444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Malaysia data center cooling market represents a rapidly expanding sector driven by the country’s digital transformation initiatives and increasing demand for cloud computing services. Malaysia’s strategic position as a regional technology hub in Southeast Asia has attracted significant investments from global hyperscale data center operators, creating substantial demand for advanced cooling solutions. The market is experiencing robust growth with a projected CAGR of 8.2% over the forecast period, reflecting the critical importance of efficient thermal management in modern data center operations.
Government initiatives such as the Malaysia Digital Economy Blueprint and the National 4IR Policy have accelerated digitalization across various sectors, driving increased data generation and storage requirements. This digital ecosystem expansion has positioned Malaysia as an attractive destination for data center investments, with Cyberjaya and Johor emerging as key data center hubs. The tropical climate presents unique challenges for data center cooling, making advanced cooling technologies essential for maintaining optimal operational efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Market dynamics indicate strong adoption of innovative cooling technologies including liquid cooling, free cooling systems, and AI-driven thermal management solutions. The increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency has prompted data center operators to invest in next-generation cooling infrastructure that can deliver improved PUE ratios while supporting high-density computing environments. MarkWide Research analysis suggests that the market is witnessing significant technological advancement with the integration of IoT-enabled cooling systems and predictive maintenance capabilities.
The Malaysia data center cooling market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of thermal management solutions, technologies, and services specifically designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures within data center facilities across Malaysia. This market encompasses various cooling methodologies including air-based cooling systems, liquid cooling solutions, evaporative cooling technologies, and hybrid cooling approaches that ensure reliable performance of critical IT infrastructure while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs.
Data center cooling involves the systematic removal of heat generated by servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and other IT hardware to prevent thermal damage and maintain consistent performance levels. In Malaysia’s tropical climate, effective cooling becomes particularly crucial due to high ambient temperatures and humidity levels that can significantly impact cooling efficiency and energy consumption patterns.
Malaysia’s data center cooling market is experiencing unprecedented growth driven by rapid digitalization, cloud adoption, and increasing data consumption across various industries. The market benefits from Malaysia’s strategic geographic location, stable political environment, and government support for digital infrastructure development. Key growth drivers include the expansion of hyperscale data centers, increasing adoption of edge computing, and growing demand for colocation services among enterprises seeking to modernize their IT infrastructure.
Technology trends shaping the market include the adoption of liquid cooling solutions for high-density computing environments, implementation of free cooling systems to leverage Malaysia’s climate conditions, and integration of artificial intelligence for predictive cooling management. The market is witnessing 65% adoption rate of precision air conditioning systems among enterprise data centers, while liquid cooling solutions are gaining traction with a 25% growth rate in deployment across hyperscale facilities.
Competitive landscape features a mix of global technology leaders and regional specialists offering comprehensive cooling solutions tailored to Malaysia’s unique environmental conditions. The market is characterized by increasing collaboration between cooling technology providers and data center operators to develop customized solutions that optimize energy efficiency while ensuring reliable thermal management performance.

Strategic market insights reveal several critical factors driving the Malaysia data center cooling market’s expansion and evolution:
Digital transformation acceleration across Malaysia’s economy serves as the primary catalyst for data center cooling market growth. The government’s commitment to becoming a digital nation by 2030 has spurred massive investments in digital infrastructure, creating substantial demand for data center facilities and associated cooling systems. Cloud adoption rates have increased by 40% annually among Malaysian enterprises, driving the need for scalable and efficient cooling solutions.
Foreign direct investment in Malaysia’s data center sector has reached unprecedented levels, with global hyperscale operators establishing regional hubs to serve Southeast Asian markets. This investment influx is creating demand for world-class cooling infrastructure capable of supporting high-density computing environments while maintaining optimal energy efficiency ratios. Hyperscale data centers require sophisticated cooling systems that can handle heat loads exceeding traditional enterprise facilities.
IoT proliferation and 5G deployment are generating massive amounts of data requiring processing and storage capabilities closer to end users. This trend is driving the development of edge data centers throughout Malaysia, creating new opportunities for compact and efficient cooling solutions. Edge computing adoption is expected to grow at a 35% CAGR, necessitating innovative cooling approaches for distributed computing environments.
