444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
The MEA automotive EPS market represents a rapidly evolving segment within the Middle East and Africa’s automotive industry, driven by increasing vehicle production, rising consumer demand for enhanced driving comfort, and stringent fuel efficiency regulations. Electric Power Steering (EPS) systems have emerged as a critical technology that significantly improves vehicle performance while reducing energy consumption compared to traditional hydraulic power steering systems.
Market dynamics in the MEA region indicate substantial growth potential, with the automotive EPS market experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% across key markets including Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, and Egypt. This growth trajectory reflects the region’s commitment to modernizing its automotive infrastructure and adopting advanced steering technologies that align with global automotive trends.
Regional adoption patterns show varying levels of EPS integration, with Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries leading in premium vehicle segments while North African markets focus on cost-effective solutions for mass-market vehicles. The technology’s ability to deliver 15-20% fuel efficiency improvements has made it particularly attractive to manufacturers and consumers seeking to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Industry transformation across the MEA region has been accelerated by government initiatives promoting sustainable transportation solutions and the establishment of local automotive manufacturing hubs. These developments have created favorable conditions for EPS market expansion, supported by increasing investments in research and development activities focused on steering system innovations.
The MEA automotive EPS market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the development, manufacturing, distribution, and implementation of electric power steering systems specifically within Middle Eastern and African automotive markets. Electric Power Steering systems utilize electric motors and electronic control units to provide steering assistance, eliminating the need for hydraulic pumps and associated fluid systems while delivering superior performance and efficiency.
Core functionality of EPS systems involves sophisticated electronic control mechanisms that adjust steering assistance based on vehicle speed, driving conditions, and driver input. This intelligent adaptation ensures optimal steering feel at low speeds for parking maneuvers while providing stability and precision during high-speed driving scenarios.
Market scope encompasses various EPS configurations including column-assist, pinion-assist, and rack-assist systems, each designed to meet specific vehicle requirements and performance objectives. The technology’s integration with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) has further expanded its relevance in modern automotive applications.
Regional significance extends beyond mere technology adoption, representing a strategic shift toward sustainable automotive solutions that align with the MEA region’s economic diversification goals and environmental sustainability commitments. The market’s evolution reflects broader trends in automotive electrification and smart mobility solutions.
Strategic market positioning of the MEA automotive EPS market demonstrates robust growth fundamentals supported by increasing vehicle production, rising consumer awareness of fuel efficiency benefits, and regulatory frameworks promoting advanced automotive technologies. The market’s expansion is characterized by significant technological advancements and growing adoption across diverse vehicle segments.
Key growth drivers include the region’s expanding automotive manufacturing base, increasing foreign direct investment in automotive technologies, and rising consumer preference for vehicles equipped with advanced steering systems. Market penetration rates have reached 42% in premium vehicle segments while showing accelerating adoption in mid-range vehicle categories.
Competitive landscape features a mix of international technology providers and emerging regional players, creating a dynamic market environment that fosters innovation and competitive pricing strategies. The presence of major automotive manufacturers establishing production facilities in the region has further stimulated demand for advanced EPS solutions.
Future prospects indicate continued market expansion driven by technological innovations, increasing vehicle electrification trends, and growing emphasis on driver safety and comfort features. The integration of EPS systems with autonomous driving technologies presents additional growth opportunities for market participants.

Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct growth patterns across different vehicle categories and geographic regions within the MEA market. Understanding these insights provides valuable guidance for stakeholders seeking to optimize their market strategies and investment decisions.
Fuel efficiency regulations across MEA countries have emerged as primary catalysts for EPS market growth, with governments implementing stringent standards that encourage adoption of energy-efficient automotive technologies. These regulatory frameworks create compelling incentives for manufacturers to integrate EPS systems into their vehicle designs.
Consumer demand evolution reflects increasing awareness of advanced automotive technologies and their benefits, driving preference for vehicles equipped with modern steering systems that enhance driving comfort and safety. This shift in consumer behavior has created sustainable demand growth across multiple market segments.
