444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market represents a rapidly expanding segment within the global advanced materials industry, driven by increasing demand across defense, automotive, and industrial applications. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and thermal resistance properties, have become indispensable materials in the region’s growing manufacturing and infrastructure sectors. The market demonstrates robust growth potential with a projected CAGR of 8.2% through the forecast period, reflecting the region’s strategic focus on industrial diversification and technological advancement.
Regional dynamics indicate that the Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market benefits from substantial investments in defense modernization programs, expanding automotive manufacturing capabilities, and growing emphasis on personal protective equipment across various industries. The market encompasses both para-aramid and meta-aramid fiber segments, with para-aramid fibers commanding approximately 72% market share due to their superior mechanical properties and versatility in high-performance applications.
Key market drivers include the region’s strategic position as a global energy hub, increasing focus on infrastructure development, and rising awareness of workplace safety standards. The market landscape is characterized by a growing preference for lightweight, high-strength materials that can withstand extreme environmental conditions prevalent in the region, making aramid fibers particularly attractive for local manufacturers and end-users.
The Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market refers to the regional trade, production, and consumption of synthetic aromatic polyamide fibers characterized by exceptional strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability. Aramid fibers are high-performance synthetic materials derived from aromatic polyamides, offering superior mechanical properties compared to conventional fibers while maintaining lightweight characteristics essential for advanced applications.
These specialized fibers encompass two primary categories: para-aramid fibers, which provide exceptional tensile strength and are commonly used in ballistic protection and reinforcement applications, and meta-aramid fibers, which offer superior thermal stability and flame resistance properties ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications. The market includes raw fiber production, intermediate processing, and finished product manufacturing across the Middle East and Africa region.
Market scope extends beyond traditional applications to include emerging sectors such as renewable energy infrastructure, aerospace components, and advanced composite materials. The regional market serves both domestic consumption and export opportunities, with several countries positioning themselves as manufacturing hubs for aramid fiber-based products destined for global markets.
The Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market demonstrates exceptional growth momentum, driven by diversification strategies across key economies and increasing demand for high-performance materials. The market benefits from strategic government initiatives promoting industrial development, particularly in the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa, which collectively account for approximately 68% of regional consumption.
Defense and security applications represent the largest market segment, reflecting ongoing military modernization programs and regional security concerns. The automotive sector emerges as a rapidly growing application area, with local manufacturers increasingly adopting aramid fiber reinforcements to meet international quality standards and export requirements. Industrial applications, including oil and gas equipment, demonstrate steady demand growth supported by the region’s energy sector prominence.
Market challenges include limited local production capabilities, dependence on imports for raw materials, and the need for specialized processing technologies. However, these challenges present significant opportunities for international partnerships and technology transfer initiatives. The market outlook remains positive, supported by favorable government policies, increasing industrial sophistication, and growing awareness of aramid fiber benefits across various applications.
Strategic market analysis reveals several critical insights shaping the Middle East and Africa aramid fibers landscape:
These insights highlight the market’s evolution from a primarily import-dependent sector toward a more sophisticated ecosystem with growing local capabilities and diverse application portfolios.
Defense modernization programs serve as the primary driver for aramid fiber demand across the Middle East and Africa region. Countries are investing substantially in military equipment upgrades, personal protective equipment, and advanced defense systems that require high-performance materials. The growing emphasis on soldier protection and equipment durability creates consistent demand for ballistic-resistant aramid fiber products.
Industrial diversification initiatives across Gulf Cooperation Council countries and other regional economies drive demand for advanced materials in manufacturing sectors. Government-led programs aimed at reducing oil dependency encourage development of high-tech industries that utilize aramid fibers in various applications, from automotive components to industrial equipment.
Automotive sector expansion represents a significant growth driver, with several countries establishing automotive manufacturing hubs to serve both domestic and export markets. The need for lightweight, fuel-efficient vehicles drives adoption of aramid fiber reinforcements in automotive components, contributing to overall market growth.
Infrastructure development projects across the region create substantial demand for high-performance materials. Large-scale construction projects, renewable energy installations, and transportation infrastructure require materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making aramid fibers increasingly attractive for these applications.
