444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The LTE IoT devices market represents a rapidly expanding segment within the global telecommunications and Internet of Things ecosystem. Long Term Evolution technology specifically designed for IoT applications has emerged as a critical enabler for massive machine-type communications, supporting billions of connected devices across diverse industries. The market encompasses various LTE-based technologies including LTE-M (LTE-Cat M1), NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT), and EC-GSM-IoT (Extended Coverage GSM IoT), each optimized for different use cases and deployment scenarios.
Market dynamics indicate substantial growth driven by increasing demand for low-power, wide-area connectivity solutions. The proliferation of smart city initiatives, industrial automation, and asset tracking applications has accelerated adoption rates significantly. LTE IoT technology offers superior coverage, extended battery life, and cost-effective connectivity compared to traditional cellular technologies, making it ideal for massive IoT deployments.
Regional deployment varies considerably, with North America and Europe leading in infrastructure development and device adoption. Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate the highest growth potential, driven by manufacturing sector digitization and smart infrastructure investments. The market benefits from strong support from major telecommunications equipment vendors and mobile network operators worldwide, creating a robust ecosystem for LTE IoT devices development and deployment.
The LTE IoT devices market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of connected devices, modules, and solutions that utilize Long Term Evolution technology specifically optimized for Internet of Things applications. These devices leverage cellular networks to provide reliable, wide-area connectivity for applications requiring low power consumption, extended coverage, and cost-effective communication capabilities.
LTE IoT technology encompasses several standardized protocols designed to address different IoT use cases. LTE-M provides higher data rates and mobility support, making it suitable for applications like asset tracking and wearable devices. NB-IoT offers ultra-low power consumption and excellent indoor penetration, ideal for static applications such as smart meters and environmental sensors. These technologies operate within existing LTE spectrum, enabling mobile network operators to deploy IoT services efficiently.
Device categories within this market include modules, gateways, sensors, trackers, and specialized IoT endpoints. The market also encompasses supporting infrastructure, development platforms, and connectivity services that enable seamless integration of LTE IoT devices into enterprise and consumer applications across multiple vertical markets.
Market momentum for LTE IoT devices continues to accelerate as organizations worldwide recognize the strategic value of cellular-based IoT connectivity. The convergence of 5G network rollouts and legacy LTE infrastructure creates unprecedented opportunities for scalable IoT deployments. Industry adoption spans manufacturing, utilities, transportation, healthcare, and smart city applications, with each sector driving specific device requirements and deployment models.
Technology evolution remains a key market driver, with continuous improvements in power efficiency, coverage enhancement, and cost reduction. The integration of artificial intelligence and edge computing capabilities into LTE IoT devices enables more sophisticated applications and real-time decision-making at the device level. Standardization efforts by 3GPP and other industry bodies ensure interoperability and global deployment consistency.
Competitive dynamics feature established semiconductor companies, module manufacturers, and emerging IoT specialists competing across different market segments. Strategic partnerships between device manufacturers, network operators, and system integrators create comprehensive solution offerings that address end-to-end IoT deployment requirements. The market demonstrates strong growth potential with increasing enterprise digitization and smart infrastructure investments driving sustained demand.
Critical market insights reveal several transformative trends shaping the LTE IoT devices landscape:
Market penetration varies significantly across geographic regions and industry verticals. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that utility sector adoption leads other industries, driven by smart meter deployments and grid modernization initiatives. The automotive sector shows rapid growth in connected vehicle applications, while healthcare demonstrates increasing adoption of remote patient monitoring devices.
Primary market drivers propelling LTE IoT devices adoption include the accelerating digital transformation across industries and the need for reliable, wide-area connectivity solutions. Smart city initiatives worldwide create substantial demand for connected infrastructure, environmental monitoring, and public safety applications. Government investments in digital infrastructure and Industry 4.0 programs provide strong market support.
Technological advantages of LTE IoT over alternative connectivity solutions drive market expansion. Superior indoor penetration, extended battery life, and global roaming capabilities make LTE IoT attractive for enterprise deployments. The ability to leverage existing cellular infrastructure reduces deployment costs and complexity compared to proprietary wireless technologies.
Regulatory support from telecommunications authorities worldwide facilitates market growth through spectrum allocation and standardization efforts. The integration of LTE IoT capabilities into 5G networks ensures long-term technology evolution and investment protection. Cost optimization through economies of scale and manufacturing improvements makes LTE IoT devices accessible to broader market segments.
Enterprise digitization trends create sustained demand for connected devices across supply chain management, asset tracking, and operational efficiency applications. The growing emphasis on data-driven decision making drives adoption of IoT sensors and monitoring devices that require reliable cellular connectivity.
