444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Malaysia digital transformation market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape that encompasses the comprehensive adoption of digital technologies across various sectors of the Malaysian economy. This transformation initiative is fundamentally reshaping how businesses operate, deliver services, and engage with customers throughout the nation. Digital transformation in Malaysia involves the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and automation solutions across government agencies, private enterprises, and public institutions.
Market dynamics indicate that Malaysia is experiencing unprecedented growth in digital adoption, driven by government initiatives like the Malaysia Digital Economy Blueprint and the MyDIGITAL initiative. The market encompasses various segments including enterprise digital transformation, government digitalization, healthcare modernization, financial services innovation, and educational technology advancement. Growth projections suggest the market is expanding at a robust CAGR of 12.8%, positioning Malaysia as a leading digital economy in Southeast Asia.
Key sectors driving this transformation include banking and financial services, manufacturing, retail and e-commerce, healthcare, education, and government services. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is particularly prominent in manufacturing, while the financial sector leads in adopting fintech solutions and digital banking platforms. Cloud adoption rates have reached approximately 78% among Malaysian enterprises, indicating strong momentum in digital infrastructure modernization.
The Malaysia digital transformation market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of technologies, services, and solutions that enable Malaysian organizations to digitize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and create new business models through digital innovation. This market encompasses the strategic adoption of digital technologies to fundamentally change how value is created and delivered across various sectors of the Malaysian economy.
Digital transformation in the Malaysian context involves more than just technology adoption; it represents a cultural and operational shift toward data-driven decision making, automated processes, and digitally-enabled customer interactions. The market includes software solutions, hardware infrastructure, professional services, and consulting offerings that support organizations in their digital journey. Core components include cloud computing platforms, enterprise resource planning systems, customer relationship management solutions, data analytics tools, cybersecurity frameworks, and mobile applications.
Strategic significance of this market extends beyond individual organizational benefits to encompass national economic competitiveness, innovation capacity, and social development objectives. The transformation supports Malaysia’s vision of becoming a high-income nation through digital economy growth and technological advancement.
Malaysia’s digital transformation journey has accelerated significantly, positioning the nation as a regional leader in digital adoption and innovation. The market demonstrates strong growth momentum across multiple sectors, with government support and private sector investment driving comprehensive modernization initiatives. Key performance indicators reveal that digital transformation investments have increased by 45% year-over-year, reflecting the strategic priority placed on technological advancement.
Market segmentation reveals diverse opportunities across enterprise solutions, government digitalization, and consumer-facing applications. The banking and financial services sector leads in digital maturity, followed by telecommunications, retail, and manufacturing industries. Government initiatives such as the National Digital Identity program and digital government services have created substantial market opportunities for technology providers and system integrators.
Competitive landscape features a mix of global technology giants, regional solution providers, and local system integrators working collaboratively to deliver comprehensive digital transformation solutions. The market benefits from strong telecommunications infrastructure, supportive regulatory frameworks, and a growing pool of digital talent. Future projections indicate sustained growth driven by emerging technologies, increased digital literacy, and expanding e-commerce activities.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical factors driving Malaysia’s digital transformation success:
Primary market drivers propelling Malaysia’s digital transformation include comprehensive government support through strategic initiatives and policy frameworks. The MyDIGITAL initiative serves as a cornerstone driver, establishing clear objectives for digital economy development and providing structured pathways for technology adoption across sectors. Government digitalization efforts, including e-government services and digital identity programs, create substantial demand for digital transformation solutions and services.
Economic competitiveness requirements drive organizations to adopt digital technologies to remain viable in increasingly competitive markets. Malaysian businesses recognize that digital transformation is essential for operational efficiency, cost reduction, and market expansion. The need to compete with regional and global players motivates comprehensive technology adoption and process modernization initiatives.
Consumer behavior changes significantly influence market dynamics, with Malaysian consumers increasingly expecting digital-first experiences across all touchpoints. The rise of e-commerce, digital banking, and online services creates pressure on organizations to digitize their customer-facing operations. Mobile-first preferences among Malaysian consumers drive demand for mobile-optimized digital solutions and services.
Technological advancement and decreasing costs of digital technologies make transformation initiatives more accessible to organizations of all sizes. Cloud computing adoption, artificial intelligence integration, and automation solutions become increasingly affordable and practical for Malaysian businesses. The availability of Software-as-a-Service solutions reduces implementation barriers and enables rapid digital transformation adoption.
