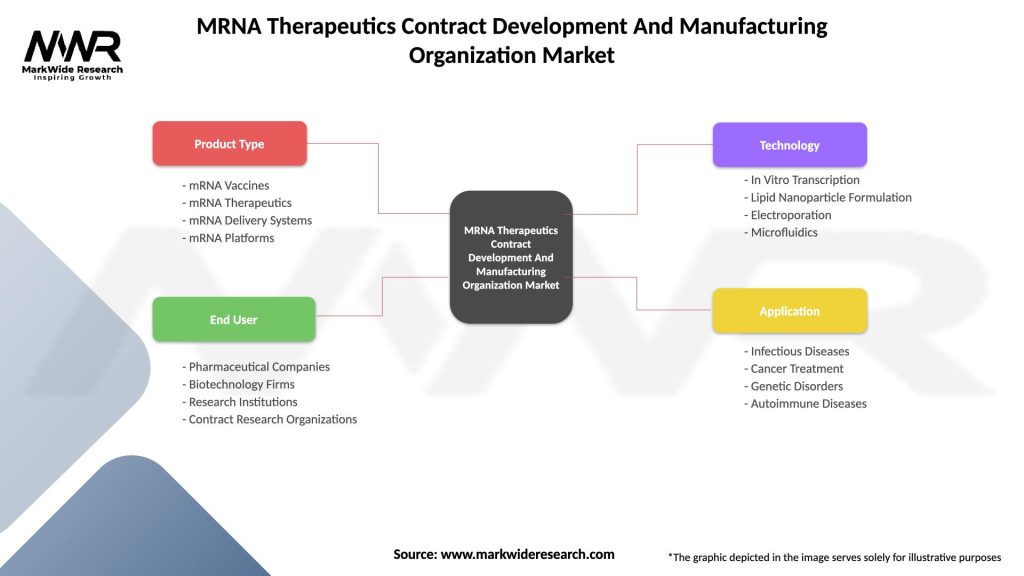
MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | mRNA Vaccines, mRNA Therapeutics, mRNA Delivery Systems, mRNA Platforms |
| End User | Pharmaceutical Companies, Biotechnology Firms, Research Institutions, Contract Research Organizations |
| Technology | In Vitro Transcription, Lipid Nanoparticle Formulation, Electroporation, Microfluidics |
| Application | Infectious Diseases, Cancer Treatment, Genetic Disorders, Autoimmune Diseases |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the MRNA Therapeutics Contract Development And Manufacturing Organization Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at