Market restraints impacting LTE IoT devices adoption include network coverage limitations in certain geographic regions and the complexity of device certification processes. Infrastructure gaps in rural and remote areas limit deployment opportunities for applications requiring ubiquitous connectivity. The fragmented nature of global LTE IoT standards creates interoperability challenges for multinational deployments.
Cost considerations remain significant for price-sensitive applications, particularly in developing markets where connectivity costs may exceed device value. The ongoing operational expenses associated with cellular connectivity can impact total cost of ownership calculations for long-term IoT deployments. Power consumption requirements, while improved, still limit applications in extremely resource-constrained environments.
Security concerns related to cellular network vulnerabilities and device management complexity create hesitation among enterprise customers. The need for specialized technical expertise in LTE IoT deployment and management can slow adoption in organizations lacking internal capabilities. Regulatory compliance requirements vary across regions, creating additional complexity for global device manufacturers.
Competition from alternative connectivity technologies including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and proprietary LPWAN solutions creates market pressure. The rapid evolution of 5G technology may cause some organizations to delay LTE IoT investments in anticipation of next-generation capabilities.
Significant opportunities exist within the LTE IoT devices market as 5G network deployments create enhanced capabilities for massive IoT applications. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities into edge devices enables new use cases in predictive maintenance, autonomous systems, and real-time analytics. Vertical market specialization offers opportunities for customized solutions addressing specific industry requirements.
Emerging applications in precision agriculture, environmental monitoring, and smart infrastructure create new market segments with substantial growth potential. The convergence of LTE IoT with other technologies such as blockchain, edge computing, and augmented reality opens innovative application possibilities. Partnership opportunities between device manufacturers, software providers, and system integrators enable comprehensive solution offerings.
Geographic expansion into developing markets presents significant growth opportunities as telecommunications infrastructure improves and digitization initiatives accelerate. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental monitoring creates demand for specialized LTE IoT devices supporting green technology initiatives. Industrial automation trends drive opportunities for ruggedized devices supporting harsh environment applications.
Platform integration opportunities enable LTE IoT devices to connect seamlessly with cloud services, enterprise software, and analytics platforms. The growing emphasis on cybersecurity creates opportunities for devices with enhanced security features and secure connectivity capabilities.
Market dynamics within the LTE IoT devices sector reflect the complex interplay between technological advancement, regulatory evolution, and customer demand patterns. Supply chain considerations significantly impact device availability and pricing, with semiconductor shortages and manufacturing capacity constraints affecting market growth rates. The competitive landscape continues evolving as traditional telecommunications equipment vendors compete with specialized IoT companies and emerging technology providers.
Customer behavior patterns show increasing preference for integrated solutions that combine devices, connectivity, and management platforms. Enterprise customers prioritize total cost of ownership optimization over initial device costs, driving demand for energy-efficient, long-life devices with minimal maintenance requirements. Deployment models vary from pilot projects to large-scale rollouts, with successful pilot programs often leading to substantial volume deployments.
Technology lifecycle management becomes increasingly important as organizations plan long-term IoT strategies. The transition from 2G/3G networks to LTE and 5G creates migration opportunities while requiring careful planning to avoid service disruptions. Ecosystem collaboration between device manufacturers, network operators, and application developers drives innovation and accelerates market development.
Pricing dynamics continue evolving with module costs declining while value-added features and services command premium pricing. The market demonstrates increasing price sensitivity in high-volume applications while maintaining willingness to pay for specialized capabilities in niche applications.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for LTE IoT devices market analysis incorporates multiple data collection and validation approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, technology leaders, and end-user organizations across different geographic regions and market segments. Survey data collection from device manufacturers, network operators, and system integrators provides quantitative insights into market trends and growth projections.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, regulatory filings, patent databases, and technical specifications from standards organizations. Market intelligence gathering includes monitoring of product launches, partnership announcements, and strategic initiatives from key market participants. Financial analysis of public companies provides insights into market performance and investment trends.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources, expert review panels, and statistical analysis to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Forecasting models incorporate historical trends, current market conditions, and future scenario analysis to project market development trajectories. Regional analysis considers local market conditions, regulatory environments, and competitive dynamics.
Analytical frameworks include Porter’s Five Forces analysis, SWOT assessment, and value chain analysis to provide comprehensive market understanding. Technology assessment includes evaluation of competing standards, performance benchmarking, and innovation trend analysis.
North America maintains market leadership in LTE IoT devices adoption, driven by advanced telecommunications infrastructure and strong enterprise digitization initiatives. The region benefits from early 5G deployments and comprehensive LTE coverage, creating favorable conditions for IoT device proliferation. United States leads in smart city projects and industrial IoT applications, while Canada shows strong growth in natural resource monitoring and environmental applications.