Implementation challenges represent significant market restraints, particularly for small and medium enterprises that may lack the technical expertise and financial resources required for comprehensive digital transformation. Many organizations struggle with legacy system integration, data migration complexities, and the need for substantial organizational change management. Technical complexity of modern digital solutions can overwhelm organizations without adequate IT capabilities or external support.
Cybersecurity concerns create hesitation among organizations considering digital transformation initiatives. The increasing frequency of cyber attacks and data breaches makes businesses cautious about expanding their digital footprint. Compliance requirements and regulatory considerations add complexity to digital transformation projects, particularly in highly regulated sectors such as banking and healthcare.
Skills shortage in digital technologies constrains market growth, as organizations struggle to find qualified professionals capable of implementing and managing digital transformation initiatives. The rapid pace of technological change creates ongoing challenges in maintaining current skills and knowledge among existing workforce members. Training and development costs associated with building digital capabilities represent significant investments for many organizations.
Cultural resistance to change within organizations can slow digital transformation adoption, particularly in traditional industries or established companies with long-standing operational practices. Employee concerns about job displacement due to automation and digital processes create internal challenges that must be addressed through comprehensive change management strategies.
Emerging technology integration presents substantial opportunities for market expansion, particularly in areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things applications. Malaysian organizations are increasingly interested in leveraging these technologies to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, and create new revenue streams. 5G network deployment creates opportunities for advanced digital applications and services that were previously not feasible.
Sector-specific digitalization offers targeted opportunities for solution providers to develop specialized offerings for industries such as agriculture, tourism, and logistics. The unique requirements of different sectors create demand for customized digital transformation solutions that address specific operational challenges and regulatory requirements. Smart city initiatives across Malaysian urban centers create opportunities for comprehensive digital infrastructure development and management solutions.
Regional expansion opportunities exist for Malaysian digital transformation providers to serve neighboring Southeast Asian markets, leveraging Malaysia’s advanced digital infrastructure and expertise. The country’s strategic location and established business relationships throughout the region position it well for cross-border digital services expansion.
Sustainability integration creates opportunities for digital solutions that support environmental objectives and corporate social responsibility goals. Organizations increasingly seek digital transformation solutions that contribute to sustainability targets while improving operational efficiency. Green technology adoption and carbon footprint reduction initiatives drive demand for environmentally conscious digital solutions.
Market dynamics in Malaysia’s digital transformation landscape are characterized by rapid technological evolution, changing customer expectations, and increasing competitive pressures. The interplay between government initiatives, private sector investment, and consumer demand creates a complex but favorable environment for digital transformation growth. Technology adoption rates continue to accelerate, with organizations recognizing the strategic importance of digital capabilities for long-term success.
Competitive dynamics involve collaboration between global technology providers, local system integrators, and specialized solution developers. This collaborative approach enables comprehensive digital transformation solutions that combine international expertise with local market knowledge. Partnership strategies are becoming increasingly important as organizations seek integrated solutions rather than point solutions.
Investment patterns show increasing allocation toward digital transformation initiatives, with organizations prioritizing technology investments over traditional capital expenditures. The shift toward operational expenditure models through cloud services and subscription-based solutions changes how organizations approach digital transformation funding. Return on investment expectations are driving more strategic and measured approaches to digital transformation implementation.
Regulatory evolution continues to shape market dynamics, with government agencies developing frameworks that support digital transformation while ensuring security, privacy, and compliance requirements. The balance between innovation enablement and risk management influences how organizations approach digital transformation initiatives and solution selection.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing Malaysia’s digital transformation market incorporates multiple data collection and analysis approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings. Primary research activities include structured interviews with industry executives, technology providers, government officials, and end-user organizations across various sectors. Survey methodologies capture quantitative data on adoption rates, investment levels, and market trends from representative samples of Malaysian organizations.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, company financial statements, and regulatory documents to understand market structure and dynamics. MarkWide Research analysts utilize proprietary databases and industry connections to gather comprehensive market intelligence and validate findings through multiple sources.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing information from multiple sources, conducting follow-up interviews to clarify findings, and applying statistical analysis techniques to ensure data accuracy. Market sizing and forecasting methodologies incorporate both bottom-up and top-down approaches to provide comprehensive market estimates and projections.
Analytical frameworks applied include Porter’s Five Forces analysis, SWOT assessment, and market segmentation analysis to provide strategic insights into competitive dynamics and market opportunities. Trend analysis and scenario planning techniques help identify future market developments and potential disruptions that may impact the digital transformation landscape.