Automotive manufacturing expansion throughout the region has established robust supply chains and production capabilities that support EPS market development. The establishment of manufacturing hubs in countries like Morocco, South Africa, and UAE has created favorable conditions for technology adoption and market growth.
Economic diversification initiatives promoted by regional governments have prioritized automotive sector development as a key component of economic transformation strategies. These initiatives include investment incentives, infrastructure development, and technology transfer programs that benefit EPS market participants.
Technological advancement integration with emerging automotive technologies such as autonomous driving systems and electric vehicles has created new applications and market opportunities for advanced EPS solutions. This technological convergence drives continuous innovation and market expansion.
High implementation costs associated with EPS system integration continue to challenge market penetration, particularly in price-sensitive vehicle segments where cost considerations significantly influence purchasing decisions. These economic barriers require strategic approaches to cost optimization and value demonstration.
Technical complexity challenges related to EPS system integration with existing vehicle architectures can create implementation difficulties for manufacturers, particularly those with limited experience in advanced steering technologies. These technical hurdles may slow adoption rates in certain market segments.
Infrastructure limitations in some MEA regions, including inadequate service networks and limited technical expertise, can hinder effective EPS system deployment and maintenance. These infrastructure gaps require targeted investments and capacity building initiatives.
Market fragmentation across diverse MEA countries with varying regulatory requirements, consumer preferences, and economic conditions creates complexity for market participants seeking to develop comprehensive regional strategies. This fragmentation can limit economies of scale and increase operational costs.
Competition from alternative technologies including improved hydraulic systems and emerging steering technologies may limit EPS market growth in certain applications where alternative solutions offer comparable benefits at lower costs.
Electric vehicle integration presents substantial growth opportunities as the MEA region accelerates its transition toward sustainable transportation solutions. EPS systems are essential components in electric vehicles, creating natural synergies that drive market expansion and technological innovation.
Autonomous driving development offers significant potential for advanced EPS systems that can interface with self-driving technologies. As autonomous vehicle development progresses in the region, demand for sophisticated steering systems with electronic control capabilities will increase substantially.
Aftermarket expansion represents an underexplored opportunity for EPS system providers, particularly in markets with large existing vehicle populations that could benefit from steering system upgrades. This segment offers potential for sustained revenue growth and market penetration.
Local manufacturing development creates opportunities for technology transfer, cost reduction, and market access optimization. Establishing regional production capabilities can significantly improve competitive positioning and market responsiveness.
Strategic partnerships with regional automotive manufacturers, technology providers, and government agencies can facilitate market entry, technology development, and business expansion across diverse MEA markets.
Supply chain evolution within the MEA automotive EPS market demonstrates increasing sophistication and regional integration, with manufacturers developing localized sourcing strategies that reduce costs and improve supply security. This evolution supports market stability and growth sustainability.
Technology transfer acceleration has facilitated rapid adoption of advanced EPS technologies across the region, with international providers establishing partnerships and joint ventures that enable knowledge sharing and capability development. These collaborations drive innovation and market competitiveness.
Regulatory harmonization efforts across MEA countries are creating more consistent market conditions that facilitate regional business strategies and reduce compliance complexity. This harmonization supports market integration and economies of scale development.
Investment flow patterns show increasing capital allocation toward automotive technology development and manufacturing capacity expansion, reflecting confidence in long-term market growth prospects and strategic importance of the automotive sector.
Competitive intensity has increased as market opportunities attract new participants and existing players expand their regional presence. This competition drives innovation, improves product quality, and creates value for customers while challenging market participants to differentiate their offerings.
Comprehensive market analysis employed multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into the MEA automotive EPS market. The research approach combined quantitative data collection with qualitative analysis to provide a complete market understanding.
Primary research activities included extensive interviews with industry executives, automotive manufacturers, technology providers, and market experts across key MEA countries. These interviews provided valuable insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities from diverse stakeholder perspectives.
Secondary research components encompassed analysis of industry reports, government publications, trade association data, and company financial statements to establish comprehensive market context and validate primary research findings. This multi-source approach ensures research reliability and accuracy.