Europe demonstrates robust market growth with 35% regional market share, supported by stringent regulatory requirements for energy efficiency and environmental monitoring. Germany leads in industrial automation applications, while Nordic countries excel in smart city and utilities implementations. The region’s focus on sustainability drives demand for environmental monitoring and energy management devices.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing regional market with projected growth rates exceeding 25% annually. China dominates manufacturing and deployment volumes, while Japan and South Korea lead in technology innovation and advanced applications. India shows significant potential in smart city initiatives and agricultural IoT applications.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa emerge as high-potential markets with increasing telecommunications infrastructure investments. These regions focus primarily on utility applications and basic connectivity solutions, with growing interest in smart agriculture and environmental monitoring applications.
Competitive landscape analysis reveals a diverse ecosystem of established telecommunications equipment vendors, specialized IoT companies, and emerging technology providers competing across different market segments and geographic regions.
Strategic positioning varies among competitors, with some focusing on cost-effective, high-volume modules while others emphasize specialized solutions for specific vertical markets. Partnership strategies play crucial roles in market success, with leading companies forming alliances with network operators, system integrators, and application developers.
Innovation focus areas include power optimization, security enhancement, and integration of edge computing capabilities. Companies invest heavily in research and development to maintain competitive advantages and address evolving customer requirements.
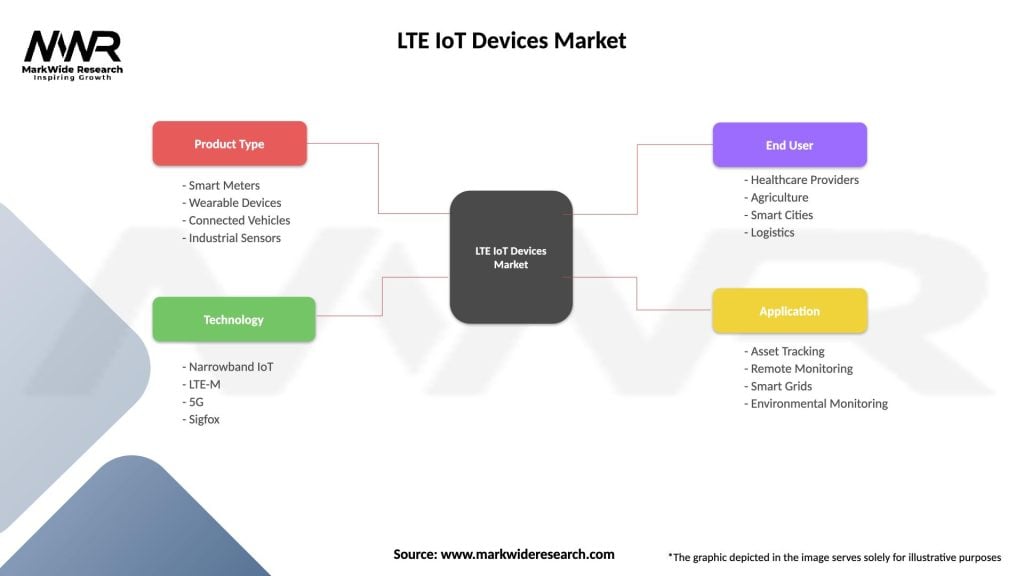
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct categories based on technology type, application, device type, and end-user industry, each demonstrating unique growth patterns and requirements.
By Technology:
By Device Type:
By Application:
Smart utilities category dominates LTE IoT devices adoption with 40% market share, driven by global smart meter deployment programs and grid modernization initiatives. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) projects create substantial volume opportunities for NB-IoT devices optimized for long battery life and reliable connectivity. Utility companies prioritize devices with 15-20 year operational lifespans and minimal maintenance requirements.
Asset tracking applications demonstrate strong growth with increasing adoption in logistics, transportation, and supply chain management. LTE-M technology proves particularly suitable for mobile tracking applications requiring regular location updates and moderate data transmission. The category benefits from growing e-commerce volumes and supply chain visibility requirements.
Industrial IoT applications show rapid expansion in manufacturing, oil and gas, and mining sectors. Predictive maintenance use cases drive demand for ruggedized devices capable of operating in harsh industrial environments. The integration of edge computing capabilities enables real-time decision making and reduces dependency on cloud connectivity.
Smart city initiatives create diverse opportunities across traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety applications. Multi-sensor devices combining air quality, noise, and traffic monitoring capabilities gain popularity among municipal customers seeking comprehensive urban intelligence solutions.
