444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Malaysia polymer industry market represents a dynamic and rapidly expanding sector that serves as a cornerstone of the nation’s manufacturing economy. Malaysia’s strategic position in Southeast Asia, combined with abundant raw material resources and established petrochemical infrastructure, has positioned the country as a significant player in the global polymer landscape. The industry encompasses a diverse range of polymer products including polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and specialty engineering plastics that serve multiple end-use industries.
Market growth in Malaysia’s polymer sector has been consistently robust, driven by increasing demand from packaging, automotive, construction, and electronics industries. The country’s polymer manufacturing capabilities have expanded significantly over the past decade, with production capacity growth averaging approximately 6.2% annually. This growth trajectory reflects Malaysia’s commitment to developing its downstream petrochemical industry and reducing dependence on raw material exports.
Government initiatives and favorable policies have played a crucial role in attracting foreign investment and promoting technological advancement within the polymer industry. The establishment of specialized industrial zones and the implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies have enhanced Malaysia’s competitiveness in the global polymer market, positioning the country as an attractive destination for polymer manufacturing and processing operations.
The Malaysia polymer industry market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of polymer production, processing, and distribution activities within Malaysia’s borders. This market encompasses the manufacture of various synthetic and natural polymers, including thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and specialty polymer compounds used across diverse industrial applications. Polymer manufacturing in Malaysia involves both upstream production of basic polymer resins and downstream processing into finished products for domestic consumption and export markets.
Industry scope extends beyond traditional polymer production to include advanced polymer processing technologies, recycling operations, and the development of bio-based and sustainable polymer alternatives. The market serves as a critical link in global supply chains, providing polymer materials to manufacturers across Asia-Pacific and beyond. Malaysia’s polymer industry leverages the country’s abundant natural gas resources and established petrochemical infrastructure to produce cost-effective polymer solutions.
Strategic importance of the polymer industry to Malaysia’s economy cannot be overstated, as it contributes significantly to industrial output, employment generation, and export revenues. The sector’s integration with other manufacturing industries creates multiplier effects that enhance overall economic growth and industrial competitiveness.
Malaysia’s polymer industry has emerged as a vital component of the country’s industrial landscape, demonstrating remarkable resilience and growth potential despite global economic uncertainties. The sector benefits from Malaysia’s strategic geographical location, well-developed infrastructure, and government support for industrial development. Production efficiency improvements have resulted in approximately 15% cost reduction over the past five years, enhancing the competitiveness of Malaysian polymer products in international markets.
Key market drivers include increasing demand from end-use industries, technological advancement in polymer processing, and growing emphasis on sustainable polymer solutions. The automotive and packaging sectors represent the largest consumers of polymer products in Malaysia, accounting for a significant portion of domestic demand. Export performance has been particularly strong, with Malaysian polymer products gaining market share in key regional markets.
Investment trends indicate continued confidence in Malaysia’s polymer industry, with both domestic and international companies expanding their manufacturing capabilities. The integration of digital technologies and automation has improved operational efficiency and product quality, supporting the industry’s long-term growth prospects. Sustainability initiatives are becoming increasingly important, with companies investing in recycling technologies and bio-based polymer development.
Market dynamics in Malaysia’s polymer industry reveal several critical insights that shape the sector’s development trajectory. The industry’s strong foundation in petrochemical feedstock availability provides a competitive advantage in polymer production costs, enabling Malaysian manufacturers to compete effectively in regional and global markets.
Market positioning strategies focus on leveraging Malaysia’s cost advantages while building capabilities in high-value polymer products. The industry’s evolution toward more sophisticated polymer solutions reflects the country’s broader economic transformation and industrial upgrading initiatives.
Primary growth drivers propelling Malaysia’s polymer industry forward include robust demand from key end-use sectors and favorable economic conditions. The packaging industry, which consumes approximately 35% of polymer production, continues to expand due to e-commerce growth and changing consumer preferences. Automotive sector demand has been particularly strong, driven by Malaysia’s position as a regional automotive manufacturing hub and increasing use of lightweight polymer components.
Infrastructure development across Malaysia and neighboring countries has created substantial demand for construction-grade polymers, including pipes, fittings, and building materials. The electronics and electrical industry, a significant contributor to Malaysia’s manufacturing sector, requires specialized polymer materials for components and housings, driving demand for engineering plastics and high-performance polymers.