Safety regulations and workplace protection standards drive demand for aramid fiber-based protective equipment across various industries, particularly in oil and gas, construction, and manufacturing sectors where worker safety is paramount.
High material costs represent a significant restraint for aramid fiber adoption across price-sensitive applications in the Middle East and Africa region. The premium pricing of aramid fibers compared to conventional materials limits market penetration in cost-conscious segments, particularly in developing economies within the region.
Limited local production capabilities create supply chain vulnerabilities and increase dependence on imports, which can be affected by global market fluctuations and trade disruptions. The lack of established manufacturing infrastructure for aramid fibers limits market development and increases overall costs for end-users.
Technical expertise requirements for processing and application of aramid fibers pose challenges for local manufacturers and end-users. The specialized knowledge needed for optimal utilization of these high-performance materials can limit adoption rates and require significant investment in training and technology transfer.
Competition from alternative materials including carbon fibers, glass fibers, and other high-performance synthetic materials creates pressure on aramid fiber market share. The availability of lower-cost alternatives for certain applications can limit market growth in price-sensitive segments.
Economic volatility in certain regional markets can impact industrial investment and infrastructure development projects, affecting overall demand for high-performance materials including aramid fibers.
Local manufacturing development presents substantial opportunities for market expansion through establishment of aramid fiber production facilities and processing capabilities within the region. Government incentives and industrial development programs create favorable conditions for international companies to establish local operations, reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
Renewable energy sector growth offers significant opportunities for aramid fiber applications in wind turbine blades, solar panel components, and energy storage systems. The region’s commitment to renewable energy development creates new markets for high-performance composite materials incorporating aramid fibers.
Aerospace industry development in countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia creates opportunities for aramid fiber applications in aircraft components, satellite systems, and space technology applications. The growing aerospace sector requires lightweight, high-strength materials that aramid fibers can provide.
Technology partnerships with international aramid fiber manufacturers offer opportunities for knowledge transfer, joint ventures, and licensing agreements that can accelerate market development while building local capabilities.
Export market potential allows regional manufacturers to serve broader markets beyond domestic consumption, leveraging strategic geographic positioning and competitive manufacturing costs to access global markets.
Supply chain dynamics in the Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market are characterized by heavy reliance on imports from established global producers, creating both challenges and opportunities for market development. The region’s strategic location between major producing regions and emerging markets provides advantages for distribution and logistics operations.
Demand patterns show strong correlation with defense spending cycles, industrial development projects, and automotive production volumes. Seasonal variations in construction and infrastructure projects can influence short-term demand fluctuations, while long-term trends remain positive driven by economic diversification efforts.
Price dynamics reflect global aramid fiber market conditions, with regional pricing influenced by import costs, currency fluctuations, and local competition. The premium nature of aramid fibers maintains relatively stable pricing structures, though volume discounts and long-term contracts can provide cost advantages for large-scale users.
Technology adoption rates vary significantly across different countries and applications within the region. Advanced economies demonstrate faster adoption of new aramid fiber technologies and applications, while developing markets focus on established applications with proven cost-effectiveness.
Competitive dynamics involve both international suppliers and emerging local players, with market share distribution reflecting the balance between established global brands and cost-competitive regional alternatives. According to MarkWide Research analysis, market consolidation trends favor companies with strong technical capabilities and comprehensive product portfolios.
Primary research methodology encompasses comprehensive interviews with industry stakeholders, including aramid fiber manufacturers, distributors, end-users, and industry associations across the Middle East and Africa region. Direct engagement with key market participants provides insights into current market conditions, future plans, and emerging trends that shape market development.
Secondary research involves extensive analysis of industry reports, government publications, trade statistics, and company financial statements to establish market baselines and validate primary research findings. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage of market segments and geographic regions within the scope of analysis.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources, statistical analysis of market trends, and expert review of findings to ensure accuracy and reliability of market insights. Triangulation of data sources helps eliminate potential biases and provides robust foundation for market projections.