Data validation processes involved cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting follow-up interviews to clarify findings, and applying statistical analysis techniques to ensure data consistency and reliability. These validation steps enhance research credibility and usefulness.
Market modeling techniques utilized advanced analytical frameworks to project market trends, assess growth scenarios, and evaluate competitive dynamics. These models provide stakeholders with actionable insights for strategic planning and decision-making purposes.
Gulf Cooperation Council markets lead the MEA automotive EPS adoption with 48% regional market share, driven by high vehicle ownership rates, preference for premium automotive features, and strong economic fundamentals that support advanced technology adoption. Countries like UAE and Saudi Arabia demonstrate particularly robust growth patterns.
North African markets represent significant growth potential with 34% market share and accelerating adoption rates driven by expanding automotive manufacturing capabilities and increasing consumer awareness of EPS benefits. Egypt and Morocco have emerged as key markets within this regional segment.
Sub-Saharan African markets account for 18% of regional demand but show promising growth trajectories as economic development and automotive sector expansion create new opportunities for EPS technology adoption. South Africa leads this segment with established automotive manufacturing infrastructure.
Market maturity levels vary significantly across the region, with GCC countries demonstrating more advanced adoption patterns while other markets show characteristics of emerging segments with substantial growth potential. This diversity creates opportunities for tailored market strategies.
Regional integration trends indicate increasing cooperation and trade relationships that facilitate technology transfer and market access across MEA countries. These trends support market development and create synergies that benefit all regional participants.
Market leadership in the MEA automotive EPS sector is characterized by a combination of established international technology providers and emerging regional players, creating a dynamic competitive environment that drives innovation and market development.
Competitive strategies focus on technology innovation, cost optimization, local partnership development, and customer service excellence. Market participants are investing in research and development activities while establishing regional manufacturing and service capabilities.
Technology-based segmentation reveals distinct market preferences and adoption patterns across different EPS system types, with each category serving specific vehicle requirements and market segments within the MEA region.
By Technology Type:
By Vehicle Type:
By Application:
Premium vehicle segment demonstrates the highest EPS adoption rates with 72% penetration levels, driven by consumer expectations for advanced features and manufacturers’ focus on differentiation through technology integration. This segment serves as a technology showcase and market development catalyst.
Mid-range vehicle category shows accelerating adoption with 38% current penetration and strong growth momentum as cost reductions and consumer awareness drive market expansion. This segment represents the largest growth opportunity for EPS providers.
Economy vehicle segment maintains 18% adoption rates but shows promising growth potential as manufacturers seek to differentiate their offerings and meet fuel efficiency requirements through advanced steering technologies.
Commercial vehicle applications are emerging as significant growth drivers with 25% adoption rates in new vehicle production, supported by operational efficiency benefits and regulatory requirements for improved fuel economy.
Electric vehicle integration demonstrates 95% EPS adoption rates due to natural compatibility and performance requirements, making this category a key growth driver for advanced steering system technologies.
Automotive manufacturers benefit from EPS integration through improved vehicle performance, reduced manufacturing complexity, enhanced fuel efficiency ratings, and competitive differentiation opportunities. These advantages support market positioning and customer satisfaction objectives.
Technology providers gain access to expanding market opportunities, revenue diversification possibilities, and strategic partnership development potential. The growing market creates sustainable business opportunities and innovation incentives.
Consumers experience enhanced driving comfort, improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance requirements, and access to advanced automotive technologies. These benefits drive consumer preference and market demand growth.
Government stakeholders achieve environmental objectives through reduced vehicle emissions, economic development through automotive sector growth, and technology advancement through innovation promotion. These outcomes support policy objectives and economic development goals.
Service providers benefit from new business opportunities in system maintenance, repair services, and technical support activities. The expanding installed base creates sustainable service revenue opportunities.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Electrification integration represents the most significant trend shaping the MEA automotive EPS market, with increasing alignment between EPS adoption and electric vehicle development. This convergence creates synergistic growth opportunities and technological advancement drivers.