Healthcare applications emerge as high-growth category with remote patient monitoring and medical asset tracking driving adoption. Regulatory compliance requirements and data security considerations influence device selection and deployment strategies in healthcare environments.
Device manufacturers benefit from expanding market opportunities across multiple vertical segments and geographic regions. The standardization of LTE IoT technologies reduces development costs and enables global product strategies. Economies of scale in module production drive cost reductions and improve profit margins for high-volume applications.
Network operators gain new revenue streams from IoT connectivity services while leveraging existing LTE infrastructure investments. Service differentiation opportunities include managed connectivity, device management, and value-added analytics services. The massive scale of IoT deployments creates sustainable, recurring revenue models.
System integrators benefit from growing demand for end-to-end IoT solutions combining devices, connectivity, and application platforms. Vertical specialization enables premium pricing for industry-specific expertise and customized solutions. Partnership opportunities with device manufacturers and network operators create comprehensive service offerings.
End-user organizations achieve operational efficiency improvements, cost reductions, and new business model opportunities through LTE IoT device deployments. Data-driven insights from connected devices enable better decision making and process optimization. The reliability and security of cellular connectivity provide confidence for mission-critical applications.
Technology providers including chipset manufacturers, software companies, and platform providers benefit from the expanding ecosystem requirements. Innovation opportunities in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and security create competitive advantages and premium value propositions.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Technology convergence emerges as a dominant trend with LTE IoT devices increasingly incorporating multiple connectivity options including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and satellite communications. Hybrid connectivity approaches enable optimal network selection based on application requirements, coverage availability, and cost considerations. This trend addresses the diverse connectivity needs of complex IoT deployments.
Edge intelligence integration transforms LTE IoT devices from simple connectivity endpoints to intelligent edge computing nodes. On-device processing capabilities reduce latency, minimize bandwidth usage, and enable autonomous operation during connectivity disruptions. Machine learning algorithms embedded in devices provide predictive analytics and automated decision-making capabilities.
Security enhancement becomes paramount with hardware-based security features becoming standard across device categories. Zero-trust security models influence device design with built-in encryption, secure boot processes, and tamper detection capabilities. The integration of blockchain technology for device identity and data integrity gains traction in high-security applications.
Sustainability focus drives development of environmentally friendly devices with recyclable materials, energy harvesting capabilities, and carbon footprint optimization. Circular economy principles influence device lifecycle management with emphasis on repairability, upgradability, and end-of-life recycling programs.
Platform integration trends show increasing demand for devices that seamlessly connect with cloud platforms, enterprise software, and analytics tools. API-first design approaches enable rapid integration and customization for specific customer requirements.
Recent industry developments highlight the dynamic nature of the LTE IoT devices market with significant technological advances and strategic initiatives shaping future growth trajectories. 5G network rollouts accelerate globally, creating enhanced capabilities for massive IoT deployments while maintaining backward compatibility with existing LTE IoT devices.
Standardization progress by 3GPP continues with Release 17 and beyond introducing new features for industrial IoT, enhanced positioning services, and improved power efficiency. RedCap (Reduced Capability) technology development bridges the gap between traditional LTE IoT and full 5G capabilities, addressing mid-tier IoT applications.
Strategic partnerships between major technology companies create comprehensive IoT ecosystems. MarkWide Research analysis indicates increasing collaboration between chipset manufacturers, device makers, and cloud platform providers to deliver integrated solutions. These partnerships accelerate time-to-market and reduce integration complexity for end customers.
Investment activities include significant funding for IoT startups focusing on specialized applications and vertical market solutions. Acquisition trends show established companies acquiring innovative IoT technology providers to enhance their product portfolios and market reach.
Regulatory developments include spectrum allocation decisions, security requirements, and environmental regulations that influence device design and deployment strategies. The introduction of new certification processes and compliance requirements creates both challenges and opportunities for market participants.
Strategic recommendations for market participants emphasize the importance of vertical market specialization and comprehensive solution offerings. Device manufacturers should focus on developing industry-specific variants that address unique requirements in healthcare, industrial, and smart city applications. Investment in edge computing capabilities and AI integration will differentiate products in competitive markets.
Partnership strategies prove crucial for success, with recommendations for collaboration across the value chain including chipset providers, network operators, and system integrators. Ecosystem participation in industry consortiums and standards organizations ensures alignment with technology evolution and customer requirements.
Geographic expansion strategies should prioritize emerging markets with growing telecommunications infrastructure and digitization initiatives. Localization efforts including regional partnerships, compliance with local regulations, and customization for regional requirements will drive market penetration.