Energy cost optimization remains a critical driver as cooling systems typically account for 30-40% of total data center energy consumption. Malaysian data center operators are increasingly investing in advanced cooling technologies that can significantly reduce operational expenses while maintaining reliable thermal management performance.
High initial capital investment requirements for advanced cooling systems present significant barriers for smaller data center operators and enterprises considering facility upgrades. The cost of implementing liquid cooling infrastructure or sophisticated air conditioning systems can be substantial, particularly for organizations with limited capital budgets or uncertain return on investment projections.
Technical complexity associated with modern cooling systems requires specialized expertise for design, installation, and maintenance. The shortage of qualified technicians and engineers familiar with advanced cooling technologies creates implementation challenges and increases operational risks for data center operators seeking to deploy next-generation thermal management solutions.
Climate-related challenges in Malaysia’s tropical environment can impact cooling system efficiency and reliability. High humidity levels, frequent temperature fluctuations, and seasonal weather patterns require cooling systems to operate under demanding conditions, potentially affecting performance consistency and maintenance requirements.
Regulatory compliance complexity involving multiple agencies and standards can create delays in cooling system approval and implementation processes. Data center operators must navigate various environmental, safety, and technical regulations while ensuring compliance with international standards and local requirements.
Sustainability-focused cooling solutions present significant opportunities as Malaysian data center operators increasingly prioritize environmental responsibility and energy efficiency. The growing demand for green data centers is driving innovation in eco-friendly cooling technologies, including natural cooling systems, renewable energy integration, and waste heat recovery solutions that can deliver both environmental and economic benefits.
Artificial intelligence integration in cooling systems offers substantial opportunities for optimization and predictive maintenance. AI-driven thermal management solutions can analyze real-time data to optimize cooling performance, predict equipment failures, and automatically adjust system parameters for maximum efficiency. This technology integration can deliver 15-20% energy savings while improving system reliability.
Liquid cooling adoption represents a major growth opportunity as data centers deploy increasingly powerful processors and high-density computing configurations. The transition from traditional air cooling to liquid cooling systems can support higher heat loads while reducing energy consumption and noise levels, making it particularly attractive for urban data center deployments.
Edge computing expansion creates opportunities for specialized cooling solutions designed for smaller, distributed data center environments. The development of compact, efficient cooling systems suitable for edge deployments can address the growing demand for localized computing capabilities while maintaining optimal thermal management performance.
Supply chain dynamics in the Malaysia data center cooling market are characterized by increasing localization of manufacturing and assembly operations. Global cooling technology providers are establishing regional facilities to reduce lead times, lower costs, and provide better customer support. This localization trend is creating opportunities for Malaysian suppliers and service providers while improving market responsiveness to customer requirements.
Technology evolution continues to reshape market dynamics with the introduction of innovative cooling approaches including immersion cooling, direct-to-chip cooling, and hybrid systems that combine multiple cooling methodologies. These technological advances are enabling data centers to support higher computing densities while achieving better energy efficiency ratios and reduced operational costs.
Customer preferences are shifting toward comprehensive cooling solutions that integrate hardware, software, and services into unified platforms. Data center operators increasingly prefer vendors who can provide end-to-end thermal management solutions including design, installation, monitoring, and maintenance services rather than individual component suppliers.
Competitive dynamics are intensifying as global cooling technology leaders compete with regional specialists and emerging technology providers. This competition is driving innovation, improving product quality, and creating more favorable pricing conditions for data center operators seeking advanced cooling solutions.
Primary research methodology employed comprehensive interviews with key stakeholders across the Malaysia data center cooling ecosystem, including data center operators, cooling technology providers, system integrators, and industry consultants. These interviews provided valuable insights into market trends, technology preferences, investment patterns, and future growth projections from industry practitioners with direct market experience.
Secondary research analysis involved extensive review of industry reports, government publications, technology specifications, and market data from various sources to validate primary research findings and provide comprehensive market coverage. This analysis included examination of regulatory frameworks, technology standards, and competitive landscape dynamics affecting the Malaysia data center cooling market.
