444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview:
The Mass Spectrometry Market stands at the forefront of analytical instrumentation, playing a pivotal role in diverse scientific and industrial applications. This market’s prominence is driven by the increasing need for precise and sensitive analysis across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, environmental monitoring, and forensic science. Mass spectrometry, as a powerful analytical technique, continues to evolve, offering advanced solutions for complex analytical challenges.
Meaning:
Mass spectrometry is a versatile analytical technique used to identify and quantify chemical compounds based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The process involves ionizing a sample, separating ions based on their mass, and detecting these ions to generate a mass spectrum. This technique provides detailed information about the molecular composition of a sample, making it indispensable in fields such as chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Executive Summary:
The Mass Spectrometry Market has witnessed significant growth due to technological advancements, expanding applications, and the increasing focus on research and development. This executive summary encapsulates key market dynamics, emphasizing insights into market drivers, restraints, and future trends. Understanding these factors is crucial for stakeholders to navigate the evolving landscape of mass spectrometry.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics:
The Mass Spectrometry Market operates in a dynamic environment influenced by factors such as technological evolution, regulatory changes, and emerging applications. Understanding the market dynamics is essential for stakeholders to adapt to industry trends and capitalize on opportunities.
Regional Analysis:
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Mass Spectrometry Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
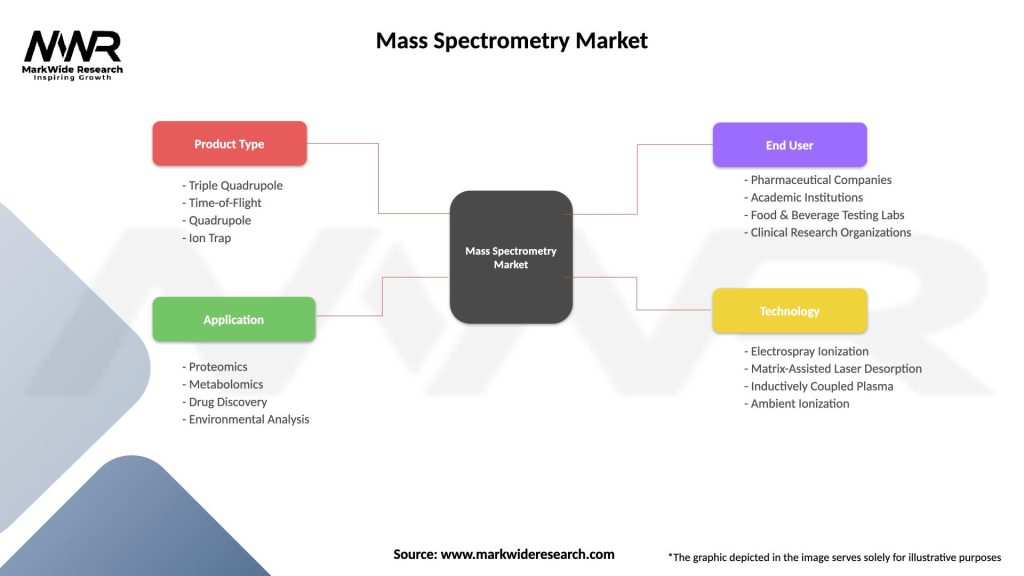
Segmentation:
The Mass Spectrometry Market can be segmented based on various factors:
Segmentation provides a detailed understanding of the market’s nuances, enabling stakeholders to tailor their strategies to specific market segments.
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
The Mass Spectrometry Market offers several benefits for industry participants:
SWOT Analysis:
A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive view of the Mass Spectrometry Market’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Understanding these factors is crucial for industry participants to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, explore opportunities, and mitigate potential threats.
Market Key Trends:
The Mass Spectrometry Market is subject to key trends that shape its evolution:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has had varied impacts on the Mass Spectrometry Market:
Key Industry Developments:
The Mass Spectrometry Market has witnessed notable industry developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Industry analysts provide valuable suggestions for stakeholders in the Mass Spectrometry Market:
Future Outlook:
The Mass Spectrometry Market is poised for significant developments in the coming years. Key factors that will shape the market’s future include:
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Mass Spectrometry Market stands at the forefront of analytical instrumentation, serving as a cornerstone in scientific research, healthcare, and industrial applications. The market’s evolution is characterized by continuous technological advancements, expanding applications, and a focus on addressing complex analytical challenges.
Stakeholders in the Mass Spectrometry Market should navigate the dynamic landscape by embracing innovation, fostering collaborations, and addressing affordability concerns. As the market continues to grow and diversify, the ability to adapt to emerging trends, invest in research and development, and enhance user accessibility will be crucial for sustained success.
By staying at the cutting edge of technology and applications, the Mass Spectrometry Market is poised to make profound contributions to scientific discovery, healthcare advancements, and the overall progress of analytical sciences in the years to come.
What is Mass Spectrometry?
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It is widely utilized in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science for applications like identifying compounds and analyzing complex mixtures.
What are the key players in the Mass Spectrometry Market?
Key players in the Mass Spectrometry Market include Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, and Waters Corporation, among others. These companies are known for their innovative technologies and comprehensive product offerings in mass spectrometry.
What are the growth factors driving the Mass Spectrometry Market?
The Mass Spectrometry Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for advanced analytical techniques in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, the growing focus on environmental testing, and the rising need for food safety and quality control.
What challenges does the Mass Spectrometry Market face?
Challenges in the Mass Spectrometry Market include the high cost of advanced mass spectrometry systems and the need for skilled professionals to operate and interpret the results. Additionally, the complexity of sample preparation can hinder widespread adoption.
What opportunities exist in the Mass Spectrometry Market?
Opportunities in the Mass Spectrometry Market include the development of miniaturized and portable mass spectrometry devices, advancements in data analysis software, and the increasing application of mass spectrometry in personalized medicine and clinical diagnostics.
What trends are shaping the Mass Spectrometry Market?
Trends in the Mass Spectrometry Market include the integration of mass spectrometry with other analytical techniques, the rise of high-resolution mass spectrometry, and the growing use of mass spectrometry in proteomics and metabolomics research.
Mass Spectrometry Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Triple Quadrupole, Time-of-Flight, Quadrupole, Ion Trap |
| Application | Proteomics, Metabolomics, Drug Discovery, Environmental Analysis |
| End User | Pharmaceutical Companies, Academic Institutions, Food & Beverage Testing Labs, Clinical Research Organizations |
| Technology | Electrospray Ionization, Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption, Inductively Coupled Plasma, Ambient Ionization |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at