Autonomous driving preparation is driving demand for advanced EPS systems capable of interfacing with self-driving technologies. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that autonomous-ready EPS systems are experiencing 22% annual growth in regional markets.
Cost optimization focus continues to drive innovation in manufacturing processes, component design, and supply chain management. These efforts have resulted in 12-15% cost reductions over recent years while maintaining performance standards.
Local manufacturing expansion is accelerating across the region as companies establish production facilities to serve regional markets more effectively. This trend supports cost reduction, supply chain security, and market responsiveness objectives.
Smart connectivity integration is emerging as EPS systems incorporate advanced sensors, communication capabilities, and data analytics features that enhance performance and enable new service opportunities.
Strategic partnerships between international technology providers and regional automotive manufacturers have accelerated market development and technology transfer activities. These collaborations facilitate market access and capability development across the MEA region.
Manufacturing facility investments have increased significantly as companies establish regional production capabilities to serve growing market demand. These investments demonstrate confidence in long-term market growth prospects and strategic importance.
Technology advancement initiatives focus on developing EPS systems optimized for regional market requirements, including climate considerations, cost constraints, and performance expectations. These developments enhance market relevance and adoption potential.
Regulatory framework development across MEA countries has created more supportive environments for advanced automotive technology adoption. These regulatory improvements facilitate market growth and investment attraction.
Research and development expansion has intensified as companies invest in innovation capabilities and technology advancement programs. These investments support competitive positioning and market leadership objectives.
Market entry strategies should prioritize partnership development with established regional players to leverage local market knowledge, distribution networks, and customer relationships. These partnerships can accelerate market penetration and reduce entry risks.
Technology adaptation recommendations emphasize developing EPS solutions optimized for regional market conditions, including climate considerations, cost requirements, and performance expectations. This customization approach enhances market acceptance and competitive positioning.
Investment prioritization should focus on markets with strong growth fundamentals, supportive regulatory environments, and established automotive manufacturing infrastructure. MWR analysis suggests that GCC and North African markets offer the most attractive near-term opportunities.
Competitive differentiation strategies should emphasize value proposition development that clearly communicates EPS benefits to customers while addressing cost concerns through innovative financing and service models.
Supply chain optimization recommendations include developing regional sourcing capabilities, establishing local manufacturing partnerships, and creating flexible supply chain structures that can adapt to market changes and growth opportunities.
Long-term growth prospects for the MEA automotive EPS market remain highly positive, supported by fundamental drivers including vehicle electrification, autonomous driving development, and continued economic growth across the region. These factors create sustainable demand growth opportunities.
Technology evolution will continue driving market advancement with integration of artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and connectivity features that enhance EPS system capabilities and create new value propositions for customers and stakeholders.
Market maturation is expected to accelerate as adoption rates increase across all vehicle segments and geographic regions. This maturation process will create more stable market conditions while maintaining growth momentum through technology advancement and market expansion.
Regional integration trends will likely strengthen as trade relationships develop and regulatory harmonization progresses. These developments will facilitate market access, reduce operational complexity, and create economies of scale opportunities.
Innovation acceleration will continue as competitive pressures and customer demands drive continuous improvement in EPS system performance, cost-effectiveness, and functionality. This innovation cycle supports long-term market vitality and growth sustainability.
The MEA automotive EPS market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector with substantial growth potential driven by technological advancement, regulatory support, and changing consumer preferences. The market’s development reflects broader trends in automotive electrification and smart mobility solutions that are reshaping the global automotive industry.
Strategic opportunities abound for market participants who can effectively navigate regional market complexities while delivering value-driven solutions that meet diverse customer requirements. Success in this market requires comprehensive understanding of local conditions, strategic partnership development, and continuous innovation commitment.
Future success will depend on the ability to adapt to evolving market conditions, leverage emerging technologies, and build sustainable competitive advantages through innovation, cost optimization, and customer service excellence. The market’s growth trajectory indicates strong potential for stakeholders who can execute effective strategies and maintain long-term commitment to regional market development.
What is Automotive EPS?
