444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The Middle East smart card market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced technologies in various sectors. Smart cards, also known as chip cards or integrated circuit cards, are embedded with a microprocessor or memory chip that stores and processes data. These cards offer enhanced security, convenience, and versatility, making them an attractive solution for numerous applications.
Meaning
Smart cards are portable devices that are typically the size of a credit card and are used for identification, authentication, payment transactions, data storage, and access control. They are commonly used in sectors such as banking, telecommunications, transportation, healthcare, and government. The embedded microprocessor or memory chip enables the card to perform cryptographic operations and securely store data.
Executive Summary
The Middle East smart card market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. The market is driven by various factors such as the increasing need for secure identification and authentication solutions, the rising adoption of contactless payment technologies, and the growing government initiatives towards digital transformation. Moreover, the market is witnessing a surge in demand due to the integration of smart cards in emerging technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile devices.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
The Middle East smart card market is characterized by the presence of both global and regional players offering a wide range of products and solutions. The market is highly competitive, with players focusing on technological advancements, product innovation, and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. The increasing emphasis on cybersecurity and data protection is driving the demand for secure smart card solutions in the region.
Market Drivers
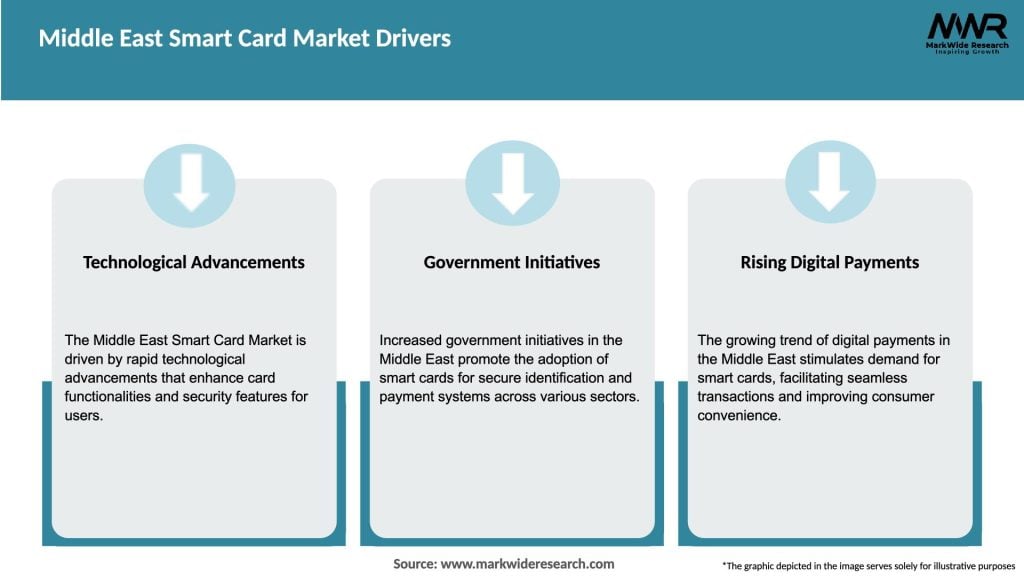
Several factors are driving the growth of the Middle East smart card market. Firstly, the increasing need for secure identification and authentication solutions across various sectors is propelling the demand for smart cards. With the rising number of cyber threats and identity thefts, organizations are adopting smart cards to enhance security and protect sensitive information.
Secondly, the growing adoption of contactless payment technologies is fueling the demand for smart cards in the region. Smart cards with near-field communication (NFC) capabilities allow users to make secure and convenient contactless payments, thereby replacing traditional payment methods.
Additionally, the Middle East governments’ initiatives towards digital transformation are boosting the adoption of smart cards in areas such as e-government services, healthcare, and transportation. These initiatives aim to enhance efficiency, reduce paperwork, and improve service delivery through the use of smart card technology.
Market Restraints
Despite the positive growth prospects, the Middle East smart card market faces certain challenges that may hinder its growth. One of the major restraints is the high initial cost associated with implementing smart card infrastructure. The deployment of smart card systems requires significant investment in hardware, software, and training, which can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and organizations with limited financial resources.
Moreover, interoperability issues and lack of standardization pose challenges for the market. Different sectors and applications have their own specific requirements, which can result in fragmented systems and compatibility issues between different smart card solutions.
Market Opportunities
The Middle East smart card market offers several lucrative opportunities for industry participants. The increasing adoption of IoT and mobile devices presents new avenues for smart card applications. Smart cards can be integrated into IoT devices to enable secure communication, data storage, and authentication.
Furthermore, the region’s growing population and rising urbanization are driving the demand for smart cards in transportation systems. Smart cards can be used for ticketing, access control, and parking services, providing convenience to commuters and reducing the reliance on cash transactions.
