444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The low-speed vehicle market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by various factors such as the increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions and the rising adoption of electric vehicles. Low-speed vehicles (LSVs) are compact vehicles that are designed for short-distance travel within a limited speed range. They are commonly used in residential communities, golf courses, resorts, and other similar settings.
Meaning
Low-speed vehicles are defined as motor vehicles that have a maximum speed capability between 20 to 25 miles per hour (mph). These vehicles are often equipped with safety features such as seat belts, headlights, and turn signals, allowing them to be driven on public roads with speed limits up to 35 mph. LSVs offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative for short-distance travel, contributing to reduced congestion and emissions in urban areas.
Executive Summary
The low-speed vehicle market has experienced substantial growth over the past few years, driven by factors such as the increasing emphasis on eco-friendly transportation and the growing popularity of electric vehicles. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the coming years, presenting significant opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders.
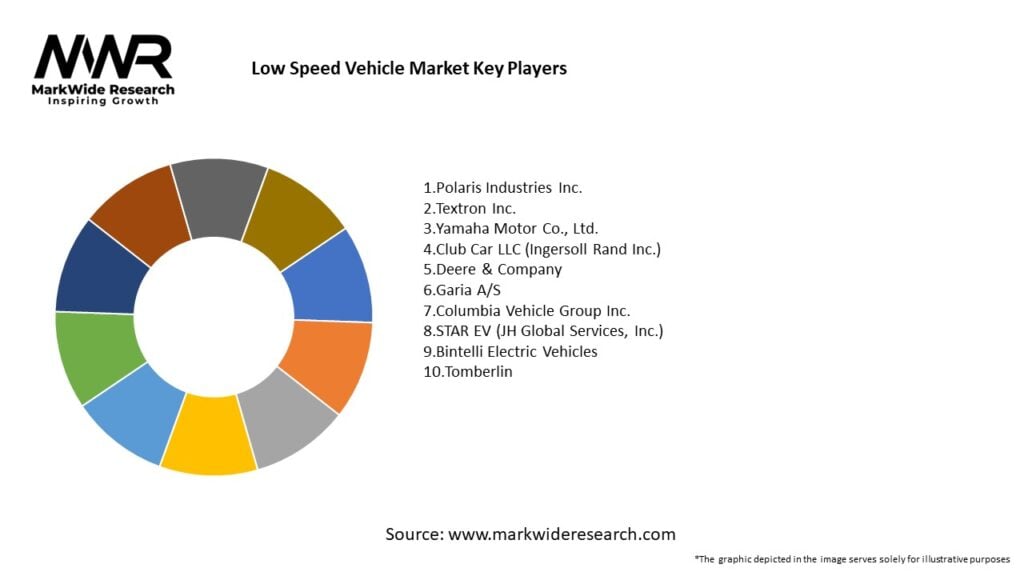
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
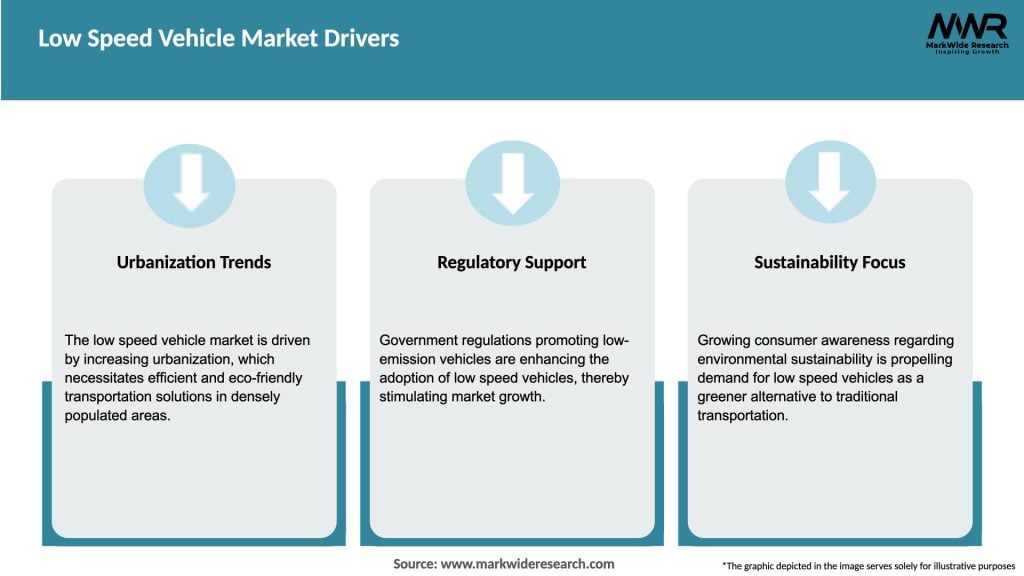
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The low-speed vehicle market is characterized by intense competition among manufacturers striving to innovate and differentiate their products. The market dynamics are influenced by various factors, including technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, consumer preferences, and environmental considerations.