Automotive EPS, or Electric Power Steering, refers to a steering system that uses electric motors to assist the driver in steering the vehicle, enhancing control and efficiency. This technology is increasingly adopted in modern vehicles for its benefits in fuel efficiency and driving comfort.
What are the key players in the MEA Automotive EPS Market?
Key players in the MEA Automotive EPS Market include Bosch, ZF Friedrichshafen, and JTEKT Corporation, which are known for their innovative steering solutions and technologies. These companies focus on enhancing vehicle performance and safety through advanced EPS systems, among others.
What are the main drivers of the MEA Automotive EPS Market?
The main drivers of the MEA Automotive EPS Market include the increasing demand for fuel-efficient vehicles, advancements in automotive technology, and the growing emphasis on vehicle safety features. Additionally, the shift towards electric vehicles is further propelling the adoption of EPS systems.
What challenges does the MEA Automotive EPS Market face?
The MEA Automotive EPS Market faces challenges such as high initial costs of EPS systems and the complexity of integrating these systems with existing vehicle architectures. Additionally, competition from traditional hydraulic steering systems poses a challenge to market growth.
What opportunities exist in the MEA Automotive EPS Market?
Opportunities in the MEA Automotive EPS Market include the rising trend of autonomous vehicles and the increasing focus on smart mobility solutions. Furthermore, the expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure presents significant growth potential for EPS technologies.
What trends are shaping the MEA Automotive EPS Market?
Trends shaping the MEA Automotive EPS Market include the integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) with EPS, the development of steer-by-wire technology, and the growing demand for lightweight materials in automotive design. These innovations are enhancing the functionality and efficiency of EPS systems.
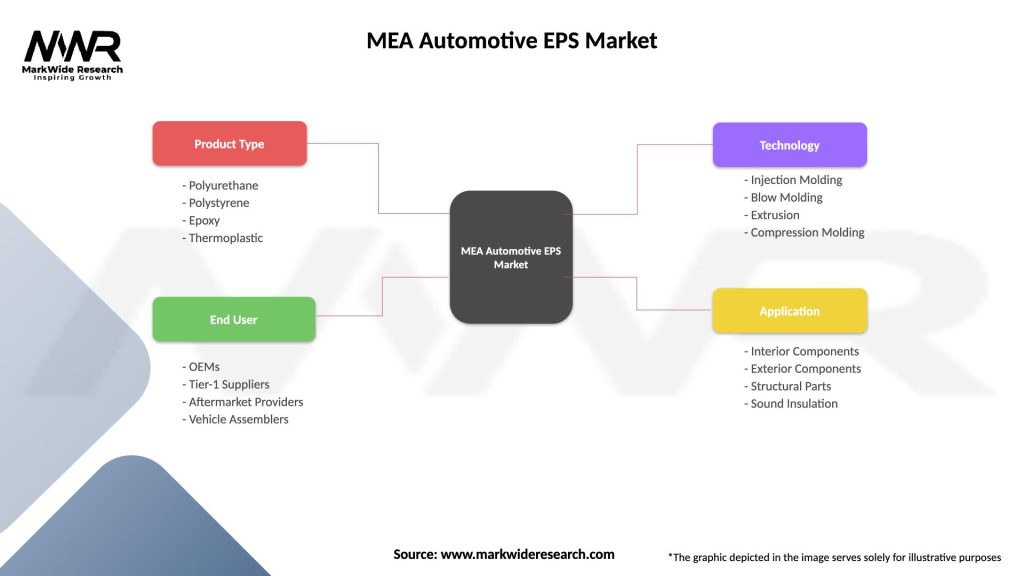
MEA Automotive EPS Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Polyurethane, Polystyrene, Epoxy, Thermoplastic |
| End User | OEMs, Tier-1 Suppliers, Aftermarket Providers, Vehicle Assemblers |
| Technology | Injection Molding, Blow Molding, Extrusion, Compression Molding |
| Application | Interior Components, Exterior Components, Structural Parts, Sound Insulation |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the MEA Automotive EPS Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at