Kuala Lumpur metropolitan area leads Malaysia’s digital transformation adoption, accounting for approximately 42% of total market activity. The capital region benefits from concentrated corporate headquarters, government agencies, and technology providers, creating a dense ecosystem of digital transformation initiatives. Financial services digitalization is particularly prominent in Kuala Lumpur, with major banks and fintech companies driving innovation in digital banking and payment solutions.
Selangor state represents the second-largest regional market, driven by manufacturing sector digitalization and the presence of major industrial zones. The state’s proximity to Kuala Lumpur and established manufacturing base create strong demand for Industry 4.0 solutions and supply chain digitalization. Technology parks and innovation hubs in Selangor contribute to the development of digital transformation capabilities and expertise.
Penang region demonstrates strong growth in digital transformation, particularly in electronics manufacturing and services sectors. The state’s established technology ecosystem and skilled workforce support advanced digital transformation initiatives. Government digitalization efforts in Penang serve as models for other states, with comprehensive e-government services and digital citizen engagement platforms.
Johor state benefits from its strategic location near Singapore and growing manufacturing sector, with cross-border digital integration creating unique opportunities for digital transformation solutions. The state’s focus on logistics and transportation digitalization supports regional trade and commerce activities. Smart city initiatives in Johor Bahru and Iskandar Malaysia drive demand for comprehensive urban digitalization solutions.
Competitive landscape in Malaysia’s digital transformation market features a diverse mix of global technology leaders, regional solution providers, and local system integrators. The market structure promotes collaboration and partnership approaches rather than purely competitive dynamics, enabling comprehensive solution delivery.
Partnership strategies are prevalent throughout the competitive landscape, with global providers collaborating with local partners to deliver culturally appropriate and regulatory-compliant solutions. This collaborative approach enables comprehensive digital transformation offerings that combine international expertise with local market knowledge and support capabilities.
Market segmentation reveals distinct categories based on technology type, industry vertical, organization size, and deployment model. Each segment demonstrates unique characteristics, growth patterns, and requirements that influence solution development and go-to-market strategies.
By Technology Type:
By Industry Vertical:
Enterprise Digital Transformation category represents the largest segment, driven by organizations seeking comprehensive modernization of their operations, customer engagement, and business models. This category includes enterprise resource planning systems, customer relationship management platforms, and business intelligence solutions. Adoption rates in this category have reached 68% among large Malaysian enterprises, indicating strong market penetration and continued growth potential.
Government Digitalization category demonstrates significant growth momentum, supported by national digital transformation initiatives and public sector modernization efforts. This category encompasses e-government services, digital identity systems, and citizen engagement platforms. Government investment in digital transformation has increased substantially, creating opportunities for solution providers and system integrators.
Industry-Specific Solutions category addresses unique requirements of different sectors, including healthcare digitalization, manufacturing automation, and financial services innovation. These specialized solutions often require deep industry knowledge and regulatory compliance capabilities. Customization requirements in this category create opportunities for local solution providers with sector expertise.
Small Business Digital Solutions category focuses on accessible and affordable digital transformation options for small and medium enterprises. This category includes cloud-based business applications, e-commerce platforms, and digital marketing solutions. Government support programs for SME digitalization are driving growth in this category, with simplified implementation approaches and subsidized access to digital technologies.
Technology providers benefit from Malaysia’s digital transformation market through access to a growing customer base, supportive government policies, and opportunities for regional expansion. The market provides platforms for innovation, partnership development, and solution refinement based on real-world implementation experiences. Revenue growth opportunities exist across multiple sectors and customer segments, with recurring revenue models becoming increasingly prevalent.
System integrators gain advantages through increased demand for implementation services, ongoing support requirements, and opportunities to develop specialized expertise in emerging technologies. The complexity of digital transformation initiatives creates sustained demand for professional services and consulting capabilities. Partnership opportunities with global technology providers enable access to advanced solutions and expanded market reach.
End-user organizations realize significant benefits including operational efficiency improvements, enhanced customer experiences, and new revenue generation opportunities. Digital transformation enables Malaysian organizations to compete more effectively in global markets and respond rapidly to changing business conditions. Cost reduction potential through automation and process optimization provides compelling return on investment justification.
Government agencies achieve policy objectives related to economic development, innovation promotion, and public service improvement through digital transformation initiatives. The development of digital capabilities supports national competitiveness and social development goals. Public-private collaboration opportunities enable efficient resource utilization and accelerated implementation of digital government services.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Cloud-first strategies are becoming predominant among Malaysian organizations, with businesses prioritizing cloud-based solutions for their digital transformation initiatives. This trend reflects the recognition that cloud computing provides scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness required for successful digital transformation. Multi-cloud adoption is increasing as organizations seek to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance across different workloads and applications.
