444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The long-term care market is a rapidly evolving sector that provides essential services and support to individuals who require assistance with their daily activities due to chronic illness, disability, or old age. Long-term care encompasses a wide range of services, including medical, social, and personal care, aiming to enhance the quality of life for those in need. The demand for long-term care services has been growing steadily in recent years, driven by various factors such as an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and changing healthcare needs.
Meaning
Long-term care refers to a continuum of services designed to support individuals who have functional limitations and need assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs) or instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) over an extended period. ADLs include basic self-care tasks like bathing, dressing, eating, toileting, and transferring, while IADLs involve more complex activities such as housekeeping, meal preparation, managing finances, and medication management. Long-term care can be provided in different settings, including nursing homes, assisted living facilities, home healthcare, and community-based care programs.
Executive Summary
The long-term care market is experiencing significant growth and transformation as the need for comprehensive care and support services continues to rise. This sector plays a crucial role in addressing the healthcare needs of the aging population and individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities. The market offers a diverse range of services and solutions to cater to the unique requirements of each individual, aiming to promote independence, dignity, and improved quality of life. As the demand for long-term care services increases, there is a growing focus on enhancing service delivery models, improving care coordination, and integrating technology to optimize outcomes.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The long-term care market is characterized by a complex interplay of various factors that influence its dynamics. These factors include demographic trends, healthcare policies, technological advancements, financial considerations, and consumer preferences. Understanding and navigating these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders in the long-term care industry to adapt and thrive in a rapidly evolving market landscape. The market dynamics are shaped by the interactions between demand and supply, regulatory environments, economic factors, and societal changes.
Regional Analysis
The long-term care market exhibits regional variations influenced by demographic, economic, and cultural factors. The demand for long-term care services is often higher in regions with aging populations and a higher prevalence of chronic diseases. Additionally, healthcare policies, reimbursement mechanisms, and cultural attitudes towards aging and care impact the delivery and utilization of long-term care services. It is essential for market participants to conduct thorough regional analyses to understand the specific dynamics and opportunities in each market.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Long Term Care Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

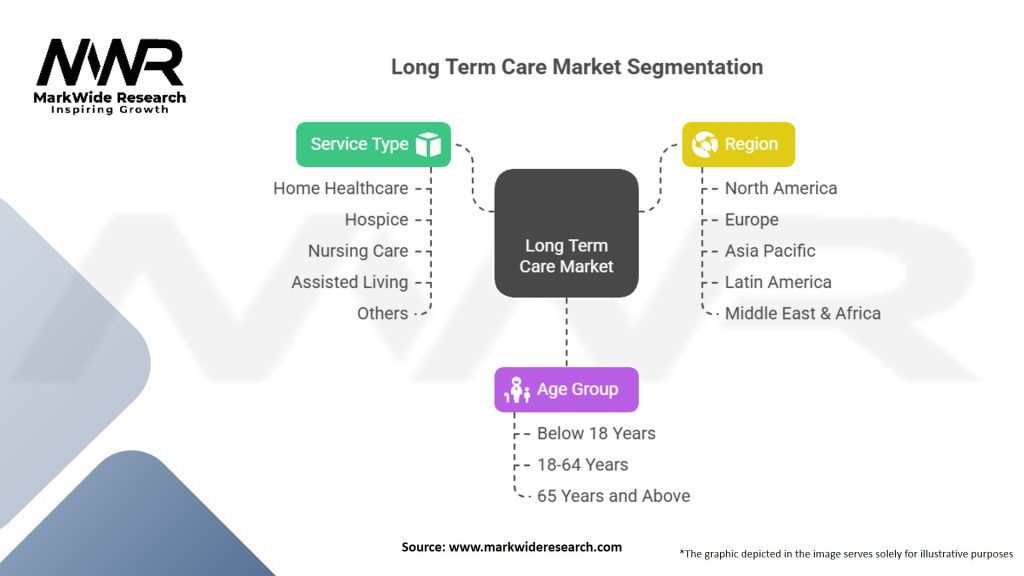
Segmentation
The long-term care market can be segmented based on various factors, including service type, setting, and geography. Service types may include skilled nursing care, personal care assistance, therapy services, hospice care, and social support services. Settings can range from institutional care facilities to home-based care and community-based programs. Geographically, the market can be segmented into regions, countries, or even specific localities, considering the variations in healthcare systems and cultural norms.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis provides a comprehensive assessment of the internal and external factors influencing a business or industry. In the context of the long-term care market, a SWOT analysis may reveal the following:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the long-term care market. Nursing homes and other long-term care facilities became hotspots for the transmission of the virus, leading to high infection rates and mortality among vulnerable populations. The pandemic highlighted the need for infection control measures, adequate staffing, and robust emergency preparedness protocols in long-term care settings. It also accelerated the adoption of telehealth services and remote monitoring technologies to minimize in-person interactions and maintain continuity of care. The pandemic served as a catalyst for change, prompting industry participants and policymakers to reevaluate and strengthen the resilience of long-term care systems.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the long-term care market holds both opportunities and challenges. With the aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the demand for long-term care services will continue to grow. The integration of technology, emphasis on person-centered care, and expansion of home-based care models will shape the future landscape of the industry. However, workforce shortages, financial considerations, regulatory complexities, and the need to address disparities in access to care will require ongoing attention and innovative solutions. The long-term care market has the potential to play a critical role in meeting the evolving healthcare needs of individuals, enhancing quality of life, and ensuring dignified care for those in need.
Conclusion
The long-term care market is a dynamic and evolving sector that addresses the healthcare needs of individuals requiring assistance with daily activities due to chronic illness, disability, or old age. The market is driven by factors such as an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and changing healthcare needs. While there are challenges related to cost, workforce shortages, and regulatory complexities, the market offers significant opportunities for growth and innovation. Embracing technological advancements, enhancing care coordination, and focusing on person-centered care will be key to success in the long-term care industry. As the demand for long-term care services continues to rise, stakeholders in the market should adapt and innovate to meet the evolving needs of individuals, improve outcomes, and foster a culture of high-quality, patient-centered care.
What is Long Term Care?
Long Term Care refers to a range of services designed to meet the medical and non-medical needs of individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities. This care can be provided in various settings, including nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and in-home care.
What are the key players in the Long Term Care Market?
Key players in the Long Term Care Market include Brookdale Senior Living, Amedisys, Inc., and Genesis HealthCare, among others. These companies provide a variety of services, including skilled nursing, rehabilitation, and personal care services.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Long Term Care Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Long Term Care Market include the aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and a growing preference for home-based care solutions. These factors contribute to a rising demand for long-term care services.
What challenges does the Long Term Care Market face?
The Long Term Care Market faces challenges such as workforce shortages, regulatory compliance issues, and the rising costs of care. These challenges can impact the availability and quality of long-term care services.
What opportunities exist in the Long Term Care Market?
Opportunities in the Long Term Care Market include the development of innovative care models, integration of technology in service delivery, and expansion into underserved regions. These opportunities can enhance service efficiency and accessibility.
What trends are shaping the Long Term Care Market?
Trends shaping the Long Term Care Market include a shift towards personalized care plans, increased use of telehealth services, and a focus on wellness and preventive care. These trends aim to improve patient outcomes and enhance the overall care experience.
Long Term Care Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Home Healthcare, Hospice, Nursing Care, Assisted Living, Others |
| Age Group | Below 18 Years, 18-64 Years, 65 Years and Above |
| Region | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Long Term Care Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at