444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
Market Overview
The LNG infrastructure market refers to the physical facilities and systems required for the liquefaction, transportation, storage, and regasification of liquefied natural gas (LNG). LNG is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state, reducing its volume for easier storage and transportation. The demand for LNG has been steadily increasing due to its cleaner burning properties compared to other fossil fuels, making it an attractive alternative for power generation and transportation.
Meaning
LNG infrastructure encompasses a range of components, including LNG liquefaction plants, LNG carriers, LNG storage tanks, LNG regasification terminals, and associated pipelines. These facilities and systems are essential for the efficient and reliable supply of LNG from production sources to end-users. The development of LNG infrastructure is a complex and capital-intensive process, involving significant investments from both public and private entities.
Executive Summary
The LNG infrastructure market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing global demand for natural gas and the growing importance of clean energy sources. The market is characterized by the presence of key players who are involved in the design, construction, and operation of LNG infrastructure projects. These players collaborate with governments, energy companies, and financial institutions to develop and expand LNG infrastructure networks.
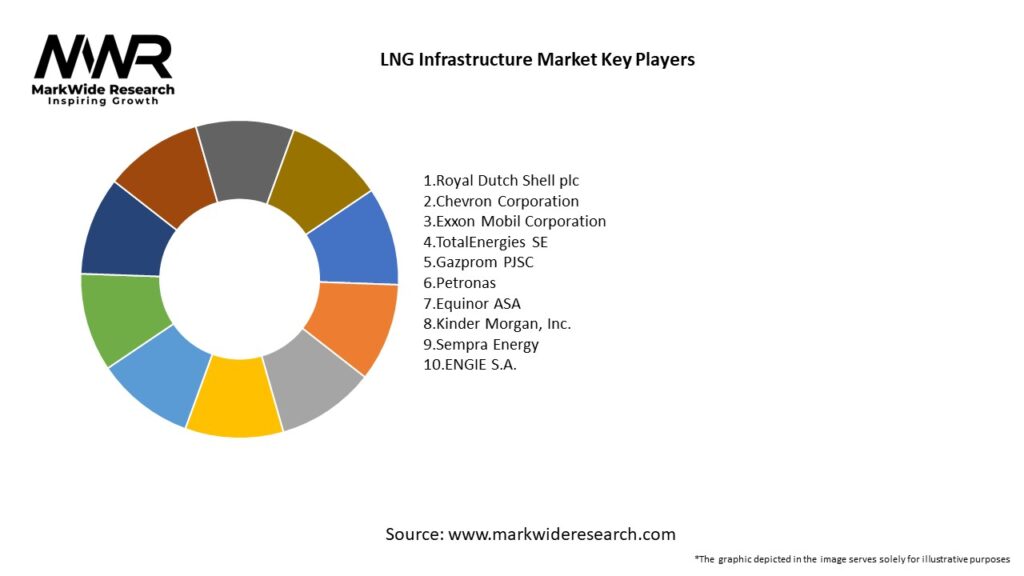
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
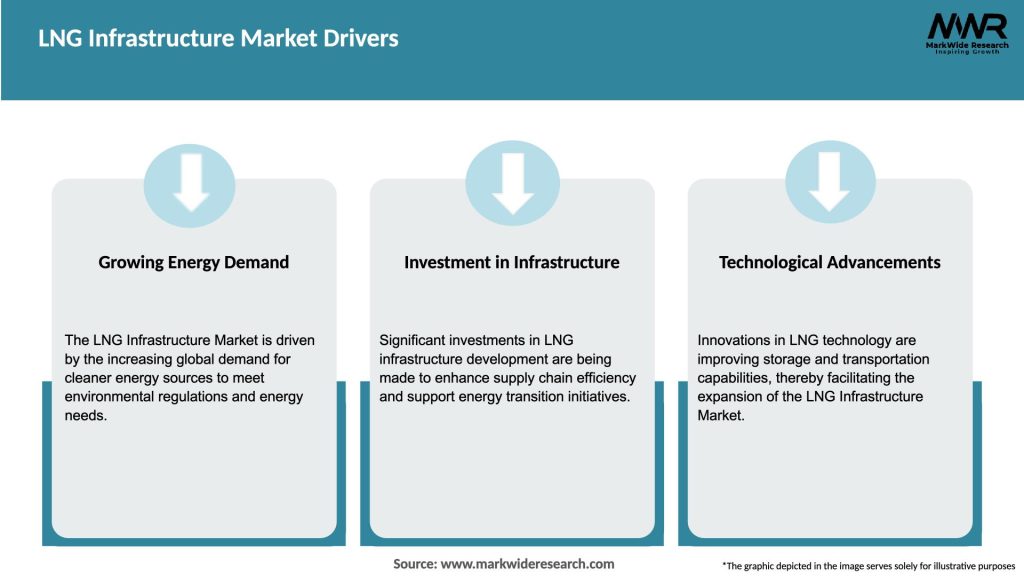
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The LNG infrastructure market is influenced by various dynamics, including technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, geopolitical factors, and market competition. These dynamics shape the development and growth of LNG infrastructure projects globally, impacting both supply and demand.