Market sizing methodology utilized bottom-up and top-down approaches to develop accurate market assessments based on data center capacity, cooling requirements, technology adoption rates, and investment patterns. The methodology incorporated regional variations, technology segments, and end-user categories to provide detailed market segmentation and growth projections.
Data validation processes ensured research accuracy through multiple verification steps, cross-referencing of data sources, and expert review of findings and conclusions. This rigorous validation approach provides confidence in market insights and projections presented throughout the analysis.
Klang Valley region dominates Malaysia’s data center cooling market, accounting for approximately 45% market share due to its concentration of data center facilities, proximity to Kuala Lumpur’s business district, and excellent connectivity infrastructure. The region benefits from established power grid reliability, fiber optic networks, and skilled workforce availability, making it the preferred location for hyperscale and enterprise data center deployments.
Cyberjaya technology hub represents a significant growth center with 25% market share, driven by government initiatives to establish Malaysia as a regional technology leader. The area’s designation as a Multimedia Super Corridor has attracted numerous technology companies and data center operators, creating substantial demand for advanced cooling solutions and supporting infrastructure.
Johor region is experiencing rapid growth with 20% market share, benefiting from its strategic location near Singapore and competitive land costs. The region’s proximity to submarine cable landing points and Singapore’s data center ecosystem makes it attractive for operators seeking cost-effective alternatives while maintaining excellent regional connectivity.
Penang and other regions collectively account for the remaining 10% market share, with growing interest from operators seeking to establish distributed data center networks and edge computing capabilities. These regions offer opportunities for specialized cooling solutions designed for smaller facilities and unique environmental conditions.
Global technology leaders dominate the Malaysia data center cooling market through comprehensive product portfolios and established customer relationships:
Regional specialists and local partners play important roles in providing customized solutions, installation services, and ongoing maintenance support tailored to Malaysia’s specific market requirements and environmental conditions.
By Cooling Type:
By Data Center Type:
By Component:
Precision air conditioning systems maintain market leadership with 55% adoption rate among Malaysian data centers due to proven reliability, established supply chains, and comprehensive service support. These systems offer precise temperature and humidity control essential for maintaining optimal IT equipment performance while providing flexibility for various data center configurations and sizes.
Liquid cooling solutions are experiencing rapid growth with 30% annual increase in deployment, driven by increasing processor power densities and heat generation requirements. Direct-to-chip cooling and immersion cooling technologies are gaining traction among hyperscale operators seeking to support next-generation computing infrastructure while achieving superior energy efficiency ratios.
Free cooling systems are becoming increasingly popular with 40% of new installations incorporating some form of economizer or free cooling capability. These systems leverage Malaysia’s cooler nighttime temperatures and seasonal variations to reduce mechanical cooling requirements, resulting in significant energy savings and improved sustainability profiles.
AI-driven cooling management is emerging as a key differentiator with 20% adoption rate among advanced data center facilities. These intelligent systems use machine learning algorithms to optimize cooling performance, predict maintenance requirements, and automatically adjust system parameters based on real-time conditions and workload patterns.
Data center operators benefit from advanced cooling solutions through reduced operational expenses, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced system reliability. Modern cooling technologies can deliver 25-30% energy savings compared to traditional systems while providing better thermal management for high-density computing environments. These improvements translate to lower total cost of ownership and improved competitive positioning in the market.
Technology providers gain opportunities to expand market presence through innovative cooling solutions that address Malaysia’s unique climate challenges and customer requirements. The growing market provides platforms for technology differentiation, customer relationship development, and revenue growth through comprehensive solution offerings including products, services, and ongoing support.
System integrators benefit from increasing demand for specialized expertise in cooling system design, installation, and optimization. The complexity of modern cooling technologies creates opportunities for value-added services and long-term customer relationships through comprehensive project management and technical support capabilities.
End-user organizations benefit from improved IT infrastructure reliability, reduced operational costs, and enhanced sustainability profiles through advanced cooling solutions. These benefits support digital transformation initiatives while providing competitive advantages through improved system performance and reduced environmental impact.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Liquid cooling mainstream adoption represents a fundamental shift in data center thermal management approaches. Malaysian operators are increasingly deploying direct-to-chip cooling and immersion cooling systems to support high-performance computing workloads while achieving superior energy efficiency. This trend is driven by increasing processor power densities and the need to support AI and machine learning applications requiring intensive computational resources.