Artificial intelligence integration represents a major trend, with Malaysian organizations increasingly incorporating AI capabilities into their business processes and customer interactions. Machine learning applications for predictive analytics, chatbots for customer service, and automated decision-making systems are becoming standard components of digital transformation initiatives. AI adoption rates have grown by 38% annually among Malaysian enterprises.
Mobile-first approaches dominate digital transformation strategies, reflecting Malaysian consumers’ preference for mobile device interactions and the need for businesses to optimize all digital touchpoints for mobile access. This trend drives demand for responsive web design, mobile applications, and mobile-optimized business processes. Mobile commerce growth continues to accelerate, influencing retail and service sector digitalization strategies.
Sustainability integration is emerging as a key trend, with organizations seeking digital transformation solutions that support environmental objectives and corporate social responsibility goals. Green technology adoption, energy-efficient data centers, and carbon footprint reduction through digitalization are becoming important considerations in solution selection and implementation planning.
Government digital identity initiatives have reached significant milestones, with the national digital identity system enabling seamless access to government services and supporting private sector digital transformation. This development creates opportunities for identity verification solutions and integrated service platforms across multiple sectors. Digital identity adoption has exceeded 75% among eligible Malaysian citizens.
5G network deployment has accelerated across major urban centers, enabling advanced digital applications and services that require high-speed, low-latency connectivity. This infrastructure development supports Internet of Things implementations, augmented reality applications, and real-time analytics solutions. 5G coverage expansion creates new opportunities for innovative digital transformation applications.
Financial sector innovation continues with the introduction of digital banking licenses and expanded fintech regulations, creating opportunities for comprehensive financial services digitalization. Open banking initiatives and digital payment system enhancements support broader digital transformation across the economy. Digital payment adoption has reached 82% among Malaysian consumers.
Smart city projects in major urban centers have progressed significantly, with comprehensive digital infrastructure implementations supporting traffic management, waste management, and citizen services. These developments create templates for digital transformation approaches that can be replicated across other cities and regions. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that smart city initiatives are driving substantial demand for integrated digital solutions.
Strategic recommendations for organizations pursuing digital transformation in Malaysia emphasize the importance of comprehensive planning, stakeholder engagement, and phased implementation approaches. Organizations should prioritize initiatives that deliver immediate business value while building foundations for long-term digital capabilities. Change management strategies must address cultural and operational challenges to ensure successful transformation outcomes.
Technology selection should focus on scalable, interoperable solutions that can evolve with changing business requirements and technological advancements. Organizations should avoid point solutions in favor of integrated platforms that support multiple business functions and processes. Vendor evaluation should consider local support capabilities, regulatory compliance, and long-term partnership potential.
Investment prioritization should balance immediate operational improvements with strategic capabilities that support future growth and competitiveness. Organizations should consider total cost of ownership, including implementation, training, and ongoing support costs when evaluating digital transformation investments. Return on investment measurement should include both quantitative and qualitative benefits to capture the full value of digital transformation initiatives.
Partnership strategies should leverage the collaborative ecosystem of technology providers, system integrators, and consulting firms available in Malaysia. Organizations should seek partners with proven experience in their industry sector and demonstrated capability in emerging technologies. MWR analysis suggests that successful digital transformation initiatives typically involve multiple partner relationships and collaborative implementation approaches.
Future market prospects for Malaysia’s digital transformation landscape appear highly favorable, with continued government support, increasing private sector investment, and growing consumer demand driving sustained growth. The market is expected to maintain strong momentum through the next five years, with projected growth rates of 11.5% annually across most segments and sectors.
Emerging technology adoption will accelerate, particularly in areas such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and advanced analytics. These technologies will become mainstream components of digital transformation initiatives, creating new market opportunities and competitive advantages for early adopters. Integration complexity will drive demand for specialized implementation services and ongoing support capabilities.
Sector expansion will continue as digital transformation spreads to traditional industries that have been slower to adopt digital technologies. Agriculture, tourism, and logistics sectors present significant growth opportunities as they recognize the competitive advantages of digital transformation. Government digitalization will expand to encompass more comprehensive citizen services and inter-agency integration.
Regional leadership positioning will strengthen as Malaysia leverages its digital transformation success to serve broader Southeast Asian markets. The country’s advanced digital infrastructure, skilled workforce, and supportive regulatory environment position it well for regional digital services expansion. Cross-border digital integration will create new opportunities for Malaysian digital transformation providers to serve international markets and support regional economic integration initiatives.