Regional Analysis
The development of LNG infrastructure varies across regions due to differences in natural gas reserves, energy policies, market demand, and infrastructure capabilities. Key regions driving the growth of the LNG infrastructure market include:
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the LNG Infrastructure Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The LNG infrastructure market can be segmented based on various factors, including infrastructure type, end-use sector, and geography.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The LNG infrastructure market offers several benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis of the LNG infrastructure market provides valuable insights into its internal and external factors:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic had both short-term and long-term impacts on the LNG infrastructure market:
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the LNG infrastructure market looks promising, driven by factors such as the increasing demand for clean energy, the availability of abundant natural gas reserves, and the ongoing energy transition. Key trends, including the rise of floating LNG facilities, small-scale LNG infrastructure, and the integration of renewable natural gas, will shape the market’s growth. However, challenges related to capital costs, regulatory frameworks, and environmental concerns need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of LNG infrastructure.
Conclusion
The LNG infrastructure market is experiencing significant growth as the demand for clean energy rises globally. LNG infrastructure plays a critical role in the production, transportation, storage, and regasification of LNG, enabling its use in power generation, industrial applications, and transportation. While the market offers numerous opportunities, it also presents challenges such as high capital costs, regulatory complexities, and environmental considerations. By embracing technological advancements, sustainability practices, and strategic collaborations, the industry can overcome these challenges and pave the way for a sustainable and efficient LNG infrastructure network in the future.
What is LNG Infrastructure?
LNG Infrastructure refers to the facilities and systems required for the production, storage, transportation, and regasification of liquefied natural gas. This includes LNG terminals, pipelines, and storage tanks that enable the efficient handling of LNG for various applications, such as power generation and industrial use.
What are the key players in the LNG Infrastructure Market?
Key players in the LNG Infrastructure Market include companies like Cheniere Energy, Royal Dutch Shell, and TotalEnergies, which are involved in various aspects of LNG production and distribution. These companies are significant contributors to the development of LNG terminals and related infrastructure, among others.
What are the main drivers of the LNG Infrastructure Market?
The LNG Infrastructure Market is driven by the increasing demand for cleaner energy sources, the expansion of natural gas consumption in emerging economies, and the need for energy security. Additionally, investments in LNG export facilities and regasification terminals are boosting market growth.
What challenges does the LNG Infrastructure Market face?
Challenges in the LNG Infrastructure Market include high capital costs associated with building and maintaining infrastructure, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative energy sources. These factors can impact project timelines and investment decisions.
What opportunities exist in the LNG Infrastructure Market?
Opportunities in the LNG Infrastructure Market include the potential for expanding LNG trade routes, the development of small-scale LNG facilities, and advancements in technology that improve efficiency and reduce emissions. These factors can enhance the market’s growth prospects.
What trends are shaping the LNG Infrastructure Market?
Trends in the LNG Infrastructure Market include the increasing adoption of floating LNG technology, the rise of LNG as a marine fuel, and the integration of digital technologies for monitoring and optimization. These trends are transforming how LNG is produced and utilized across various sectors.
LNG Infrastructure Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Liquefaction, Regasification, Storage, Transportation |
| Technology | Membrane, Cascade, Mixed Refrigerant, Air Products |
| End User | Utilities, Industrial, Marine, Power Generation |
| Application | Power Plants, Shipping, Heating, Industrial Processes |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the LNG Infrastructure Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at