Government support through various incentive programs and industrial development policies has encouraged investment in polymer manufacturing facilities. The establishment of specialized industrial parks and the promotion of downstream petrochemical activities have created an enabling environment for industry growth. Regional trade agreements and Malaysia’s participation in global supply chains have opened new market opportunities for polymer exports.
Technological advancement in polymer processing and the development of new polymer grades have expanded application possibilities, creating new market segments and driving industry growth. The increasing focus on sustainable packaging solutions and circular economy principles has spurred innovation in recyclable and bio-based polymer development.
Significant challenges facing Malaysia’s polymer industry include volatile raw material prices and intense competition from regional producers. Feedstock price fluctuations, particularly for petroleum-based raw materials, can significantly impact production costs and profit margins. The industry’s dependence on imported additives and specialty chemicals also creates vulnerability to supply chain disruptions and currency fluctuations.
Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, requiring substantial investments in emission control systems and waste management infrastructure. Compliance with international environmental standards, while necessary for market access, increases operational costs and complexity. Skilled labor shortage in specialized polymer processing and quality control functions poses challenges for industry expansion and technological advancement.
Competition from low-cost producers in other Asian countries puts pressure on Malaysian polymer manufacturers to continuously improve efficiency and reduce costs. The emergence of new production facilities in neighboring countries has intensified regional competition, particularly in commodity polymer segments. Trade tensions and protectionist policies in some markets have created uncertainties for export-oriented polymer manufacturers.
Infrastructure limitations in certain regions of Malaysia can constrain industry expansion and increase logistics costs. The need for continuous investment in technology upgrades and equipment modernization requires significant capital commitments that may strain smaller industry players.
Emerging opportunities in Malaysia’s polymer industry are driven by evolving market demands and technological innovations. The growing emphasis on sustainable packaging solutions presents significant opportunities for companies developing biodegradable and recyclable polymer products. Circular economy initiatives are creating demand for advanced recycling technologies and recycled polymer content, opening new business models and revenue streams.
Specialty polymer segments offer attractive growth prospects, particularly in high-performance applications for aerospace, medical devices, and advanced electronics. The development of smart polymers and functional materials for emerging technologies presents opportunities for value-added product development. Bio-based polymers represent a rapidly growing segment with strong potential for Malaysian companies leveraging the country’s agricultural resources.
Regional market expansion opportunities exist in emerging economies across Southeast Asia and beyond, where infrastructure development and industrialization are driving polymer demand. The Belt and Road Initiative and other regional development programs create potential for Malaysian polymer companies to participate in large-scale infrastructure projects. Digital transformation opportunities include the implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies to improve operational efficiency and product customization capabilities.
Strategic partnerships with international technology providers and end-users can facilitate access to advanced technologies and new markets. The development of integrated polymer value chains, from raw materials to finished products, offers opportunities for vertical integration and improved margins.
Dynamic market forces shaping Malaysia’s polymer industry reflect the complex interplay of global trends, regional developments, and local factors. Supply chain resilience has become a critical focus following recent global disruptions, with companies investing in diversified sourcing strategies and local supplier development. The industry’s response to these challenges has demonstrated remarkable adaptability and innovation capacity.
Technological evolution continues to transform polymer manufacturing processes, with automation and digitalization improving production efficiency by approximately 12% annually. Advanced process control systems and predictive maintenance technologies are reducing downtime and improving product quality consistency. Sustainability pressures from customers and regulators are driving innovation in eco-friendly polymer solutions and circular economy practices.
Market consolidation trends are evident as larger companies acquire smaller players to achieve economies of scale and expand product portfolios. This consolidation is creating more integrated and efficient industry structures while maintaining competitive dynamics. Customer relationship evolution toward longer-term partnerships and collaborative product development is changing traditional supplier-buyer dynamics.
Regulatory landscape changes continue to influence industry operations, with new standards for product safety, environmental impact, and quality assurance. Companies are investing in compliance systems and sustainable practices to meet evolving regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
Comprehensive research approach employed in analyzing Malaysia’s polymer industry market combines primary and secondary research methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings. Primary research involves extensive interviews with industry executives, government officials, and market participants to gather firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, government publications, trade association data, and company financial statements to build a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. Data triangulation methods are used to validate findings from multiple sources and ensure consistency of information. Statistical analysis techniques are applied to identify trends, correlations, and market patterns.
