444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview:
The missile defense system market is an integral part of national defense strategies globally, aiming to protect against missile threats from adversaries. These systems encompass a range of technologies designed to detect, track, intercept, and neutralize incoming missiles, thereby safeguarding critical assets, populations, and infrastructure from potential attacks.
Meaning:
Missile defense systems refer to a diverse array of technologies and platforms designed to intercept and destroy incoming missiles, including ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and hypersonic weapons. These systems utilize sensors, interceptors, command and control networks, and defensive measures to detect and neutralize missile threats, thereby enhancing national security and deterrence capabilities.
Executive Summary:
The missile defense system market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing geopolitical tensions, evolving security threats, and advancements in missile technology. Rising investments in defense modernization, along with the proliferation of ballistic missiles and other advanced weaponry, have spurred the demand for robust missile defense capabilities worldwide. Key market players are focusing on innovation, collaboration, and strategic partnerships to develop next-generation missile defense solutions tailored to emerging threats and operational requirements.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
The missile defense system market operates in a dynamic environment characterized by evolving threats, technological advancements, regulatory constraints, and geopolitical uncertainties. Market dynamics such as defense budgets, strategic priorities, industry consolidation, and innovation cycles influence market growth, investment decisions, and competitive dynamics.
Regional Analysis:
The missile defense system market exhibits regional variations influenced by geopolitical factors, security threats, defense spending, and technological capabilities. Key regions include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East, and Latin America, each with unique market dynamics and growth drivers.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in the Missile Defence System Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
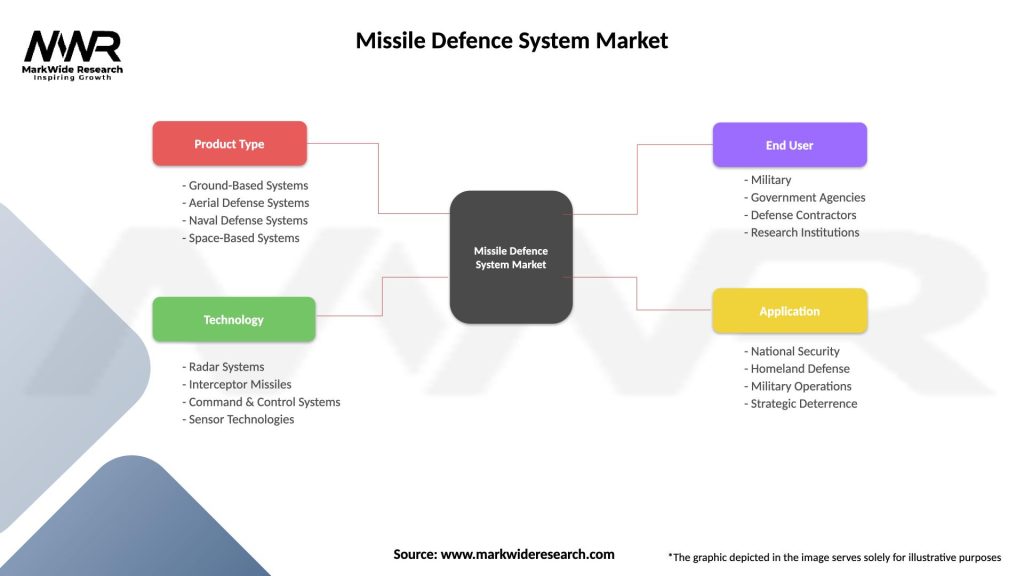
Segmentation:
The missile defense system market can be segmented based on technology, platform, application, and region, providing insights into market trends, customer requirements, and growth opportunities. Segmentation enables suppliers to tailor their offerings to specific market segments and customer needs, driving competitiveness and market penetration.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
A SWOT analysis provides insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the missile defense system market, enabling industry participants to formulate effective strategies and mitigate risks.
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has had limited direct impact on the missile defense system market, given its essential role in national defense and security. However, the pandemic has disrupted supply chains, delayed procurement programs, and strained defense budgets in some regions, leading to temporary disruptions and delays in missile defense projects and initiatives.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The missile defense system market is poised for continued growth and innovation driven by evolving security threats, technological advancements, and geopolitical dynamics. Rising investments in missile defense capabilities, coupled with ongoing modernization programs and international collaboration, will shape the future landscape of missile defense. Key trends such as multi-domain integration, directed energy weapons, and space-based surveillance will influence market dynamics and drive demand for next-generation missile defense solutions.
Conclusion:
The missile defense system market plays a critical role in safeguarding national security, deterring aggression, and maintaining strategic stability in an increasingly complex and uncertain security environment. With escalating missile threats, advancing technologies, and evolving defense requirements, the demand for robust and reliable missile defense capabilities continues to grow. Industry participants, governments, and defense organizations must collaborate, innovate, and invest in cutting-edge technologies to address emerging challenges and secure a safer future.
What is Missile Defence System?
A Missile Defence System is a technology designed to detect, track, intercept, and destroy incoming missiles, particularly ballistic and cruise missiles. These systems are crucial for national security and are used by various countries to protect against potential threats.
What are the key players in the Missile Defence System Market?
Key players in the Missile Defence System Market include Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, and BAE Systems, among others. These companies are involved in the development and deployment of advanced missile defense technologies.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Missile Defence System Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Missile Defence System Market include increasing geopolitical tensions, the rise in missile threats from rogue states, and advancements in defense technology. Additionally, government spending on defense and security is also a significant factor.
What challenges does the Missile Defence System Market face?
The Missile Defence System Market faces challenges such as high development costs, technological complexities, and the evolving nature of missile threats. Additionally, political and budgetary constraints can impact the deployment of these systems.
What opportunities exist in the Missile Defence System Market?
Opportunities in the Missile Defence System Market include the development of next-generation interceptors, integration of artificial intelligence for improved targeting, and collaboration with international defense partners. These advancements can enhance the effectiveness of missile defense strategies.
What trends are shaping the Missile Defence System Market?
Trends shaping the Missile Defence System Market include the increasing focus on multi-layered defense systems, the integration of cyber defense capabilities, and the shift towards space-based missile defense technologies. These trends reflect the need for more comprehensive defense solutions.
Missile Defence System Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Ground-Based Systems, Aerial Defense Systems, Naval Defense Systems, Space-Based Systems |
| Technology | Radar Systems, Interceptor Missiles, Command & Control Systems, Sensor Technologies |
| End User | Military, Government Agencies, Defense Contractors, Research Institutions |
| Application | National Security, Homeland Defense, Military Operations, Strategic Deterrence |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Missile Defence System Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at