444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The maize market is a thriving sector in the global agricultural industry, characterized by the cultivation and commercialization of maize, also known as corn. Maize is one of the most widely grown and consumed crops worldwide, with its versatile applications spanning various industries, including food, animal feed, biofuel production, and industrial use. The market for maize is driven by its high demand, nutritional value, and diverse product range. This article delves into the various aspects of the maize market, providing insights into its meaning, executive summary, key market insights, market drivers, market restraints, market opportunities, market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, market key trends, the impact of Covid-19, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and conclusion.
Meaning
Maize, scientifically known as Zea mays, is a cereal crop that belongs to the grass family Poaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible kernels, which are used in various forms such as whole corn, cornmeal, corn flour, corn oil, and corn starch. Maize is a staple food in many countries, particularly in regions like North America, South America, and Africa. It serves as a primary source of carbohydrates and provides essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. Additionally, maize is a valuable source of feed for livestock, contributing to the growth and development of the animal agriculture industry.
Executive Summary
The maize market is experiencing steady growth globally, driven by factors such as population growth, increasing demand for food, feed, and industrial applications, and the rising popularity of biofuels. The market has witnessed significant advancements in production techniques, seed varieties, and processing technologies, leading to improved yields and quality. However, the maize market also faces challenges such as climate change, fluctuating prices, and regulatory restrictions. Nevertheless, numerous opportunities exist in the market, including the development of value-added products, expansion into emerging markets, and the adoption of sustainable farming practices. The future outlook for the maize market remains promising, with continuous innovation and investment expected to fuel its growth.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
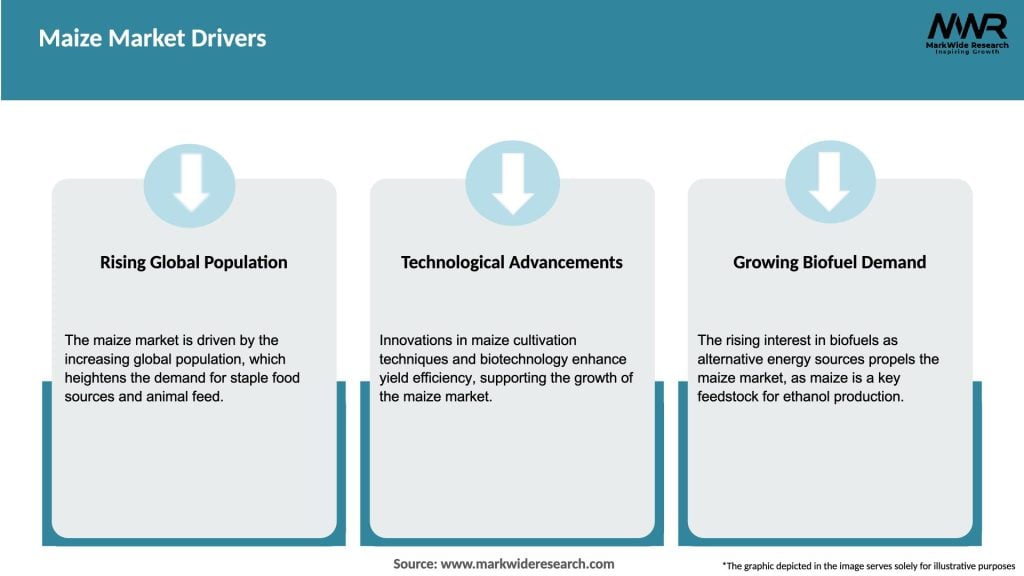
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The maize market is dynamic and influenced by various factors that shape its growth and development. These factors include changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, climate conditions, government policies, market competition, and global trade dynamics. Understanding the market dynamics is crucial for industry participants to make informed decisions, identify growth opportunities, and mitigate risks. The maize market’s dynamics are shaped by the interplay of supply and demand forces, which drive production, trade, and pricing patterns in the industry.