Sustainability integration is becoming a core requirement rather than an optional feature, with data center operators seeking cooling solutions that minimize environmental impact while reducing operational costs. MWR analysis indicates growing adoption of renewable energy integration, waste heat recovery systems, and eco-friendly refrigerants in cooling system designs.
Edge computing proliferation is creating demand for compact, efficient cooling solutions suitable for distributed data center environments. These edge facilities require cooling systems that can operate reliably with minimal maintenance while fitting within space-constrained environments and supporting varying workload patterns.
Predictive maintenance adoption is transforming cooling system management through IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time monitoring capabilities. These technologies enable proactive maintenance scheduling, performance optimization, and failure prevention, resulting in improved system reliability and reduced operational costs.
Major hyperscale investments continue to reshape Malaysia’s data center landscape with global cloud providers establishing large-scale facilities requiring advanced cooling infrastructure. These investments are driving demand for high-capacity cooling systems capable of supporting massive computing environments while maintaining optimal energy efficiency ratios.
Technology partnerships between cooling system providers and data center operators are becoming increasingly common, focusing on customized solutions that address Malaysia’s specific climate challenges and operational requirements. These collaborations are resulting in innovative cooling approaches optimized for tropical environments and local market conditions.
Regulatory framework evolution is establishing clearer guidelines for data center cooling systems, energy efficiency requirements, and environmental compliance standards. These developments are creating more predictable operating environments while encouraging adoption of advanced cooling technologies and sustainable practices.
Local ecosystem development is expanding through establishment of regional service centers, training programs, and technical support capabilities. This ecosystem growth is improving market responsiveness, reducing costs, and creating opportunities for local suppliers and service providers to participate in the data center cooling market.
Technology investment priorities should focus on cooling solutions that can deliver measurable energy efficiency improvements while supporting increasing computing densities. Data center operators should evaluate liquid cooling technologies for high-performance computing applications and consider hybrid cooling approaches that optimize performance across varying workload conditions.
Partnership strategies should emphasize collaboration with cooling technology providers who offer comprehensive solutions including design, installation, monitoring, and maintenance services. These partnerships can provide access to latest technologies, technical expertise, and ongoing support while reducing operational complexity and risk.
Sustainability planning should integrate cooling system efficiency with broader environmental goals including renewable energy adoption, waste heat recovery, and carbon footprint reduction. Organizations should evaluate cooling technologies based on total environmental impact rather than initial cost considerations alone.
Skills development initiatives should address the growing need for technical expertise in advanced cooling technologies through training programs, certification courses, and knowledge transfer arrangements with technology providers. Building internal capabilities can improve operational efficiency and reduce dependence on external service providers.
Market growth trajectory indicates continued expansion driven by digital transformation acceleration, cloud adoption, and increasing data generation across Malaysian industries. The market is expected to maintain robust growth with projected CAGR of 8.2% as organizations continue investing in digital infrastructure and data center capabilities to support business transformation initiatives.
Technology evolution will continue advancing toward more efficient, intelligent, and sustainable cooling solutions. MarkWide Research projects that liquid cooling adoption will reach 45% market penetration within five years, while AI-driven cooling management systems will become standard features in new data center deployments.
Market consolidation may occur as smaller cooling technology providers seek partnerships or acquisition opportunities with larger organizations having comprehensive solution portfolios and global service capabilities. This consolidation could result in more integrated solution offerings and improved customer support capabilities.
Regulatory influence will likely increase with stricter energy efficiency requirements, environmental compliance standards, and sustainability reporting obligations affecting cooling system selection and operation. These regulatory developments will favor advanced cooling technologies that can demonstrate superior environmental performance and energy efficiency.
Malaysia’s data center cooling market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation driven by the country’s digital transformation journey and strategic position as a regional technology hub. The market benefits from strong government support, increasing foreign investment, and growing demand for digital services across various industries. However, success requires addressing unique challenges including tropical climate conditions, energy efficiency requirements, and evolving customer expectations for sustainable solutions.
