444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The maize chopper market encompasses agricultural machinery designed for efficient harvesting and processing of maize (corn) crops. These machines are integral to modern farming operations, offering capabilities such as cutting, chopping, and processing maize into silage for animal feed. Maize choppers vary in size and complexity, catering to diverse farm sizes and operational needs, from small-scale family farms to large commercial enterprises.
Meaning
Maize choppers, also known as maize harvesters or forage harvesters, are specialized agricultural equipment used to harvest and process maize plants. They typically include components for cutting maize stalks, chopping them into fine pieces, and collecting the chopped material in a storage container or trailer. Maize choppers are essential for livestock farming, providing high-quality silage feed that preserves nutritional value and supports animal health.
Executive Summary
The maize chopper market is driven by the increasing demand for efficient maize harvesting solutions, particularly in dairy and livestock farming sectors. Key market players focus on enhancing machine efficiency, productivity, and user-friendliness to meet the evolving needs of farmers. The market benefits from technological advancements in machine design, automation, and integration of digital technologies for precision farming.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors propel the growth of the maize chopper market:
Market Restraints
Despite its growth prospects, the maize chopper market faces challenges:
Market Opportunities
The maize chopper market presents opportunities for growth and innovation:
Market Dynamics
Key dynamics shaping the maize chopper market include:
Regional Analysis
The maize chopper market varies regionally based on agricultural practices, crop cultivation patterns, and economic factors influencing demand and adoption rates. Key regions include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Maize Chopper Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
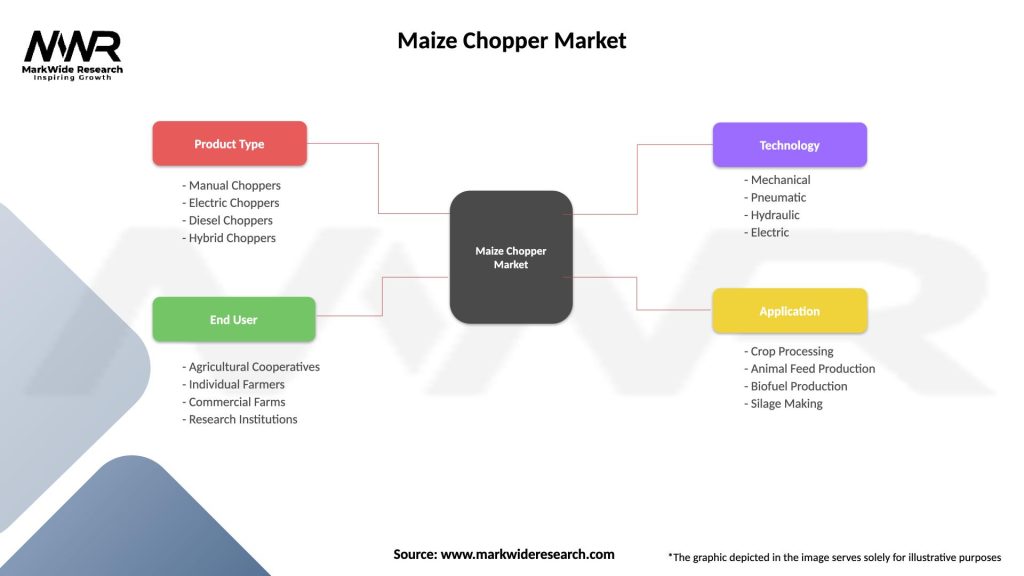
Segmentation
The maize chopper market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Each category of maize choppers offers unique benefits and features tailored to specific farming applications:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
Stakeholders in the maize chopper market benefit from:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Key trends influencing the maize chopper market include:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has impacted the maize chopper market in several ways:
Key Industry Developments
Recent industry developments in the maize chopper market include:
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts suggest the following strategies for stakeholders in the maize chopper market:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the maize chopper market is optimistic, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for efficient farming practices, and growing awareness of sustainable agriculture. As farmers worldwide seek to enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and meet evolving consumer demands for high-quality livestock feed, the adoption of maize choppers is expected to expand. Manufacturers and suppliers that innovate, collaborate, and invest in sustainable, technology-driven solutions are well-positioned to capitalize on this growing market opportunity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the maize chopper market plays a vital role in modern agriculture, providing farmers with essential equipment for efficient maize harvesting and silage production. Despite challenges such as high initial costs and technical complexities, the market continues to grow driven by advancements in technology, increasing agricultural productivity, and shifting consumer preferences towards sustainable farming practices. By focusing on innovation, sustainability, and customer-centric strategies, stakeholders can navigate market dynamics, capitalize on growth opportunities, and contribute to the future of smart agriculture.
What is Maize Chopper?
A maize chopper is a machine designed for cutting maize into smaller pieces, facilitating easier handling and processing. It is commonly used in agricultural settings for silage production and feed preparation.
What are the key players in the Maize Chopper Market?
Key players in the maize chopper market include John Deere, AGCO Corporation, and CLAAS, among others. These companies are known for their innovative agricultural machinery and technology.
What are the growth factors driving the Maize Chopper Market?
The maize chopper market is driven by the increasing demand for efficient agricultural practices, the rise in maize production for food and biofuel, and advancements in machinery technology that enhance productivity.
What challenges does the Maize Chopper Market face?
Challenges in the maize chopper market include high initial investment costs, maintenance issues, and competition from alternative harvesting technologies. These factors can hinder market growth and adoption.
What opportunities exist in the Maize Chopper Market?
Opportunities in the maize chopper market include the development of smart and automated choppers, increasing adoption in developing countries, and the growing trend of sustainable farming practices.
What trends are shaping the Maize Chopper Market?
Trends in the maize chopper market include the integration of precision agriculture technologies, the use of eco-friendly materials in manufacturing, and the rise of multifunctional machines that can perform various agricultural tasks.
Maize Chopper Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Manual Choppers, Electric Choppers, Diesel Choppers, Hybrid Choppers |
| End User | Agricultural Cooperatives, Individual Farmers, Commercial Farms, Research Institutions |
| Technology | Mechanical, Pneumatic, Hydraulic, Electric |
| Application | Crop Processing, Animal Feed Production, Biofuel Production, Silage Making |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Maize Chopper Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at