Market modeling techniques utilize both top-down and bottom-up approaches to estimate market sizes, growth rates, and segment distributions. Economic indicators, industry growth patterns, and application-specific demand drivers inform quantitative projections and scenario analysis.
Regional analysis methodology considers country-specific factors including economic conditions, regulatory environments, industrial development levels, and market maturity stages to provide accurate regional market assessments and growth projections.
Gulf Cooperation Council countries dominate the Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market, accounting for approximately 45% of regional consumption. The United Arab Emirates leads regional demand driven by defense requirements, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace industry development. Saudi Arabia demonstrates strong growth potential supported by Vision 2030 diversification initiatives and substantial defense modernization programs.
North African markets, particularly Egypt and Morocco, show increasing demand for aramid fibers in automotive and industrial applications. These countries benefit from established manufacturing sectors and growing export-oriented industries that require high-performance materials for international competitiveness.
South Africa represents the largest single-country market in the Africa region, with well-developed automotive, mining, and defense industries driving consistent demand for aramid fiber products. The country’s advanced manufacturing capabilities and established supply chains support market growth across multiple application segments.
Sub-Saharan Africa demonstrates emerging market potential with growing industrial development and infrastructure investment. Countries like Nigeria and Kenya show increasing awareness of aramid fiber benefits, though market development remains in early stages compared to more established regional markets.
Regional trade dynamics facilitate market development through established distribution networks and cross-border commerce. Free trade agreements and economic partnerships within the region support market expansion and create opportunities for regional manufacturing and distribution strategies.
The competitive landscape in the Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market features a mix of international suppliers and emerging regional players, each contributing to market development through different strategies and capabilities:
Market competition centers on product quality, technical support, pricing strategies, and local service capabilities. Established international players leverage brand recognition and proven performance records, while emerging competitors focus on cost competitiveness and specialized applications.
By Fiber Type:
By Application:
By End-User Industry:
Para-aramid fiber category demonstrates superior market performance driven by exceptional tensile strength and versatility across multiple applications. This category benefits from established supply chains, proven performance records, and strong demand from defense and automotive sectors. Growth opportunities include expanding applications in renewable energy and infrastructure projects.
Meta-aramid fiber category shows steady growth supported by increasing emphasis on worker safety and thermal protection requirements. This segment benefits from regulatory support for protective equipment standards and growing industrial safety awareness. Market development focuses on specialized applications requiring superior thermal stability and flame resistance.
Defense application category maintains market leadership through consistent government spending and ongoing modernization programs. This category demonstrates resilience to economic fluctuations and provides stable demand foundation for market growth. Future development depends on regional security conditions and defense budget allocations.
Automotive application category represents the fastest-growing segment with substantial potential for market expansion. This category benefits from industry trends toward lightweighting, fuel efficiency, and performance enhancement. Growth drivers include local automotive manufacturing development and export market opportunities.
Industrial application category provides diversified demand across multiple sectors, offering stability and growth potential. This category benefits from ongoing industrial development and infrastructure investment across the region. Market opportunities include specialized applications in energy, chemical processing, and manufacturing sectors.
Manufacturers benefit from growing market demand, opportunities for local production development, and potential for technology partnerships with international suppliers. The expanding market provides revenue growth opportunities and justification for investment in specialized manufacturing capabilities and technical expertise development.
End-users gain access to high-performance materials that enhance product quality, safety, and competitiveness in both domestic and export markets. Aramid fiber adoption enables compliance with international standards and specifications required for global market participation.
Distributors and suppliers benefit from growing market demand and opportunities to develop specialized distribution networks serving diverse application segments. The premium nature of aramid fibers provides attractive margin opportunities for value-added services and technical support.
Government stakeholders benefit from industrial development, technology transfer, and economic diversification achieved through aramid fiber market growth. The sector contributes to strategic objectives including defense capability enhancement and advanced manufacturing development.
Research institutions gain opportunities for collaboration with industry partners, development of specialized expertise, and contribution to regional technological advancement. The growing market creates demand for research and development services supporting market expansion.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainability focus emerges as a significant trend driving demand for recyclable and environmentally responsible aramid fiber products. Manufacturers increasingly emphasize sustainable production processes and end-of-life recycling capabilities to meet growing environmental consciousness among end-users and regulatory requirements.