The market is witnessing a shift towards electric low-speed vehicles due to their environmental advantages and the increasing emphasis on sustainable transportation. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to enhance the performance, range, and safety features of electric LSVs. Additionally, partnerships and collaborations between industry players and government agencies are promoting the adoption of low-speed vehicles in urban mobility plans.
Regional Analysis
The low-speed vehicle market exhibits regional variations in terms of adoption and market potential. North America and Europe have been at the forefront of LSV adoption, driven by stringent emission regulations, government incentives, and a strong emphasis on sustainable transportation. The presence of well-developed charging infrastructure and a favorable regulatory framework has contributed to the growth of the market in these regions.
Asia Pacific is emerging as a significant market for low-speed vehicles, primarily due to rapid urbanization, increasing pollution concerns, and supportive government policies. Countries like China, Japan, and India are witnessing a rise in the adoption of electric LSVs as part of their efforts to promote clean and green transportation solutions.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa region also present opportunities for low-speed vehicle manufacturers. The growing urban population, rising disposable income, and the need for affordable transportation options contribute to the market’s growth in these regions. However, the lack of charging infrastructure and limited awareness about low-speed vehicles pose challenges to their widespread adoption.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Low Speed Vehicle Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
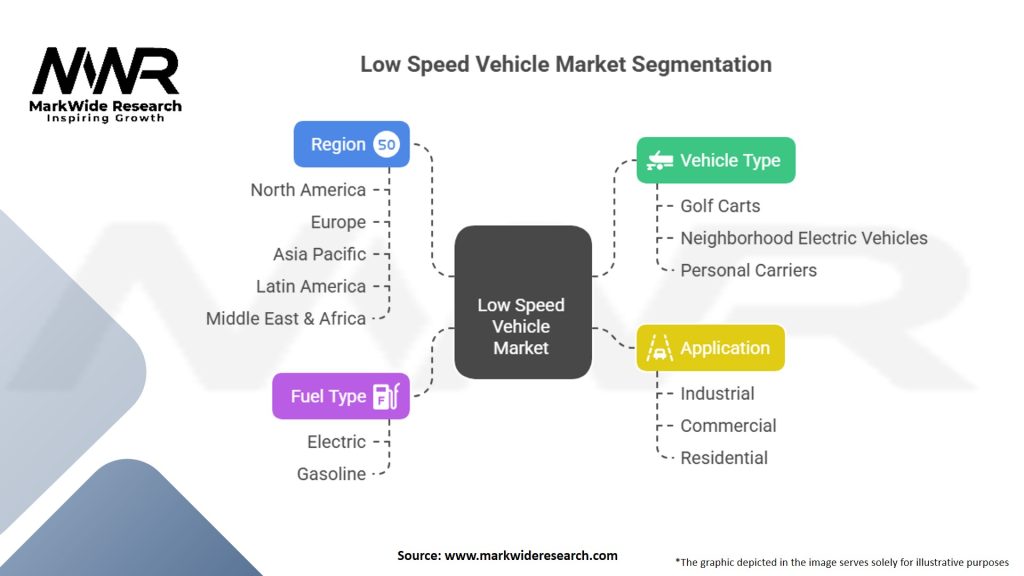
Segmentation
The low-speed vehicle market can be segmented based on vehicle type, power source, end-use industry, and region.