Malaysia’s digital transformation market represents a compelling growth opportunity characterized by strong government support, advanced infrastructure, and increasing organizational recognition of digital transformation’s strategic importance. The market demonstrates robust fundamentals with diverse opportunities across multiple sectors, technology categories, and organizational sizes. Sustained growth momentum is supported by comprehensive policy frameworks, substantial investment commitments, and evolving consumer expectations that drive continuous innovation and adoption.
Strategic positioning of Malaysia as a regional digital hub creates additional opportunities for market expansion and international collaboration. The combination of local market growth and regional expansion potential provides multiple pathways for success for technology providers, system integrators, and consulting firms operating in the digital transformation space. Collaborative ecosystem approaches that leverage partnerships and shared expertise will be essential for capturing the full potential of this dynamic market.
Long-term prospects remain highly favorable, with digital transformation becoming increasingly central to Malaysia’s economic development strategy and organizational competitiveness requirements. The market’s evolution toward more sophisticated, integrated solutions creates opportunities for innovation and differentiation while supporting the nation’s broader digital economy objectives and regional leadership aspirations in Southeast Asia.
What is Digital Transformation?
Digital Transformation refers to the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value to customers. It encompasses various aspects such as process automation, data analytics, and customer engagement strategies.
What are the key players in the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market?
Key players in the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market include companies like Telekom Malaysia, Digi Telecommunications, and Maxis Berhad, which are actively involved in providing digital solutions and services to enhance business operations, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market?
The main drivers of the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market include the increasing demand for improved operational efficiency, the rise of cloud computing, and the growing need for enhanced customer experiences. These factors are pushing businesses to adopt digital technologies.
What challenges does the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market face?
Challenges in the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market include resistance to change within organizations, a shortage of skilled workforce, and concerns over data security and privacy. These issues can hinder the effective implementation of digital initiatives.
What opportunities exist in the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market?
Opportunities in the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market include the potential for small and medium enterprises to leverage digital tools for growth, the expansion of e-commerce platforms, and the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies.
What trends are shaping the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market?
Trends shaping the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market include the rise of remote work solutions, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and the focus on data-driven decision-making. These trends are influencing how businesses operate and interact with customers.
Malaysia Digital Transformation Market
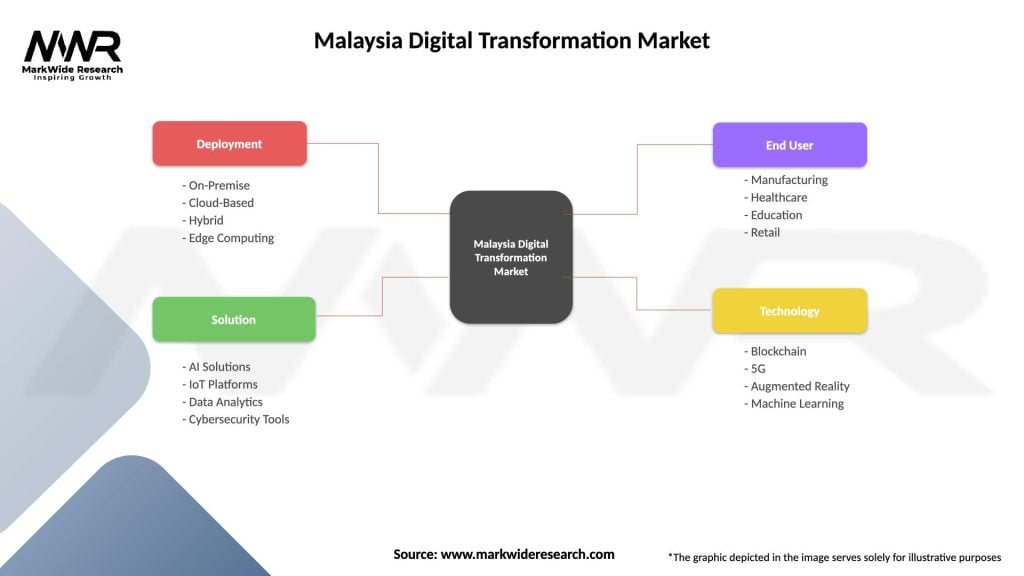
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Deployment | On-Premise, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Edge Computing |
| Solution | AI Solutions, IoT Platforms, Data Analytics, Cybersecurity Tools |
| End User | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Education, Retail |
| Technology | Blockchain, 5G, Augmented Reality, Machine Learning |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Malaysia Digital Transformation Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at