Localization initiatives gain momentum as regional governments and companies seek to reduce import dependency and develop domestic manufacturing capabilities. This trend creates opportunities for technology transfer, joint ventures, and establishment of local production facilities serving regional markets.
Application diversification expands beyond traditional defense and industrial uses to include emerging sectors such as renewable energy, aerospace, and advanced composites. This trend broadens market opportunities and reduces dependence on specific application segments.
Quality standardization increases as regional markets mature and demand for international certification grows. End-users increasingly require compliance with global standards and specifications, driving demand for premium-quality aramid fiber products.
Digital integration transforms supply chain management and customer service through digital platforms, predictive maintenance, and smart manufacturing technologies. This trend enhances efficiency and customer satisfaction while reducing operational costs.
Customization demand grows as end-users seek specialized aramid fiber solutions tailored to specific regional requirements and applications. This trend creates opportunities for value-added services and premium pricing strategies.
Manufacturing investments across the region demonstrate growing commitment to local aramid fiber production capabilities. Several countries announce plans for advanced materials manufacturing facilities, supported by government incentives and international partnerships that facilitate technology transfer and expertise development.
Research and development initiatives expand through collaboration between regional universities, research institutions, and international aramid fiber manufacturers. These partnerships focus on developing specialized applications and processing technologies suited to regional requirements and market conditions.
Strategic partnerships between international suppliers and regional distributors strengthen market presence and customer service capabilities. These alliances combine global expertise with local market knowledge to better serve diverse customer requirements across the region.
Regulatory developments include updated safety standards and quality requirements that favor high-performance materials like aramid fibers. New regulations in automotive, construction, and industrial sectors create additional demand drivers for aramid fiber adoption.
Technology advancements in aramid fiber processing and application techniques improve performance characteristics and expand potential uses. These developments include enhanced fiber treatments, improved composite integration, and specialized finishing processes for specific applications.
Market entry strategies should focus on establishing strong local partnerships and distribution networks to navigate diverse regulatory environments and customer requirements across the Middle East and Africa region. MarkWide Research recommends prioritizing countries with established industrial bases and favorable government policies supporting advanced materials adoption.
Investment priorities should emphasize technical support capabilities, customer education programs, and supply chain optimization to address current market limitations and build competitive advantages. Companies should consider establishing regional technical centers to provide specialized support and application development services.
Product development focus should address specific regional requirements including extreme temperature performance, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness for price-sensitive applications. Customization capabilities and rapid response to customer needs provide competitive differentiation in diverse regional markets.
Partnership strategies should leverage international expertise with local market knowledge through joint ventures, licensing agreements, and technology transfer arrangements. These partnerships can accelerate market development while building sustainable competitive positions.
Long-term positioning should anticipate market evolution toward greater sophistication and local production capabilities. Companies should invest in relationships and capabilities that support this transition while maintaining competitive advantages through innovation and service excellence.
Market growth prospects remain positive with projected expansion driven by continued industrial development, defense modernization, and emerging applications in renewable energy and aerospace sectors. The market is expected to achieve sustained growth rates above 8% annually, supported by favorable economic conditions and government policies promoting advanced manufacturing.
Technology evolution will drive development of specialized aramid fiber products tailored to regional requirements and emerging applications. Advanced processing techniques and improved fiber characteristics will expand market opportunities while enhancing performance in existing applications.
Local manufacturing development is expected to accelerate through international partnerships and government incentives, reducing import dependency and improving supply chain efficiency. This trend will create new competitive dynamics and market opportunities for both international and regional players.
Application expansion into renewable energy, infrastructure, and advanced composites will diversify market demand and reduce dependence on traditional defense and industrial applications. These emerging sectors offer substantial growth potential with attractive margin opportunities.
Regional integration through trade agreements and economic partnerships will facilitate market expansion and create opportunities for specialized manufacturing and distribution strategies. According to MWR projections, regional market integration will accelerate growth and improve overall market efficiency.