Market Dynamics
The Middle East smart card market is characterized by dynamic trends and evolving consumer preferences. Technological advancements, such as the development of contactless smart cards and biometric authentication, are shaping the market landscape. The market is also witnessing increased partnerships and collaborations between smart card manufacturers and solution providers to offer integrated solutions and cater to diverse customer needs.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a shift towards mobile-based smart card solutions. With the widespread adoption of smartphones, mobile wallets, and mobile banking applications, there is a growing demand for virtual smart cards that can be stored and accessed through mobile devices.
Regional Analysis
The Middle East smart card market is geographically segmented into several key regions, including the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, and Bahrain. The UAE holds a significant share in the market, driven by the country’s rapid economic growth, technological advancements, and government initiatives towards digital transformation.
Saudi Arabia is also a key market in the region, owing to its large population and investments in infrastructure development. The country’s Vision 2030 initiative, aimed at diversifying the economy and reducing dependence on oil, is driving the adoption of smart card solutions in various sectors.
Other countries in the region, such as Qatar and Kuwait, are witnessing increased investments in smart city projects, which are expected to drive the demand for smart card applications in areas such as transportation, healthcare, and government services.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Middle East Smart Card Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
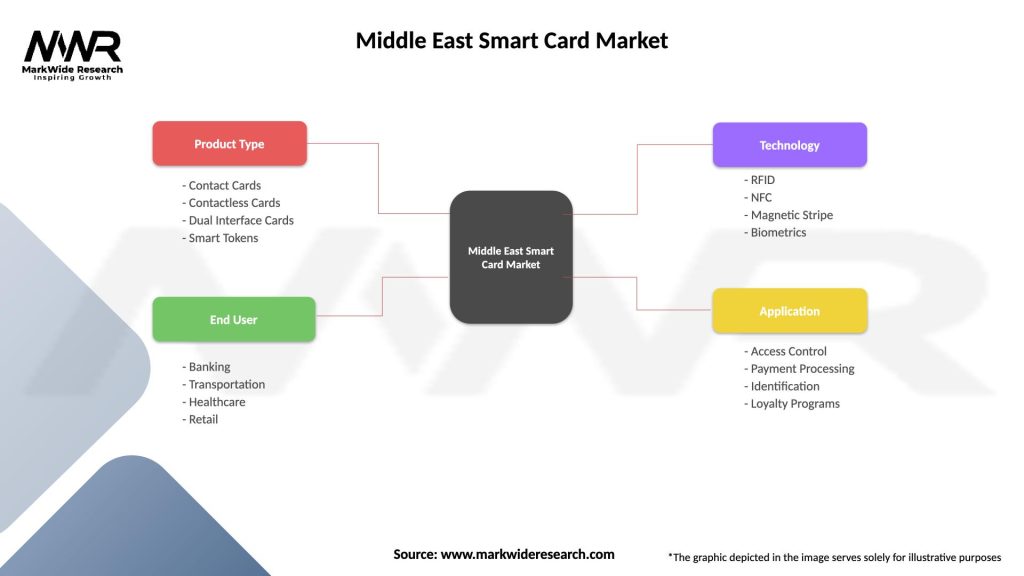
The Middle East smart card market can be segmented based on card type, component, application, and end-user industry. By card type, the market can be categorized into contact-based smart cards and contactless smart cards. The contact-based smart cards require physical contact with a card reader, while contactless smart cards use radio frequency identification (RFID) or NFC technology for wireless communication.
Based on component, the market can be divided into microcontroller-based smart cards and memory-based smart cards. Microcontroller-based smart cards offer advanced features such as secure processing and encryption, while memory-based smart cards focus on data storage and retrieval.
In terms of application, the market can be segmented into banking and financial services, telecommunications, healthcare, transportation, government, and others. The banking and financial services sector is a major adopter of smart cards for secure payment transactions and ATM access.
Based on the end-user industry, the market can be categorized into BFSI (banking, financial services, and insurance), retail, healthcare, transportation, government, and others.
Category-wise Insights
In the banking and financial services sector, smart cards are widely used for secure transactions, online banking, and ATM access. The adoption of EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) standards has further accelerated the demand for smart cards in this sector.
In the telecommunications industry, smart cards are used for SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards in mobile devices, enabling secure communication and authentication. The increasing penetration of smartphones and the demand for mobile data services are driving the growth of smart card applications in this sector.
The healthcare industry is also witnessing the adoption of smart cards for patient identification, electronic medical records, and secure access to healthcare facilities. Smart cards enable healthcare providers to streamline administrative processes and enhance patient safety.
The transportation sector is another significant user of smart cards, particularly for ticketing, access control, and parking services. Smart cards provide convenience to commuters and help transportation authorities improve efficiency and reduce cash handling.
The government sector is increasingly adopting smart cards for e-government servicessuch as national identification cards, driver’s licenses, and electronic passports. Smart cards enable secure authentication, data storage, and access control, facilitating efficient service delivery and reducing paperwork.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The Middle East smart card market offers several key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders. Firstly, smart cards provide enhanced security and data protection, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft. This is particularly crucial in sectors such as banking, healthcare, and government, where sensitive information is involved.