Regional Analysis
The maize market exhibits regional variations in terms of production, consumption, and trade. Major maize-producing countries include the United States, China, Brazil, Argentina, India, and Ukraine. The consumption patterns are influenced by cultural preferences, dietary habits, and economic factors in each region. North America and South America dominate the global maize production, with the United States being the largest producer. Africa is a significant consumer of maize, where it serves as a staple food. Asia-Pacific and Europe also contribute to the global maize market, with diverse consumption patterns and growing industrial applications. The regional analysis helps identify specific market dynamics and opportunities within each geographical area.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Maize Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
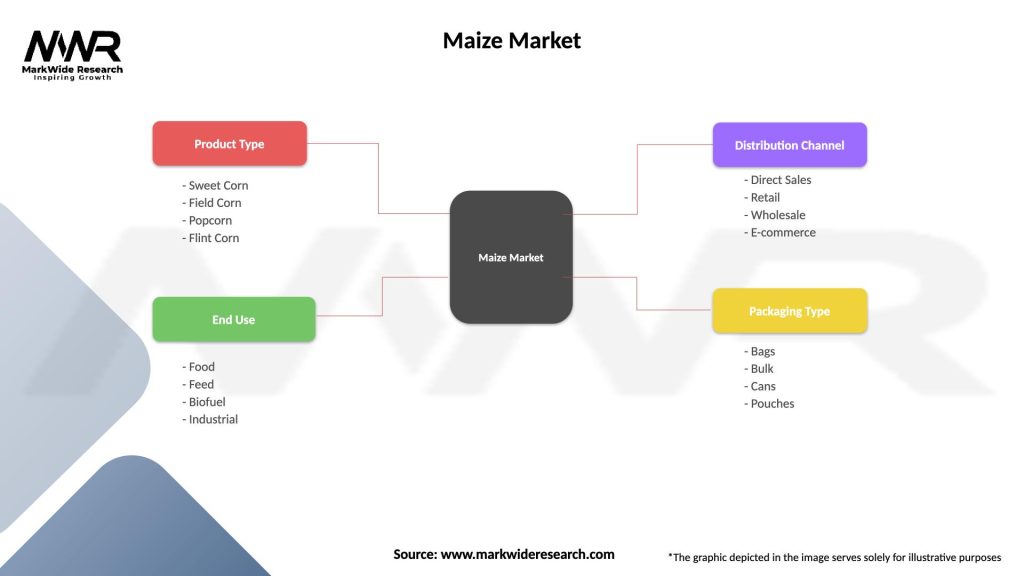
Segmentation
The maize market can be segmented based on various factors, including product type, end-use industry, and geography. Common segmentation parameters include:
Segmentation provides a comprehensive view of the market, allowing stakeholders to target specific segments, identify growth opportunities, and tailor their strategies accordingly.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive assessment of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the maize market.
Analyzing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats helps market participants formulate effective strategies, mitigate risks, and capitalize on market advantages.
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the maize market, affecting various aspects of production, distribution, and consumption. The pandemic disrupted supply chains, leading to logistical challenges and temporary disruptions in maize trade. The closure of restaurants, hotels, and other food service establishments resulted in a shift in demand from bulk maize products to retail-packaged goods. The pandemic also highlighted the importance of food security and self-sufficiency, leading to increased support for local agriculture and domestic production. However, the maize market proved to be resilient, with the essential nature of maize as a staple food and feed ingredient ensuring its continued demand. The pandemic prompted industry participants to implement safety measures, adapt to changing consumer preferences, and explore e-commerce and online platforms for product distribution.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the maize market remains promising. The increasing global population, rising demand for food, feed, and industrial applications, and the growing focus on renewable energy sources will continue to drive market growth. Technological advancements, research and development activities, and the adoption of sustainable farming practices will contribute to improved productivity, quality, and profitability. The development of value-added maize products and expansion into emerging markets offer significant growth opportunities. However, market participants should remain vigilant to challenges such as climate change impacts, price volatility, and regulatory restrictions. By leveraging market trends, embracing innovation, and adopting strategic approaches, industry participants can position themselves for success in the evolving maize market.
Conclusion
The maize market is a thriving sector in the global agricultural industry, driven by its versatile applications, high demand, and nutritional value. Maize serves as a staple food, animal feed ingredient, and raw material for various industries. The market is influenced by factors such as population growth, changing dietary patterns, technological advancements, and sustainable farming practices. While the market faces challenges such as climate change impact and price volatility, numerous opportunities exist for market expansion, innovation, and collaboration. The future outlook for the maize market is positive, with continuous growth expected through strategic approaches, diversification, and the adoption of sustainable practices. By staying informed about market dynamics, industry participants can navigate the maize market successfully and capitalize on its potential for long-term growth.
What is Maize?
Maize, also known as corn, is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico. It is a staple food in many countries and is used for various applications, including food products, animal feed, and industrial uses.
What are the key players in the Maize Market?
Key players in the Maize Market include companies such as Cargill, Archer Daniels Midland Company, Bunge Limited, and DuPont, among others. These companies are involved in various aspects of maize production, processing, and distribution.
What are the main drivers of the Maize Market?
The main drivers of the Maize Market include the increasing demand for animal feed, the growing biofuel industry, and the rising consumption of maize-based food products. Additionally, advancements in agricultural technology are enhancing maize yields.
What challenges does the Maize Market face?
The Maize Market faces challenges such as climate change affecting crop yields, fluctuating prices due to market volatility, and competition from alternative crops. These factors can impact the overall stability of maize production.
What opportunities exist in the Maize Market?
Opportunities in the Maize Market include the development of genetically modified maize varieties that offer higher resistance to pests and diseases, as well as the potential for expanding maize-based biofuels. Additionally, increasing health consciousness among consumers is driving demand for maize-based health products.
What trends are shaping the Maize Market?
Trends shaping the Maize Market include the rise of organic maize farming, the integration of precision agriculture technologies, and the growing popularity of maize in gluten-free products. These trends reflect changing consumer preferences and advancements in farming practices.
Maize Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Sweet Corn, Field Corn, Popcorn, Flint Corn |
| End Use | Food, Feed, Biofuel, Industrial |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Retail, Wholesale, E-commerce |
| Packaging Type | Bags, Bulk, Cans, Pouches |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Maize Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at