The Middle East and Africa aramid fibers market presents substantial opportunities for growth and development, driven by strong fundamentals including defense requirements, industrial diversification, and emerging applications across multiple sectors. The market benefits from favorable government policies, strategic geographic positioning, and growing awareness of aramid fiber benefits among regional manufacturers and end-users.
Key success factors for market participants include establishing strong local partnerships, investing in technical support capabilities, and developing products tailored to regional requirements and applications. The market rewards companies that combine international expertise with local market knowledge and customer service excellence.
Future market development will be shaped by continued industrial growth, technology advancement, and increasing local manufacturing capabilities. Companies that position themselves to support this evolution while maintaining competitive advantages through innovation and service excellence will achieve sustainable success in this dynamic and growing market.
What is Aramid Fibers?
Aramid fibers are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers used in various applications, including aerospace, automotive, and protective clothing. They are known for their high tensile strength and thermal stability.
What are the key players in the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market?
Key players in the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market include DuPont, Teijin Limited, and Kordsa Teknik Tekstil, among others. These companies are involved in the production and supply of aramid fibers for various industries.
What are the growth factors driving the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market?
The growth of the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market is driven by increasing demand from the automotive and aerospace sectors, as well as the rising need for protective clothing in industrial applications. Additionally, advancements in technology are enhancing fiber performance.
What challenges does the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market face?
The Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market faces challenges such as high production costs and competition from alternative materials. Additionally, fluctuating raw material prices can impact profitability for manufacturers.
What opportunities exist in the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market?
Opportunities in the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market include the growing demand for lightweight materials in automotive manufacturing and the expansion of the defense sector. Furthermore, increasing investments in research and development are likely to foster innovation.
What trends are shaping the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market?
Trends in the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market include the development of eco-friendly aramid fibers and the integration of smart textiles in protective gear. Additionally, there is a growing focus on enhancing the durability and performance of aramid products.
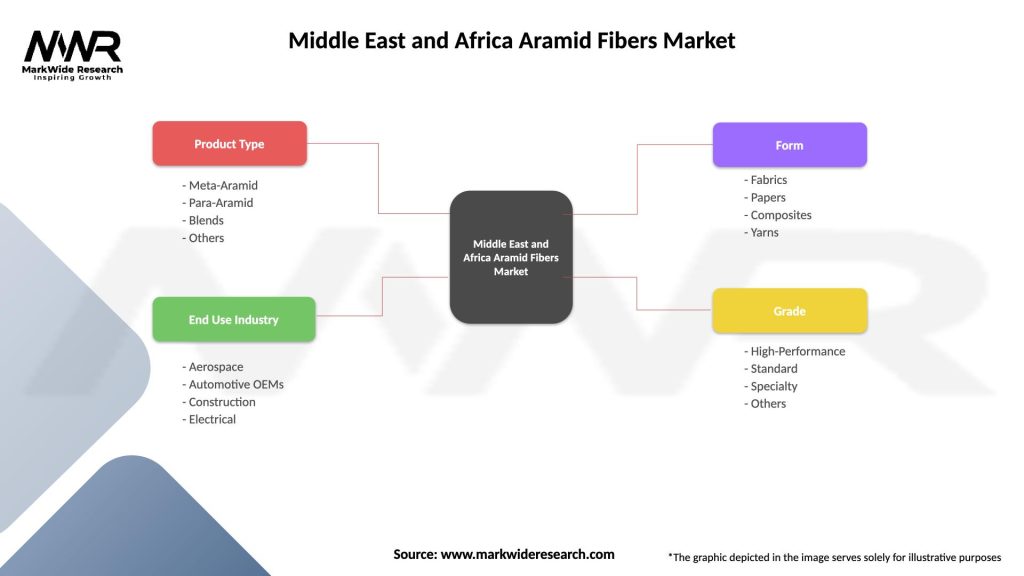
Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Meta-Aramid, Para-Aramid, Blends, Others |
| End Use Industry | Aerospace, Automotive OEMs, Construction, Electrical |
| Form | Fabrics, Papers, Composites, Yarns |
| Grade | High-Performance, Standard, Specialty, Others |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Middle East and Africa Aramid Fibers Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at