444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The Madeira Wine market encompasses the production, distribution, and consumption of fortified wines originating from the Madeira Islands of Portugal. Known for their unique aging process and distinct flavor profiles, Madeira wines are fortified with grape spirits and subjected to heat treatment, resulting in a range of styles from dry to sweet. These wines are prized globally for their longevity, complexity, and versatility in culinary pairings, making them a staple in the dessert wine category.
Meaning
Madeira Wine refers to fortified wines produced exclusively in the Madeira Islands, characterized by oxidative aging and heat treatment (estufagem). The aging process involves exposing the wines to heat and oxygen, contributing to their distinctive flavors of caramel, nuts, and spices. Madeira wines are classified based on grape varieties, aging periods, and sweetness levels, offering a diverse range of styles suitable for various occasions and culinary applications.
Executive Summary
The Madeira Wine market is experiencing resurgence driven by growing international demand for premium fortified wines with historical significance. Key producers focus on traditional winemaking techniques, grape varietals unique to the region, and sustainable viticulture practices. With expanding global distribution channels and increasing consumer appreciation for artisanal wines, the market presents opportunities for growth, innovation, and cultural heritage preservation.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the Madeira Wine market:
Market Restraints
Despite its growth prospects, the Madeira Wine market faces challenges:
Market Opportunities
The Madeira Wine market presents several opportunities for industry expansion:
Market Dynamics
The Madeira Wine market dynamics are influenced by cultural heritage, consumer trends, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and environmental sustainability initiatives. Adapting to these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to capitalize on growth opportunities, navigate market challenges, and sustain competitive advantage in the global wine industry.
Regional Analysis
The Madeira Wine market exhibits regional variations and consumption patterns:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Madeira Wine Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
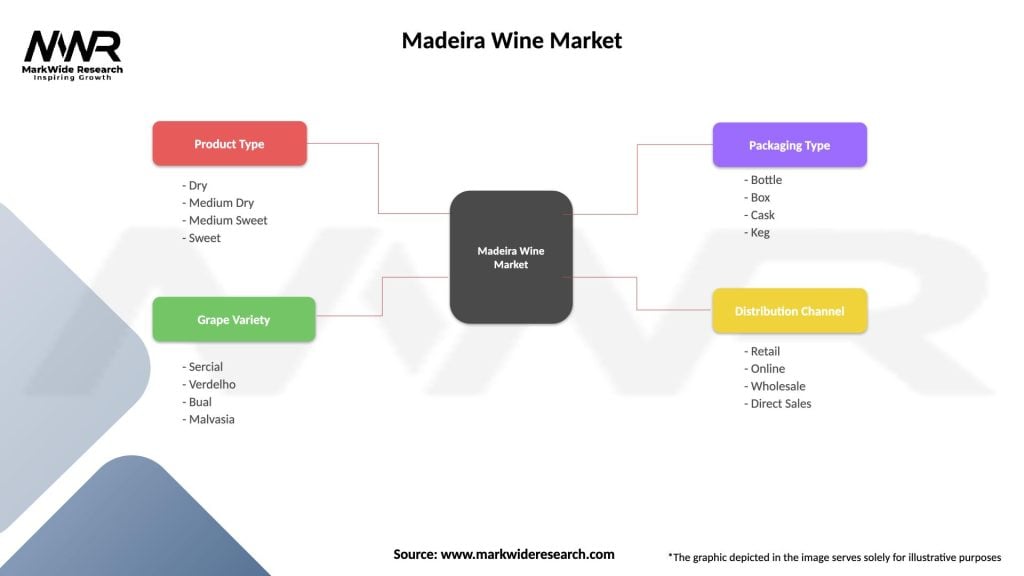
Segmentation
The Madeira Wine market can be segmented based on:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The Madeira Wine market offers several benefits for stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Key trends shaping the Madeira Wine market include:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has influenced the Madeira Wine market:
Key Industry Developments
Recent developments in the Madeira Wine market include:
Analyst Suggestions
Based on current trends and market dynamics, analysts recommend the following strategies for stakeholders in the Madeira Wine market:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Madeira Wine market is promising, driven by consumer demand for premium, artisanal wines with cultural heritage appeal. As stakeholders innovate with sustainable practices, digital strategies, and product diversification, Madeira wines will continue to evolve as a symbol of luxury, quality, and tradition in the global wine industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Madeira Wine market offers significant growth opportunities amidst evolving consumer preferences, regulatory landscapes, and technological advancements. By leveraging historical prestige, product differentiation, and sustainability initiatives, stakeholders can navigate market challenges, capitalize on emerging trends, and foster sustainable growth in the competitive landscape of Madeira wines.
What is Madeira Wine?
Madeira Wine is a fortified wine produced on the Portuguese Madeira Islands, known for its unique aging process and diverse flavor profiles. It is made from various grape varieties and is characterized by its rich, complex taste and high acidity.
What are the key players in the Madeira Wine Market?
Key players in the Madeira Wine Market include Blandy’s Madeira, Barbeito Madeira, and Madeira Wine Company, among others. These companies are known for their traditional production methods and a wide range of wine offerings.
What are the growth factors driving the Madeira Wine Market?
The growth of the Madeira Wine Market is driven by increasing consumer interest in premium and fortified wines, as well as the rising popularity of wine tourism in Madeira. Additionally, the unique characteristics of Madeira Wine appeal to both connoisseurs and casual drinkers.
What challenges does the Madeira Wine Market face?
The Madeira Wine Market faces challenges such as competition from other fortified wines and changing consumer preferences towards lighter wines. Additionally, the limited production area on the Madeira Islands can restrict supply.
What opportunities exist in the Madeira Wine Market?
Opportunities in the Madeira Wine Market include expanding into new international markets and developing innovative wine products that cater to evolving consumer tastes. There is also potential for growth in online sales and wine subscription services.
What trends are shaping the Madeira Wine Market?
Trends in the Madeira Wine Market include a growing interest in sustainable and organic wine production, as well as the revival of traditional winemaking techniques. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on food pairings and cocktail applications for Madeira Wine.
Madeira Wine Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Dry, Medium Dry, Medium Sweet, Sweet |
| Grape Variety | Sercial, Verdelho, Bual, Malvasia |
| Packaging Type | Bottle, Box, Cask, Keg |
| Distribution Channel | Retail, Online, Wholesale, Direct Sales |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Madeira Wine Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at