444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The MAARS (Modular Advanced Armed Robotic System) robot market is witnessing significant growth, propelled by advancements in robotics technology, increasing military modernization efforts, and growing demand for unmanned systems in defense and security applications. Designed for various missions ranging from reconnaissance and surveillance to direct combat support, MAARS robots offer versatility, mobility, and firepower, making them indispensable assets for military and law enforcement agencies worldwide.
Meaning
MAARS robots, developed by QinetiQ North America, are versatile unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) designed for military and security applications. These modular robots can be configured with different payloads, including cameras, sensors, manipulator arms, and weapons systems, to perform a wide range of tasks autonomously or under remote human control. MAARS robots enhance situational awareness, increase operational effectiveness, and minimize risks to personnel in complex and hazardous environments.
Executive Summary
The MAARS robot market is experiencing robust growth, driven by factors such as the rising demand for unmanned systems in military and security operations, technological advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI), and the need for force multiplication and operational efficiency. Key market players focus on innovation, product development, and strategic collaborations to expand their market presence and meet the evolving needs of defense and security organizations worldwide. With increasing investments in defense modernization and the integration of autonomous systems, the MAARS robot market presents lucrative opportunities for growth and expansion.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of the MAARS robot market:
Market Restraints
Despite the positive growth outlook, the MAARS robot market faces several challenges:
Market Opportunities
Despite the challenges, the MAARS robot market offers several opportunities for growth and innovation:
Market Dynamics
The MAARS robot market is characterized by dynamic trends and evolving customer requirements influenced by factors such as geopolitical tensions, military conflicts, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Key market players must stay abreast of these dynamics, anticipate future trends, and adapt their strategies accordingly to maintain a competitive edge and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Regional Analysis
The MAARS robot market exhibits varying trends and opportunities across different regions:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the MAARS Robot Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
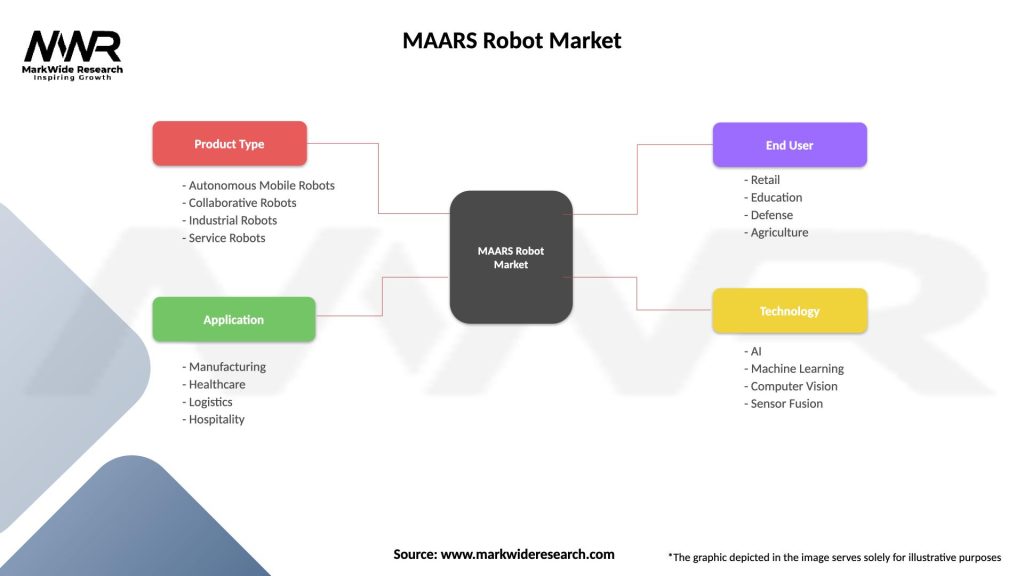
Segmentation
The MAARS robot market can be segmented based on various factors, including:
Category-wise Insights
Each category of MAARS robots offers unique capabilities, features, and applications tailored to different operational requirements and end-user verticals:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The MAARS robot market offers several benefits for manufacturers, suppliers, end-users, and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Several key trends are shaping the MAARS robot market:
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the MAARS robot market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Based on market trends and developments, analysts suggest the following strategies for industry participants:
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the MAARS robot market is optimistic, with continued growth and innovation expected in the coming years. As defense and security organizations prioritize unmanned systems to enhance operational effectiveness, reduce risks to personnel, and address emerging threats, the demand for MAARS robots is expected to rise. Manufacturers that invest in technology innovation, product development, and market expansion are well-positioned to capitalize on this growing market opportunity and shape the future of unmanned ground robotics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the MAARS robot market offers significant opportunities for manufacturers, suppliers, end-users, and stakeholders seeking to leverage unmanned systems for military and security applications. Despite challenges such as high initial costs, regulatory constraints, and ethical considerations, the market continues to grow and evolve, driven by factors such as technological advancements, increasing demand for autonomy, and evolving threat landscapes. By focusing on innovation, collaboration, and customer engagement, industry participants can unlock the full potential of MAARS robots and contribute to enhancing defense and security capabilities worldwide.
What is MAARS Robot?
MAARS Robot refers to a type of autonomous mobile robot designed for various applications, including logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing. These robots are equipped with advanced navigation and sensing technologies to operate efficiently in dynamic environments.
What are the key companies in the MAARS Robot Market?
Key companies in the MAARS Robot Market include Fetch Robotics, Mobile Industrial Robots, and Omron Adept Technologies, among others. These companies are known for their innovative solutions and contributions to the development of autonomous mobile robots.
What are the growth factors driving the MAARS Robot Market?
The MAARS Robot Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for automation in warehouses, the need for efficient material handling solutions, and advancements in robotics technology. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce is boosting the adoption of these robots in logistics.
What challenges does the MAARS Robot Market face?
Challenges in the MAARS Robot Market include high initial investment costs, integration complexities with existing systems, and concerns regarding safety and reliability in dynamic environments. These factors can hinder widespread adoption in certain industries.
What opportunities exist in the MAARS Robot Market?
The MAARS Robot Market presents opportunities in sectors such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, where automation can enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. Furthermore, the growing trend of smart factories and Industry Four Point O is expected to drive demand for these robots.
What trends are shaping the MAARS Robot Market?
Trends in the MAARS Robot Market include the integration of artificial intelligence for improved decision-making, the development of collaborative robots that work alongside humans, and advancements in battery technology for longer operational times. These innovations are enhancing the capabilities and applications of MAARS robots.
MAARS Robot Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Autonomous Mobile Robots, Collaborative Robots, Industrial Robots, Service Robots |
| Application | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Logistics, Hospitality |
| End User | Retail, Education, Defense, Agriculture |
| Technology | AI, Machine Learning, Computer Vision, Sensor Fusion |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the MAARS Robot Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at