By vehicle type, the market can be categorized into golf carts, commercial turf utility vehicles, industrial utility vehicles, and personnel carriers.
Based on the power source, the market can be divided into electric LSVs and gasoline-powered LSVs.
In terms of end-use industry, the market finds applications in residential communities, golf courses, resorts, airports, educational institutions, industrial facilities, and others.
Geographically, the market can be segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had a mixed impact on the low-speed vehicle market. While the global lockdowns and restrictions initially led to a slowdown in manufacturing and disrupted supply chains, the market quickly recovered as restrictions eased. The pandemic highlighted the need for sustainable transportation options and increased the focus on personal mobility. This, in turn, drove the demand for low-speed vehicles, particularly electric ones, as individuals sought efficient and eco-friendly modes of transportation.
The pandemic also led to a surge in e-commerce and home deliveries, creating opportunities for low-speed vehicle applications in last-mile logistics. The market witnessed increased demand for commercial turf utility vehicles and industrial utility vehicles as businesses adapted to changing consumer behaviors.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the low-speed vehicle market looks promising, driven by factors such as the increasing demand for sustainable transportation, advancements in electric vehicle technology, and supportive government initiatives. The market is expected to witness significant growth, with electric LSVs gaining prominence over gasoline-powered counterparts.
Manufacturers will continue to focus on product innovation, safety enhancements, and customization options to cater to diverse consumer preferences. The expansion of charging infrastructure and the integration of advanced technologies will further contribute to market growth. With increased urbanization and the need for efficient mobility solutions, low-speed vehicles are poised to play a significant role in the future of transportation.
Conclusion
The low-speed vehicle market is witnessing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions and the growing adoption of electric vehicles. Low-speed vehicles offer cost advantages, reduce environmental impact, and find versatile applications across various industries and settings.
While there are challenges such as limited speed and range, safety concerns, and the need for charging infrastructure, the market presents significant opportunities for industry participants and stakeholders. Collaborations, technological advancements, and favorable government policies will shape the future of the low-speed vehicle market, leading to a more sustainable and efficient transportation landscape.
What is Low Speed Vehicle?
Low Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are small, electric or gas-powered vehicles designed for low-speed travel, typically under twenty-five miles per hour. They are commonly used in residential areas, golf courses, and campuses for short-distance transportation.
What are the key players in the Low Speed Vehicle Market?
Key players in the Low Speed Vehicle Market include Polaris Industries, Club Car, and GEM, which manufacture a range of electric and gas-powered low-speed vehicles for various applications, including personal transport and utility purposes, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Low Speed Vehicle Market?
The growth of the Low Speed Vehicle Market is driven by increasing urbanization, the demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions, and the rising popularity of electric vehicles. Additionally, government incentives for low-emission vehicles contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the Low Speed Vehicle Market face?
The Low Speed Vehicle Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, limited speed capabilities that restrict usage, and competition from traditional vehicles. These factors can hinder widespread adoption in certain regions.
What opportunities exist in the Low Speed Vehicle Market?
Opportunities in the Low Speed Vehicle Market include the development of advanced battery technologies, expansion into new geographic markets, and increasing demand for sustainable transport solutions in urban areas. These factors can enhance market growth and innovation.
What trends are shaping the Low Speed Vehicle Market?
Trends in the Low Speed Vehicle Market include the integration of smart technologies for enhanced safety and connectivity, the rise of shared mobility services, and a growing focus on sustainability. These trends are influencing consumer preferences and shaping future vehicle designs.
Low Speed Vehicle Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Type | Golf Carts, Neighborhood Electric Vehicles, Personal Carriers |
| Fuel Type | Electric, Gasoline |
| Application | Industrial, Commercial, Residential |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Low Speed Vehicle Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at