444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The locomotive parking brake market plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and operational efficiency of rail transport systems. Locomotives, as powerful and heavy vehicles, require robust parking brake systems to secure them during stationary periods. These braking systems contribute to preventing unintended movements, ensuring the safety of both railway personnel and passengers. The market for locomotive parking brakes encompasses a range of technologies and innovations aimed at enhancing braking efficiency and meeting evolving safety standards.
Meaning
A locomotive parking brake is a specialized braking system designed for securing locomotives in a stationary position when not in motion. Unlike dynamic or service brakes used during train operation, parking brakes are engaged when the locomotive is parked or stationary. These brakes are crucial for preventing unintended rolling or movement, especially when the locomotive is stationed on an incline or at a platform for loading and unloading operations.
Executive Summary
The locomotive parking brake market is witnessing advancements driven by the need for enhanced safety features, compliance with industry regulations, and the integration of modern technologies. The efficient functioning of parking brakes is essential not only for safety but also for preventing damage to locomotives and surrounding infrastructure. As the global railway industry undergoes transformations to meet the demands of modern transportation, the locomotive parking brake market becomes a focal point for innovation and development.
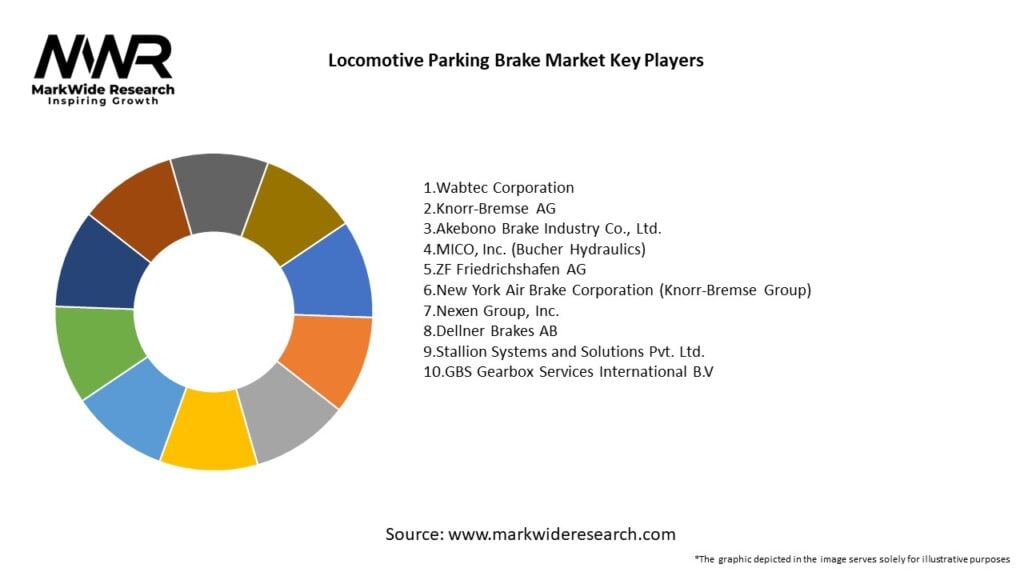
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The locomotive parking brake market operates within a dynamic environment shaped by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, market competition, and the evolving needs of the railway industry. Navigating these dynamics requires a strategic approach to capitalize on opportunities and address challenges effectively.