Market segmentation analysis involves detailed examination of different polymer types, applications, and end-use industries to understand specific market dynamics and growth drivers. Competitive landscape assessment includes analysis of major market players, their strategies, and market positioning. Regional analysis considers variations in market conditions, regulatory environments, and growth prospects across different areas of Malaysia.
Forecasting methodologies combine quantitative modeling with qualitative insights to project future market developments. Expert opinions and industry feedback are incorporated to validate research findings and ensure practical relevance of conclusions.
Regional distribution of Malaysia’s polymer industry reveals distinct patterns of concentration and specialization across different states and economic zones. Peninsular Malaysia hosts approximately 75% of polymer production capacity, with major facilities concentrated in Johor, Selangor, and Perak states. These regions benefit from proximity to ports, established infrastructure, and skilled labor availability.
Johor state serves as a major polymer manufacturing hub, leveraging its strategic location near Singapore and well-developed industrial infrastructure. The state’s polymer industry focuses on both commodity and specialty products, serving domestic and export markets. Selangor’s polymer sector is characterized by a strong presence of multinational companies and advanced manufacturing facilities producing high-value polymer products.
East Malaysia regions, particularly Sarawak and Sabah, are emerging as important polymer production centers due to abundant natural gas resources and government incentives for industrial development. Sarawak’s polymer industry benefits from integrated petrochemical complexes and access to low-cost feedstock, making it competitive in commodity polymer production.
Industrial park development across different regions has created specialized clusters for polymer manufacturing and processing. These parks offer integrated infrastructure, utilities, and services that support efficient polymer industry operations. Logistics connectivity through ports, highways, and rail networks varies across regions, influencing location decisions for polymer manufacturing facilities.
Competitive environment in Malaysia’s polymer industry features a mix of large multinational corporations, regional players, and specialized local companies. Market leadership is distributed among several key players who have established strong positions through strategic investments, technological capabilities, and market reach.
Competitive strategies focus on product differentiation, cost optimization, and market expansion. Companies are investing in research and development to develop innovative polymer solutions and maintain technological leadership. Strategic partnerships and joint ventures are common approaches for accessing new technologies and markets while sharing investment risks.
Market positioning varies among competitors, with some focusing on high-volume commodity products while others specialize in niche, high-value applications. The competitive landscape continues to evolve as companies adapt to changing market conditions and customer requirements.
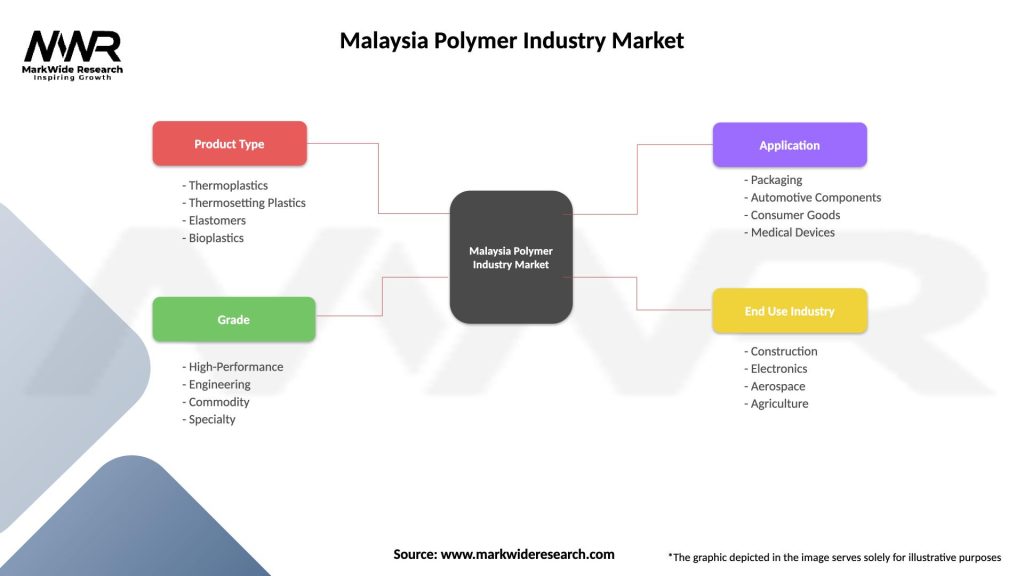
Market segmentation of Malaysia’s polymer industry reveals diverse product categories and application areas that drive industry growth and development. By polymer type, the market encompasses thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and specialty polymers, each serving distinct application requirements and market segments.