Secondly, smart cards offer convenience and ease of use for both businesses and consumers. With contactless payment technologies, users can make quick and secure transactions without the need for physical cash or traditional payment methods. This improves the overall customer experience and accelerates transaction processing.
Furthermore, the adoption of smart cards enables organizations to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. Smart cards can automate various processes, such as identification, authentication, and data storage, reducing manual tasks and paperwork. This leads to cost savings and increased productivity for businesses.
Additionally, the integration of smart cards with emerging technologies like IoT and mobile devices opens up new opportunities for innovation and value-added services. Smart cards can be utilized in various IoT applications, such as smart homes, connected cars, and industrial automation, enhancing connectivity and enabling secure communication.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis of the Middle East smart card market provides insights into the market’s internal and external factors.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the Middle East smart card market:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the Middle East smart card market. While the pandemic initially led to a slowdown in economic activities and disrupted supply chains, it also accelerated the adoption of digital technologies and contactless solutions.
During the pandemic, there was a surge in demand for contactless payment options to minimize physical contact and reduce the risk of virus transmission. This led to increased adoption of contactless smart cards and mobile payment solutions across various sectors, including retail, transportation, and hospitality.
Moreover, the pandemic highlighted the importance of secure identification and authentication solutions in healthcare and government sectors. Smart cards played a crucial role in enabling secure access to healthcare facilities, electronic medical records, and contact tracing applications.
However, the pandemic also presented challenges for the market, such as supply chain disruptions and financial constraints faced by businesses. The high initial cost of implementing smart card infrastructure and the economic uncertainties resulted in a cautious approach towards investments in some sectors.
Key Industry Developments
The Middle East smart card market has witnessed several key industry developments in recent years:
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts suggest the following strategies for industry participants in the Middle East smart card market:
Future Outlook
The Middle East smart card market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. The increasing digitalization efforts by governments, coupled with the rising demand for secure identification and payment solutions, will drive market expansion.
The integration of smart cards with emerging technologies like IoT, blockchain, and biometrics will further enhance their capabilities and open up new opportunities for market players. The growing adoption of mobile-based smart cards and contactless payment technologies will also contribute to market growth.
Moreover, the region’s rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and smart city initiatives will create a favorable environment for smart card applications in sectors such as transportation, healthcare, and government services.
However, market players need to address challenges such as high implementation costs, interoperability issues, and security concerns to fully capitalize on the market opportunities. By focusing on innovation, strategic partnerships, and customer-centric solutions, industry participants can position themselves for success in the evolving Middle East smart card market.
Conclusion
The Middle East smart card market is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing need for secure identification and payment solutions. Smart cards offer enhanced security, convenience, and efficiency in various sectors such as banking, telecommunications, healthcare, and government.
The market is characterized by the presence of global and regional players competing through technological advancements and strategic partnerships. While the market faces challenges such as high implementation costs and interoperability issues, there are lucrative opportunities emerging from the integration of smart cards with emerging technologies and the growing demand for contactless payment options.
What is Smart Card?
Smart cards are secure, portable devices that store and process data, often used for identification, payment, and access control. They can be embedded with microprocessors or memory chips, enabling various applications across different sectors.
What are the key players in the Middle East Smart Card Market?
Key players in the Middle East Smart Card Market include Gemalto, HID Global, and NXP Semiconductors, which provide a range of smart card solutions for payment systems, identification, and access management, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Middle East Smart Card Market?
The growth of the Middle East Smart Card Market is driven by increasing demand for secure payment solutions, the rise in digital transactions, and government initiatives promoting cashless economies. Additionally, the expansion of e-governance and smart city projects contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the Middle East Smart Card Market face?
The Middle East Smart Card Market faces challenges such as cybersecurity threats, high initial implementation costs, and the need for interoperability among different systems. These factors can hinder widespread adoption and integration of smart card technologies.
What opportunities exist in the Middle East Smart Card Market?
Opportunities in the Middle East Smart Card Market include the growing adoption of contactless payment solutions, advancements in biometric authentication, and the increasing use of smart cards in transportation and healthcare sectors. These trends indicate a promising future for smart card technologies.
What trends are shaping the Middle East Smart Card Market?
Trends shaping the Middle East Smart Card Market include the integration of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, the rise of mobile wallets, and the increasing focus on enhancing security features. These innovations are transforming how consumers and businesses utilize smart cards.
Middle East Smart Card Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Contact Cards, Contactless Cards, Dual Interface Cards, Smart Tokens |
| End User | Banking, Transportation, Healthcare, Retail |
| Technology | RFID, NFC, Magnetic Stripe, Biometrics |
| Application | Access Control, Payment Processing, Identification, Loyalty Programs |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Middle East Smart Card Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at