444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview: The medical self-service platform market encompasses a range of digital solutions and technologies that empower patients to access healthcare services, manage their medical records, and engage in self-care activities through online platforms and mobile applications. These platforms leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, telemedicine, and electronic health records to enhance patient convenience, improve healthcare outcomes, and optimize resource utilization in the healthcare ecosystem. The market for medical self-service platforms is driven by factors such as the growing demand for telehealth services, increasing patient-centric care models, and the need for efficient healthcare delivery systems.
Meaning: Medical self-service platforms refer to digital tools and applications that enable patients to take an active role in managing their healthcare needs and accessing medical services without the need for traditional in-person interactions. These platforms provide functionalities such as appointment scheduling, prescription refills, remote consultations, health information access, and wellness tracking, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Medical self-service platforms aim to improve patient engagement, enhance care coordination, and streamline healthcare workflows for both patients and providers.
Executive Summary: The medical self-service platform market is experiencing rapid growth driven by the shift towards patient-centered care delivery models, increasing adoption of digital health technologies, and the need to address healthcare access disparities. Key market players are investing in innovative solutions to enhance user experience, ensure data security, and expand platform functionalities to meet the evolving needs of patients and healthcare providers. With the continued emphasis on patient empowerment and digital transformation in healthcare, the medical self-service platform market is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The medical self-service platform market is characterized by dynamic interactions between technological innovation, regulatory evolution, and shifting consumer preferences. Market players need to navigate these dynamics by leveraging user-centered design principles, interoperable standards, and data-driven insights to develop scalable, sustainable, and patient-centric solutions that drive value for all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem.
Regional Analysis: The adoption of medical self-service platforms varies across regions based on factors such as healthcare infrastructure, regulatory environment, digital health maturity, and patient preferences. Developed markets in North America and Europe lead the adoption of digital health technologies, driven by favorable reimbursement policies, robust IT infrastructure, and consumer demand for convenience and accessibility. Emerging markets in Asia Pacific and Latin America offer significant growth opportunities due to increasing smartphone penetration, rising healthcare expenditures, and government initiatives to promote digital health innovation.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Medical Self Service Platform Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
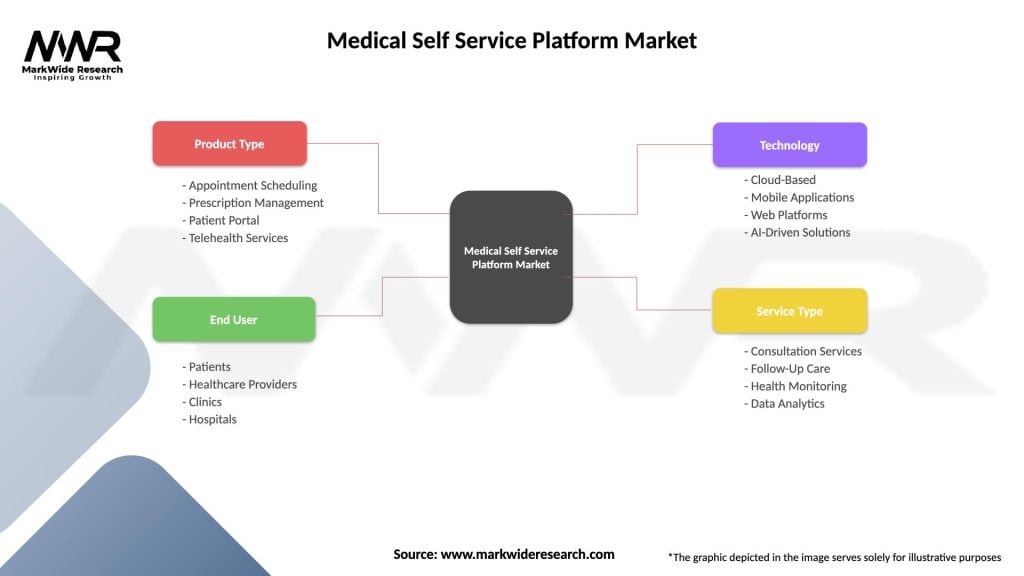
Segmentation: The medical self-service platform market can be segmented based on platform type, application, end-user, and geography. Platform types include web-based portals, mobile health apps, wearable devices, and virtual care platforms. Applications range from appointment scheduling and teleconsultations to remote monitoring and chronic disease management. End-users encompass patients, healthcare providers, payers, and employers seeking to improve health outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance patient satisfaction through digital health solutions.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of medical self-service platforms and digital health solutions, driven by the need for remote care delivery, social distancing measures, and infection control protocols. The crisis has underscored the importance of telemedicine, virtual care, and self-service tools in ensuring continuity of care, reducing healthcare disparities, and enhancing resilience in the face of public health emergencies.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The medical self-service platform market is poised for continued growth and innovation driven by the convergence of consumer technology trends, healthcare industry shifts, and regulatory reforms. By harnessing the power of digital health technologies, patient engagement strategies, and collaborative partnerships, stakeholders can unlock new opportunities for improving access to care, enhancing care delivery efficiency, and promoting patient-centered healthcare models in the digital age.
Conclusion: The medical self-service platform market represents a transformative force in healthcare, empowering patients with the tools and technologies to take control of their health and well-being. With the rise of telemedicine, virtual care, and patient-centered care models, medical self-service platforms have become essential components of modern healthcare delivery, offering convenience, accessibility, and empowerment to patients and providers alike. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and patient-centricity, stakeholders can harness the full potential of medical self-service platforms to drive positive health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and transform the future of healthcare delivery worldwide.
What is Medical Self Service Platform?
A Medical Self Service Platform is a digital solution that allows patients to manage their healthcare needs independently. This includes scheduling appointments, accessing medical records, and communicating with healthcare providers without direct assistance.
What are the key players in the Medical Self Service Platform Market?
Key players in the Medical Self Service Platform Market include companies like Zocdoc, HealthTap, and MyChart, which provide various self-service solutions for patients. These companies focus on enhancing patient engagement and streamlining healthcare processes, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Medical Self Service Platform Market?
The growth of the Medical Self Service Platform Market is driven by increasing patient demand for convenience, the rise of telehealth services, and the need for healthcare providers to improve operational efficiency. Additionally, the growing adoption of mobile health applications contributes to this trend.
What challenges does the Medical Self Service Platform Market face?
Challenges in the Medical Self Service Platform Market include concerns over data privacy and security, the need for interoperability between different healthcare systems, and resistance from some healthcare providers to adopt new technologies. These factors can hinder widespread implementation.
What opportunities exist in the Medical Self Service Platform Market?
Opportunities in the Medical Self Service Platform Market include the potential for integrating artificial intelligence to enhance user experience, expanding services to underserved populations, and developing features that cater to chronic disease management. These innovations can significantly improve patient outcomes.
What trends are shaping the Medical Self Service Platform Market?
Trends in the Medical Self Service Platform Market include the increasing use of mobile applications for healthcare management, the integration of telemedicine features, and a focus on personalized patient experiences. These trends reflect a shift towards more patient-centered care.
Medical Self Service Platform Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Appointment Scheduling, Prescription Management, Patient Portal, Telehealth Services |
| End User | Patients, Healthcare Providers, Clinics, Hospitals |
| Technology | Cloud-Based, Mobile Applications, Web Platforms, AI-Driven Solutions |
| Service Type | Consultation Services, Follow-Up Care, Health Monitoring, Data Analytics |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Medical Self Service Platform Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at