By Application:
By End-Use Industry:
Geographic segmentation considers domestic consumption patterns and export market destinations, with significant variations in product mix and growth rates across different regions and countries.
Thermoplastics category dominates Malaysia’s polymer industry, accounting for the majority of production volume and revenue. Polyethylene products represent the largest segment within thermoplastics, driven by strong demand from packaging and consumer goods industries. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) production has expanded significantly to meet growing regional demand.
Polypropylene segment has shown robust growth, particularly in automotive and packaging applications where its lightweight properties and chemical resistance provide advantages. Engineering plastics category, while smaller in volume, generates higher margins and serves specialized applications in electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Specialty polymers represent a growing category with strong potential for value creation. These include high-performance polymers, bio-based materials, and functional polymers designed for specific applications. Market demand for specialty polymers is growing at approximately 8.5% annually, driven by technological advancement and application innovation.
Recycled polymers category is emerging as an important segment, supported by sustainability initiatives and circular economy principles. Companies are investing in advanced recycling technologies to produce high-quality recycled polymer products that meet stringent performance requirements. Bio-based polymers represent another growing category, leveraging Malaysia’s agricultural resources and biotechnology capabilities.
Industry participants in Malaysia’s polymer market enjoy numerous advantages stemming from the country’s strategic position and supportive business environment. Cost competitiveness remains a key benefit, with access to competitively priced feedstock and efficient manufacturing infrastructure enabling attractive production economics.
Strategic location benefits include proximity to major Asian markets and established trade relationships that facilitate export market access. Malaysia’s membership in regional trade agreements provides preferential market access and reduces trade barriers for polymer products. Infrastructure advantages encompass well-developed ports, transportation networks, and industrial utilities that support efficient operations.
Government support through various incentive programs, tax benefits, and industrial development policies creates favorable conditions for investment and expansion. Skilled workforce availability and established technical education programs provide access to qualified personnel for polymer industry operations.
Stakeholder benefits extend to customers who gain access to reliable polymer supply, competitive pricing, and technical support services. Supply chain integration opportunities allow for closer collaboration between polymer producers and end-users, resulting in improved product development and market responsiveness.
Environmental benefits include access to cleaner production technologies and sustainable polymer solutions that help stakeholders meet environmental objectives and regulatory requirements.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainability transformation represents the most significant trend reshaping Malaysia’s polymer industry, with companies increasingly focusing on circular economy principles and environmental responsibility. Recycling technology advancement has enabled the production of high-quality recycled polymers that meet stringent performance requirements, with recycled content adoption growing at approximately 18% annually.
Digital transformation is revolutionizing polymer manufacturing operations through the implementation of smart manufacturing technologies, predictive maintenance systems, and data analytics platforms. These technologies are improving operational efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling more responsive customer service. Automation adoption continues to accelerate, with companies investing in robotic systems and automated quality control processes.
Product innovation trends focus on developing high-performance polymers for emerging applications in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and advanced electronics. Bio-based polymer development is gaining momentum, leveraging Malaysia’s agricultural resources and biotechnology capabilities to create sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polymers.
Supply chain localization has become a priority following recent global disruptions, with companies investing in regional supplier networks and reducing dependence on distant supply sources. Customer collaboration is intensifying, with polymer producers working closely with end-users to develop customized solutions and improve application performance.
Recent industry developments in Malaysia’s polymer sector reflect the dynamic nature of the market and ongoing transformation initiatives. Capacity expansion projects by major producers have added significant production capability, with new facilities incorporating advanced technologies and environmental controls. These expansions are strategically positioned to serve growing regional demand and export opportunities.
Technology partnerships between Malaysian companies and international technology providers have facilitated knowledge transfer and capability building in advanced polymer processing. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that such partnerships have contributed to approximately 25% improvement in production efficiency across participating companies.
Sustainability initiatives have gained prominence, with several companies launching comprehensive programs to reduce environmental impact and develop sustainable polymer solutions. These initiatives include investments in renewable energy, waste reduction programs, and the development of biodegradable polymer products.
Market consolidation activities have reshaped the competitive landscape, with strategic acquisitions and mergers creating larger, more integrated companies capable of serving diverse market segments. Government policy updates have introduced new incentives for sustainable manufacturing and technology adoption, supporting industry transformation efforts.
International expansion by Malaysian polymer companies has accelerated, with several firms establishing operations in neighboring countries to serve regional markets more effectively and reduce logistics costs.