Technology roadmap planning should incorporate 5G evolution, edge computing integration, and security enhancement priorities. Investment allocation recommendations include research and development for next-generation capabilities while maintaining cost competitiveness in current product lines.
Customer engagement strategies should emphasize total cost of ownership value propositions rather than initial device costs. Service offerings including device management, analytics, and support services create recurring revenue opportunities and strengthen customer relationships.
Future market outlook for LTE IoT devices remains highly positive with sustained growth expected across all major segments and geographic regions. Technology evolution toward 5G integration will enhance device capabilities while maintaining backward compatibility with existing LTE networks. The convergence of IoT, artificial intelligence, and edge computing creates unprecedented opportunities for innovative applications and business models.
Market expansion will be driven by increasing digitization across traditional industries and the emergence of new use cases in autonomous systems, smart infrastructure, and environmental monitoring. Volume growth projections indicate continued acceleration with billions of devices expected to be deployed globally over the next decade.
Technological advancement will focus on power efficiency improvements, security enhancements, and integration of advanced processing capabilities. Cost optimization through manufacturing scale and technology improvements will make LTE IoT devices accessible to broader market segments and price-sensitive applications.
Ecosystem maturity will simplify deployment processes and reduce integration complexity through standardized interfaces, comprehensive development tools, and proven reference designs. MWR projections suggest that market consolidation among smaller players will create opportunities for leading companies to expand market share and geographic reach.
Regulatory evolution will continue supporting market growth through spectrum allocation, standardization efforts, and policies promoting digital transformation and smart infrastructure development. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility will drive demand for energy-efficient, long-life IoT devices.
The LTE IoT devices market represents a transformative force in the global telecommunications and Internet of Things landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for connectivity, automation, and digital transformation across diverse industries. The convergence of mature cellular technology, standardized protocols, and growing enterprise digitization creates a robust foundation for sustained market growth and innovation.
Market dynamics indicate strong momentum driven by smart city initiatives, industrial automation requirements, and the need for reliable, wide-area connectivity solutions. The technology’s ability to leverage existing cellular infrastructure while providing optimized performance for IoT applications positions LTE IoT devices as a critical enabler for massive machine-type communications and Industry 4.0 implementations.
Future success in this market will depend on continued innovation in power efficiency, security enhancement, and edge computing integration. Companies that successfully navigate the evolving competitive landscape through strategic partnerships, vertical specialization, and comprehensive solution offerings will capture the greatest opportunities in this expanding market. The LTE IoT devices market stands poised for continued growth as organizations worldwide embrace connected technologies to drive operational efficiency, enable new business models, and create sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly digital economy.
What is LTE IoT Devices?
LTE IoT Devices refer to a category of devices that utilize Long-Term Evolution (LTE) technology to connect to the Internet of Things (IoT). These devices are designed for various applications, including smart cities, industrial automation, and connected vehicles.
What are the key players in the LTE IoT Devices Market?
Key players in the LTE IoT Devices Market include companies like Qualcomm, Ericsson, and Nokia, which are known for their advancements in LTE technology and IoT solutions. Other notable companies include Sierra Wireless and Gemalto, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the LTE IoT Devices Market?
The growth of the LTE IoT Devices Market is driven by the increasing demand for connected devices, advancements in LTE technology, and the expansion of smart city initiatives. Additionally, the need for efficient data transmission in various sectors, such as healthcare and transportation, contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the LTE IoT Devices Market face?
The LTE IoT Devices Market faces challenges such as security concerns related to data privacy and the high costs associated with deploying LTE infrastructure. Additionally, the fragmentation of standards and protocols can hinder interoperability among devices.
What opportunities exist in the LTE IoT Devices Market?
Opportunities in the LTE IoT Devices Market include the potential for growth in sectors like agriculture, where IoT devices can enhance monitoring and efficiency. Furthermore, the rise of 5G technology presents new avenues for innovation and improved connectivity.
What trends are shaping the LTE IoT Devices Market?
Trends shaping the LTE IoT Devices Market include the increasing integration of artificial intelligence for data analysis and decision-making, as well as the growing focus on energy-efficient devices. Additionally, the expansion of edge computing is enhancing the capabilities of LTE IoT Devices.
LTE IoT Devices Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Smart Meters, Wearable Devices, Connected Vehicles, Industrial Sensors |
| Technology | Narrowband IoT, LTE-M, 5G, Sigfox |
| End User | Healthcare Providers, Agriculture, Smart Cities, Logistics |
| Application | Asset Tracking, Remote Monitoring, Smart Grids, Environmental Monitoring |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the LTE IoT Devices Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at