Regional Analysis
The demand for locomotive parking brakes varies across regions based on factors such as the extent of railway networks, urbanization levels, and the regulatory landscape.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Locomotive Parking Brake Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
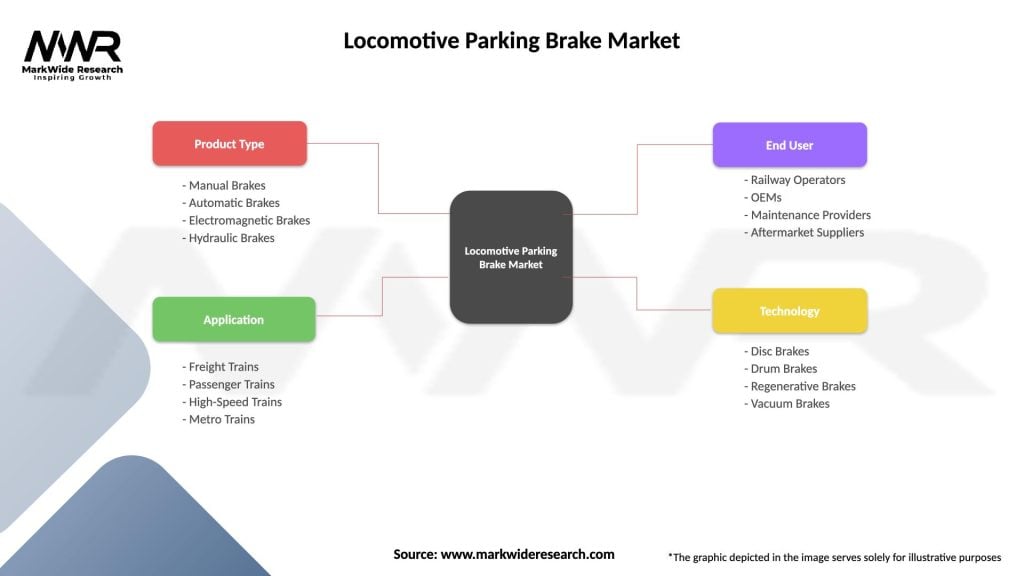
Segmentation
The locomotive parking brake market can be segmented based on various factors to provide a comprehensive understanding of its dynamics:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides a strategic overview of the locomotive parking brake market:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had varying impacts on the locomotive parking brake market. While some regions experienced disruptions in railway operations and projects, the essential nature of freight transportation and the resilience of the railway industry contributed to the market’s stability. The pandemic also underscored the importance of safety and efficient braking systems in ensuring the reliability of transportation networks.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the locomotive parking brake market is optimistic, driven by the continual emphasis on safety, technological advancements, and the expansion of railway networks globally. The industry’s ability to adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes, embrace innovations, and collaborate on research and development initiatives will shape its growth trajectory.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the locomotive parking brake market plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and operational efficiency of railway systems. As the industry evolves to meet modern transportation needs, the demand for advanced parking brake solutions continues to grow. Industry participants must navigate challenges such as resistance to technology adoption and high initial costs while capitalizing on opportunities presented by global infrastructure projects and the need for retrofitting existing fleets. By prioritizing safety, embracing innovation, and collaborating on research and development, the locomotive parking brake market can contribute to the advancement of efficient, sustainable, and safe rail transport systems.
What is Locomotive Parking Brake?
A Locomotive Parking Brake is a safety mechanism used to secure a locomotive when it is not in operation, preventing it from rolling or moving unintentionally. It is crucial for ensuring the safety of both the equipment and personnel in rail operations.
What are the key players in the Locomotive Parking Brake Market?
Key players in the Locomotive Parking Brake Market include Wabtec Corporation, Knorr-Bremse AG, and Faiveley Transport, among others. These companies are known for their innovative braking solutions and contributions to rail safety.
What are the growth factors driving the Locomotive Parking Brake Market?
The growth of the Locomotive Parking Brake Market is driven by increasing rail transport activities, advancements in braking technologies, and a growing emphasis on safety regulations in the rail industry. Additionally, the expansion of freight and passenger rail networks contributes to market demand.
What challenges does the Locomotive Parking Brake Market face?
The Locomotive Parking Brake Market faces challenges such as the high costs associated with advanced braking systems and the need for regular maintenance and inspections. Additionally, competition from alternative transport modes can impact market growth.
What opportunities exist in the Locomotive Parking Brake Market?
Opportunities in the Locomotive Parking Brake Market include the development of smart braking systems and the integration of IoT technologies for enhanced monitoring and control. Furthermore, increasing investments in rail infrastructure present significant growth potential.
What trends are shaping the Locomotive Parking Brake Market?
Trends in the Locomotive Parking Brake Market include the shift towards automated braking systems and the adoption of lightweight materials to improve efficiency. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of rail operations.
Locomotive Parking Brake Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Manual Brakes, Automatic Brakes, Electromagnetic Brakes, Hydraulic Brakes |
| Application | Freight Trains, Passenger Trains, High-Speed Trains, Metro Trains |
| End User | Railway Operators, OEMs, Maintenance Providers, Aftermarket Suppliers |
| Technology | Disc Brakes, Drum Brakes, Regenerative Brakes, Vacuum Brakes |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at