Strategic recommendations for Malaysia’s polymer industry focus on enhancing competitiveness and sustainability while capitalizing on emerging market opportunities. Technology investment should prioritize automation, digitalization, and advanced process control systems to improve efficiency and product quality. Companies should consider partnerships with technology providers to access cutting-edge innovations without bearing full development costs.
Sustainability integration should become a core business strategy rather than a compliance requirement, with companies investing in circular economy solutions and bio-based polymer development. Market diversification efforts should focus on reducing dependence on traditional sectors by developing capabilities in high-growth applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, and advanced electronics.
Supply chain resilience improvements should include diversification of raw material sources, development of local supplier networks, and implementation of risk management systems. Talent development programs should focus on building capabilities in emerging technologies, sustainability practices, and digital manufacturing systems.
Regional expansion strategies should leverage Malaysia’s strategic position and trade relationships to access growing markets in Southeast Asia and beyond. Innovation investment should prioritize customer-centric product development and collaborative research initiatives that address specific market needs and application challenges.
Future prospects for Malaysia’s polymer industry appear promising, supported by strong fundamentals and favorable market trends. Growth trajectory is expected to continue, driven by expanding end-use industries, technological advancement, and increasing regional demand. The industry’s evolution toward higher-value products and sustainable solutions positions Malaysia competitively for long-term success.
Sustainability transformation will likely accelerate, with companies increasingly adopting circular economy principles and developing eco-friendly polymer solutions. MWR projections suggest that sustainable polymer products could account for approximately 30% of total production within the next decade, reflecting growing market demand and regulatory requirements.
Technology integration will continue to reshape manufacturing operations, with Industry 4.0 technologies becoming standard practice across the industry. Digital transformation initiatives are expected to improve operational efficiency by an additional 20% over the next five years, enhancing competitiveness and customer service capabilities.
Market expansion opportunities in emerging economies and new application areas will drive industry growth and diversification. The development of specialty polymer capabilities and bio-based alternatives will create new revenue streams and competitive advantages. Regional integration through trade agreements and economic partnerships will facilitate market access and business expansion.
Malaysia’s polymer industry stands at a pivotal juncture, with strong fundamentals and promising growth prospects supported by strategic advantages and market opportunities. The industry’s evolution from commodity production toward high-value specialty products and sustainable solutions reflects broader economic transformation and technological advancement. Strategic positioning in the global polymer value chain continues to strengthen through investments in technology, sustainability, and market development.
Key success factors for the industry’s future development include continued investment in technology and innovation, sustainable manufacturing practices, and strategic market expansion. The industry’s ability to adapt to changing market conditions and customer requirements while maintaining cost competitiveness will determine long-term success. Collaboration between industry players, government agencies, and international partners will be essential for addressing challenges and capitalizing on opportunities.
Long-term outlook remains positive, with the Malaysia polymer industry market well-positioned to benefit from regional economic growth, technological advancement, and increasing demand for sustainable polymer solutions. The industry’s commitment to innovation, sustainability, and operational excellence provides a solid foundation for continued growth and development in the years ahead.
What is Polymer?
Polymer refers to a large molecule composed of repeating structural units, typically connected by covalent chemical bonds. In the context of the Malaysia Polymer Industry, these materials are widely used in various applications such as packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
What are the key players in the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market?
Key players in the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market include companies like Petronas Chemicals Group Berhad, Lotte Chemical Titan Holding Berhad, and BASF Petronas Chemicals among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market?
The growth of the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market is driven by increasing demand for lightweight materials in automotive manufacturing, the expansion of the packaging sector, and advancements in polymer technology that enhance product performance.
What challenges does the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market face?
The Malaysia Polymer Industry Market faces challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices, environmental regulations regarding plastic waste, and competition from alternative materials like bioplastics.
What opportunities exist in the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market?
Opportunities in the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market include the development of sustainable polymers, growth in the electronics sector requiring advanced materials, and increasing investments in research and development for innovative applications.
What trends are shaping the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market?
Trends shaping the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market include a shift towards biodegradable polymers, the integration of smart materials in consumer products, and the increasing use of recycled materials in production processes.
Malaysia Polymer Industry Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Thermoplastics, Thermosetting Plastics, Elastomers, Bioplastics |
| Grade | High-Performance, Engineering, Commodity, Specialty |
| Application | Packaging, Automotive Components, Consumer Goods, Medical Devices |
| End Use Industry | Construction, Electronics, Aerospace, Agriculture |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Malaysia Polymer Industry Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at