444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Military Autonomous Robot Market encompasses a wide range of robotic systems and platforms designed for military applications, including reconnaissance, surveillance, logistics support, combat operations, and disaster response. Military autonomous robots leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, sensors, and autonomy algorithms to operate in complex and dynamic environments autonomously or semi-autonomously.
Meaning
Military autonomous robots are robotic systems deployed by armed forces for various tasks and missions, ranging from reconnaissance and surveillance to logistics support and combat operations. These robots are equipped with sensors, cameras, manipulators, and mobility systems, enabling them to navigate, interact with the environment, and execute tasks with minimal human intervention.
Executive Summary
The Military Autonomous Robot Market is experiencing rapid growth driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of unmanned systems for military operations, advancements in robotics and AI technologies, and the need to enhance military capabilities while reducing human risk. This market offers opportunities for defense contractors, technology firms, and research institutions to develop innovative autonomous solutions for military applications. However, challenges such as ethical concerns, regulatory frameworks, and technological limitations require careful consideration to ensure the safe and effective deployment of military autonomous robots.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Military Autonomous Robot Market operates within a dynamic ecosystem shaped by factors such as technological advancements, defense policies, geopolitical tensions, budgetary constraints, and evolving threat landscapes. These dynamics drive innovation, competition, and collaboration among defense contractors, technology providers, research institutions, and military end-users, influencing the development and deployment of autonomous robotic systems for military applications.
Regional Analysis
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Military Autonomous Robot Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
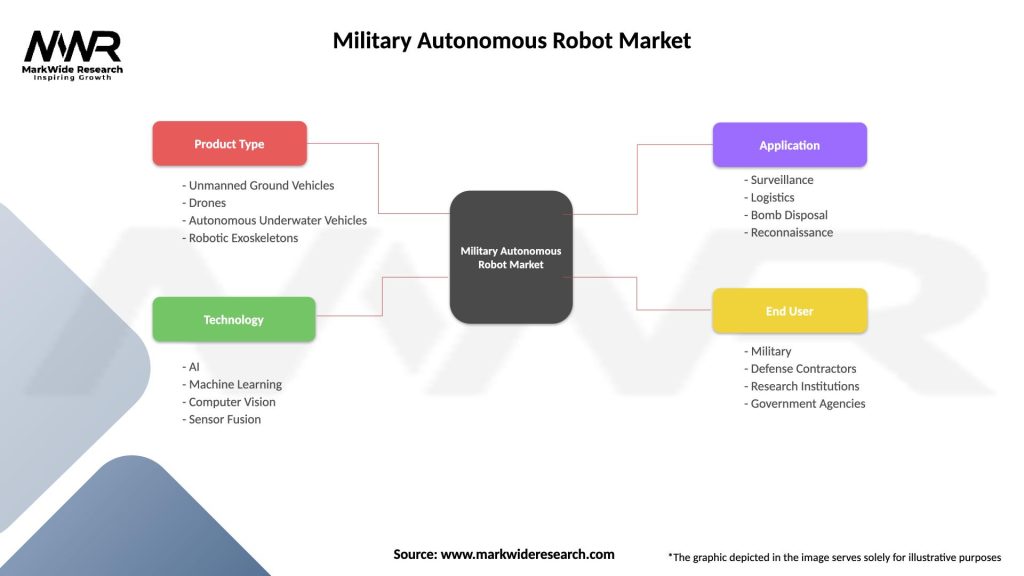
Segmentation
The Military Autonomous Robot Market can be segmented based on various factors, including platform type, mission profile, application, and geographic region. Segmentation enables defense organizations, technology providers, and industry stakeholders to target specific market segments, tailor solutions to end-user requirements, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in unmanned systems.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption and deployment of military autonomous robots in various roles, including surveillance, disinfection, logistics support, and medical assistance. Key impacts of the pandemic on the Military Autonomous Robot Market include:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The Military Autonomous Robot Market is poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years, driven by advancements in AI and robotics technologies, increasing demand for unmanned systems, and evolving military requirements for autonomous capabilities. The future of military autonomous robots will be shaped by trends such as autonomy and AI, multi-domain operations, human-machine teaming, and interoperability, as well as emerging opportunities in counter-UAS solutions, humanitarian robotics, and autonomous logistics support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Military Autonomous Robot Market offers vast opportunities for defense contractors, technology firms, and research institutions to develop innovative, mission-critical solutions for military applications. By leveraging advancements in AI, robotics, and autonomy, military autonomous robots enhance situational awareness, operational effectiveness, and force protection for military forces worldwide. However, addressing challenges such as ethical concerns, technological limitations, and regulatory constraints is essential to ensure the safe, ethical, and responsible use of autonomous robotic systems in defense and security operations. With strategic investments in technology, collaboration, and risk management, the Military Autonomous Robot Market can continue to drive innovation, resilience, and mission success in an increasingly complex and dynamic security environment.
What is Military Autonomous Robot?
Military Autonomous Robots are advanced robotic systems designed to perform tasks in military operations without direct human control. They can be utilized for surveillance, logistics, and combat support, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
What are the key players in the Military Autonomous Robot Market?
Key players in the Military Autonomous Robot Market include companies like Northrop Grumman, General Dynamics, and BAE Systems, which are known for their innovations in defense technology and robotics, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Military Autonomous Robot Market?
The Military Autonomous Robot Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for unmanned systems in combat scenarios, advancements in artificial intelligence, and the need for enhanced operational capabilities in defense.
What challenges does the Military Autonomous Robot Market face?
Challenges in the Military Autonomous Robot Market include high development costs, regulatory hurdles regarding the use of autonomous systems in warfare, and ethical concerns surrounding the deployment of robots in combat.
What future opportunities exist in the Military Autonomous Robot Market?
Future opportunities in the Military Autonomous Robot Market include the integration of AI for improved decision-making, the development of swarm robotics for coordinated operations, and expanding applications in logistics and reconnaissance.
What trends are shaping the Military Autonomous Robot Market?
Trends in the Military Autonomous Robot Market include the increasing use of drones for surveillance, the development of ground-based autonomous vehicles, and the focus on enhancing human-robot collaboration in military operations.
Military Autonomous Robot Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Unmanned Ground Vehicles, Drones, Autonomous Underwater Vehicles, Robotic Exoskeletons |
| Technology | AI, Machine Learning, Computer Vision, Sensor Fusion |
| Application | Surveillance, Logistics, Bomb Disposal, Reconnaissance |
| End User | Military, Defense Contractors, Research Institutions, Government Agencies |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Military Autonomous Robot Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at