444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) market is experiencing significant growth and is poised to witness substantial development in the coming years. Whole exome sequencing is a revolutionary technique used to analyze the protein-coding region of the human genome. It allows researchers and clinicians to identify genetic variations that may be associated with various diseases, including cancer, rare genetic disorders, and inherited conditions.
Meaning
Whole exome sequencing involves capturing and sequencing the exome, which constitutes only about 1-2% of the entire human genome. Despite its relatively small size, the exome contains a majority of disease-causing variants. By focusing on this critical region, researchers can gain insights into the genetic basis of diseases and develop personalized treatment plans.
Executive Summary
The MEA Whole Exome Sequencing market has witnessed substantial growth due to the increasing demand for personalized medicine and advancements in genomic research. The market is driven by factors such as rising awareness about genetic disorders, technological advancements in sequencing technologies, and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases in the region. However, there are certain challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed to maximize the market potential.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The MEA Whole Exome Sequencing market is characterized by intense competition among market players, technological advancements, and increasing collaborations between industry stakeholders. Market dynamics are influenced by factors such as regulatory frameworks, reimbursement policies, and advancements in bioinformatics tools for data analysis.
Regional Analysis
The MEA region is witnessing significant growth in the Whole Exome Sequencing market, driven by factors such as increasing investments in genomics research, rising awareness about genetic disorders, and the implementation of precision medicine initiatives. Countries like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, South Africa, and Nigeria are emerging as key markets in the region due to their focus on healthcare infrastructure development and genomic research.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
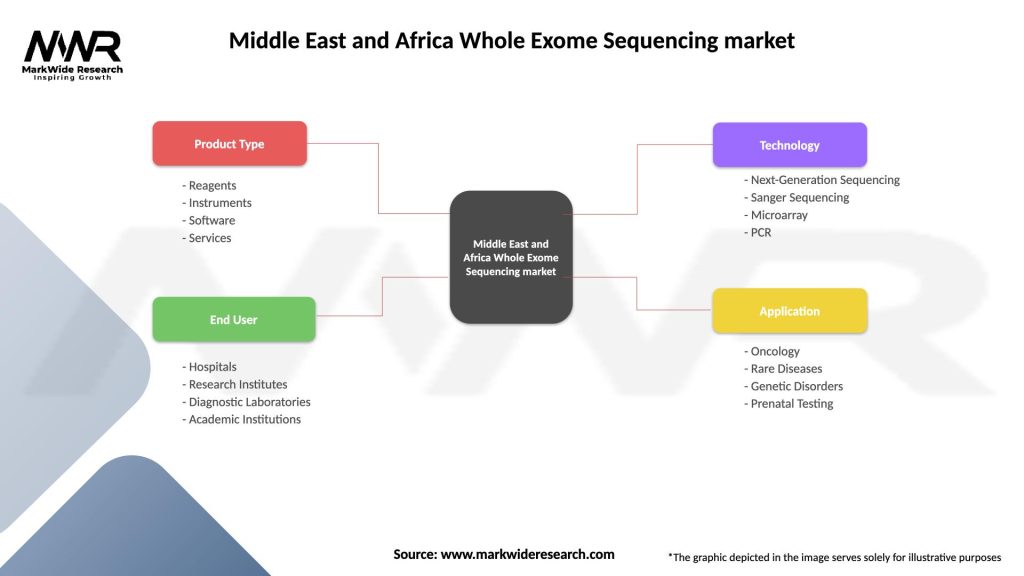
The MEA Whole Exome Sequencing market can be segmented based on the application, end-user, and region. By application, the market can be divided into diagnostics, drug discovery, and precision medicine. Based on the end-user, the market can be categorized into academic and research institutes, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, and diagnostic laboratories.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the MEA Whole Exome Sequencing market. While the pandemic initially disrupted theroutine healthcare services and research activities, it also highlighted the importance of genomics and personalized medicine in understanding and combating the virus. The pandemic led to an increased focus on genomic surveillance and sequencing efforts to track virus variants and understand their impact on transmission and vaccine effectiveness.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The MEA Whole Exome Sequencing market is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years. Factors such as increasing investments in genomics research, rising awareness about genetic disorders, and the implementation of precision medicine initiatives will drive market expansion. Technological advancements in sequencing platforms, bioinformatics tools, and data analysis techniques will further enhance the capabilities and accessibility of whole exome sequencing.
Conclusion
The Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market is experiencing remarkable growth and presents immense opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. The demand for personalized medicine, advancements in sequencing technologies, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases are driving the market forward. However, challenges such as high costs and ethical concerns need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Strategic collaborations, government initiatives, and a focus on affordability will shape the future of the market, with a positive outlook for the MEA region in genomics research and precision medicine.
What is Whole Exome Sequencing?
Whole Exome Sequencing refers to the process of sequencing all the protein-coding regions in a genome, known as exomes. This technique is widely used in genetic research and clinical diagnostics to identify mutations associated with various diseases.
What are the key players in the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market?
Key players in the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market include Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and BGI, among others. These companies are involved in providing advanced sequencing technologies and services to healthcare and research institutions.
What are the growth factors driving the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market?
The growth of the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market is driven by increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, advancements in sequencing technologies, and rising investments in genomics research. Additionally, the demand for personalized medicine is also contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market face?
The Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market faces challenges such as high costs of sequencing technologies, limited access to advanced healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory hurdles. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption of whole exome sequencing in the region.
What opportunities exist in the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market?
Opportunities in the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market include the potential for collaborations between research institutions and healthcare providers, growth in genetic testing services, and increasing awareness of genomics among healthcare professionals. These factors can enhance the market landscape.
What trends are shaping the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market?
Trends shaping the Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market include the integration of artificial intelligence in data analysis, the rise of direct-to-consumer genetic testing, and the development of cost-effective sequencing solutions. These trends are expected to influence the future of genomic research and diagnostics.
Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Reagents, Instruments, Software, Services |
| End User | Hospitals, Research Institutes, Diagnostic Laboratories, Academic Institutions |
| Technology | Next-Generation Sequencing, Sanger Sequencing, Microarray, PCR |
| Application | Oncology, Rare Diseases, Genetic Disorders, Prenatal Testing |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Middle East and Africa Whole Exome Sequencing Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at