Technology advancement will continue reshaping the market landscape with liquid cooling, AI-driven management systems, and sustainable cooling approaches gaining prominence. Organizations that invest in advanced cooling technologies and develop comprehensive solution capabilities will be best positioned to capitalize on market opportunities while delivering superior value to customers.
Strategic focus on energy efficiency, sustainability, and operational excellence will differentiate successful market participants as data center operators increasingly prioritize total cost of ownership and environmental responsibility. The market’s future growth depends on continued innovation, skills development, and collaborative partnerships that can address Malaysia’s unique requirements while supporting the country’s digital economy ambitions.
What is Data Center Cooling?
Data Center Cooling refers to the methods and technologies used to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels in data centers, ensuring the efficient operation of servers and IT equipment. Effective cooling is crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring reliability in data processing environments.
What are the key players in the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market?
Key players in the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market include companies like Schneider Electric, Vertiv, and Rittal, which provide innovative cooling solutions and technologies. These companies focus on energy efficiency and advanced cooling systems to meet the growing demands of data centers, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market?
The main drivers of the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market include the increasing demand for data storage and processing, the rise of cloud computing, and the need for energy-efficient cooling solutions. Additionally, the growth of digital transformation initiatives across various industries is contributing to market expansion.
What challenges does the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market face?
The Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market faces challenges such as high operational costs associated with advanced cooling technologies and the need for skilled personnel to manage these systems. Additionally, environmental regulations and the push for sustainability can complicate cooling system implementations.
What opportunities exist in the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market?
Opportunities in the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market include the development of innovative cooling technologies, such as liquid cooling and AI-driven systems. Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency presents avenues for growth and investment in eco-friendly cooling solutions.
What trends are shaping the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market?
Trends shaping the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market include the adoption of modular cooling systems, the integration of IoT for monitoring and optimization, and the shift towards renewable energy sources for powering cooling solutions. These trends reflect the industry’s response to evolving technological and environmental demands.
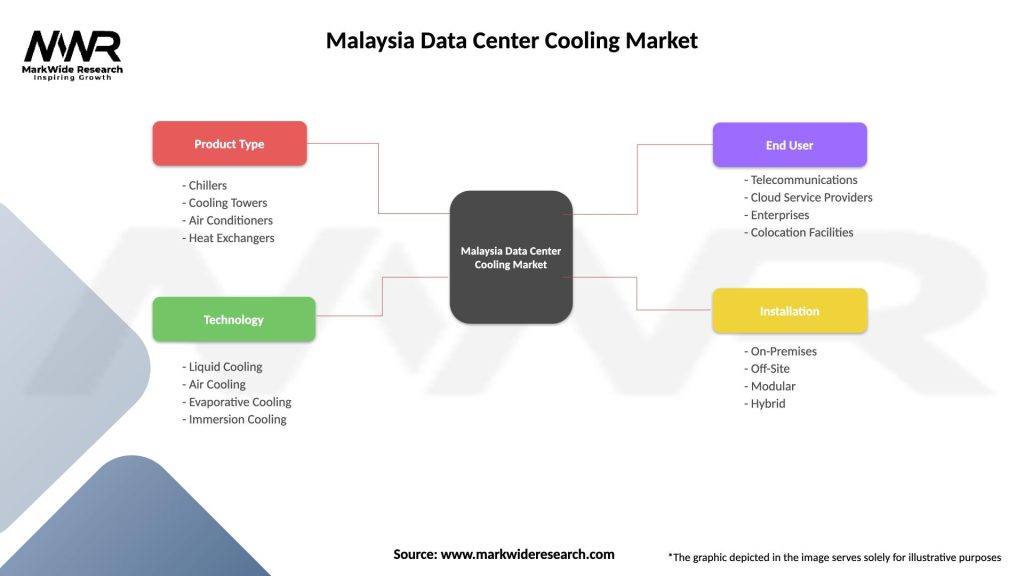
Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Chillers, Cooling Towers, Air Conditioners, Heat Exchangers |
| Technology | Liquid Cooling, Air Cooling, Evaporative Cooling, Immersion Cooling |
| End User | Telecommunications, Cloud Service Providers, Enterprises, Colocation Facilities |
| Installation | On-Premises, Off-Site, Modular, Hybrid |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Malaysia Data Center Cooling Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at