444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2750
Market Overview: The LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market emerges as a transformative force in the realm of sustainable transportation. As the world grapples with the imperative to reduce carbon emissions, hydrogen fuel cell trains represent a promising solution for the rail transport sector. These trains leverage hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional diesel-powered locomotives.
Meaning: Hydrogen fuel cell trains operate on the principle of converting hydrogen gas into electricity through fuel cells. This electricity powers the train’s electric motors, propelling it forward. Unlike diesel trains that emit harmful pollutants, hydrogen fuel cell trains produce only water vapor as a byproduct, making them a environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
Executive Summary: The LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market is witnessing a surge in interest and investment as countries in the region seek sustainable alternatives for their rail networks. The market’s growth is fueled by the global push towards decarbonization, with hydrogen fuel cell trains emerging as a viable solution for reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector. As the market evolves, key players are collaborating to address challenges and unlock the full potential of hydrogen fuel cell trains.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
Market Dynamics: The LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market operates within dynamic dynamics shaped by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, public perception, and global trends in sustainable transportation. Navigating these dynamics requires strategic collaboration and a forward-looking approach to meet the evolving needs of the market.
Regional Analysis: The market’s landscape varies across the LAMEA region, with countries taking distinct approaches to hydrogen fuel cell train adoption. Let’s explore key regions:
Latin America: Countries like Brazil and Mexico are showing interest in hydrogen fuel cell trains, driven by environmental concerns and the pursuit of sustainable transportation solutions. Pilot projects and feasibility studies are underway to assess the viability of hydrogen fuel cell trains in the region.
Middle East: The Middle East, with its abundant renewable energy resources, is exploring hydrogen as a key component of its energy transition. Hydrogen fuel cell trains align with the region’s ambitions to diversify its energy mix and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Africa: Some African nations are considering hydrogen fuel cell trains as part of their efforts to modernize rail infrastructure and promote sustainable development. Collaboration with international partners is aiding the integration of this technology into Africa’s transportation landscape.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
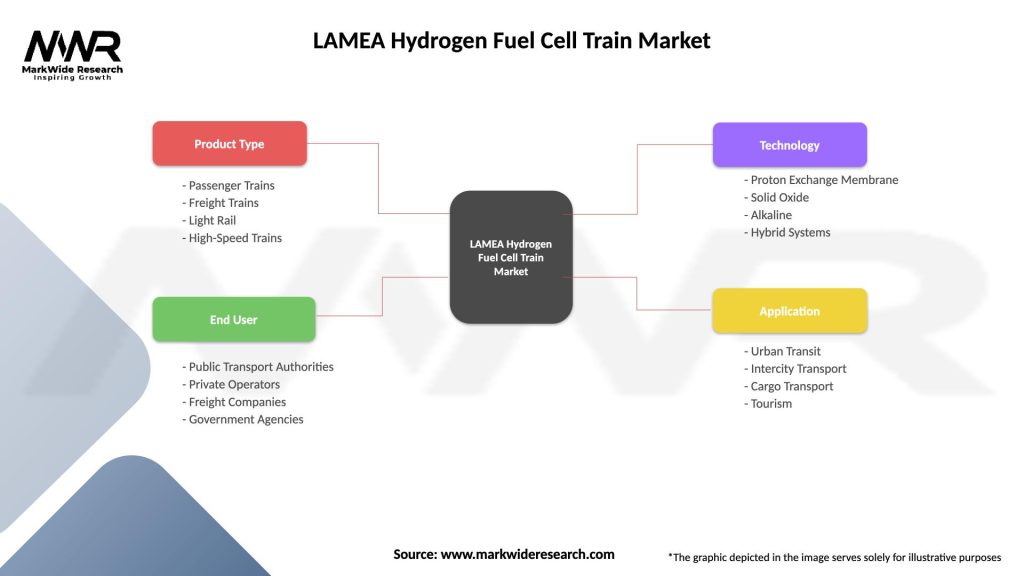
Segmentation: The LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market can be segmented based on various factors:
Category-wise Insights:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis provides an overview of the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of resilient and sustainable transportation systems. While the initial phase of the pandemic may have slowed down certain projects, the focus on environmental sustainability and the need for cleaner modes of transport have accelerated the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell trains post-pandemic. Governments and industry stakeholders are recognizing the role of hydrogen fuel cell trains in building more resilient and eco-friendly transportation networks.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook: The future of the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market looks promising, driven by a collective commitment to sustainable transportation solutions. As technology matures, infrastructure develops, and public acceptance grows, hydrogen fuel cell trains are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of rail transport in the region. The market’s trajectory will be influenced by ongoing research, policy frameworks, and strategic investments in a hydrogen-powered future.
Conclusion: The LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market represents a paradigm shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly rail transportation. With the potential to revolutionize the region’s rail networks, hydrogen fuel cell trains align with global efforts to combat climate change and reduce dependence on conventional fossil fuels. As governments, industry players, and the public rally behind the transition to cleaner modes of transport, the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market stands at the forefront of a transformative journey towards a greener and more sustainable future.
What is Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train?
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train refers to a type of train that uses hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, which powers the train’s electric motors. This technology is considered a cleaner alternative to traditional diesel-powered trains, contributing to reduced emissions and improved energy efficiency.
What are the key players in the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market?
Key players in the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market include Alstom, Siemens, and Bombardier, which are actively developing and deploying hydrogen fuel cell technology for rail applications. These companies are focusing on enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of train operations, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market?
The growth of the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market is driven by increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions, government initiatives promoting clean energy, and advancements in hydrogen fuel cell technology. Additionally, the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the transportation sector is a significant factor.
What challenges does the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market face?
The LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs, limited hydrogen infrastructure, and competition from other alternative fuel technologies. These factors can hinder the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell trains in the region.
What opportunities exist in the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market?
Opportunities in the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market include the potential for partnerships between governments and private companies to develop hydrogen infrastructure, as well as the growing interest in green technologies among consumers. Additionally, advancements in fuel cell technology may lead to more efficient and cost-effective solutions.
What trends are shaping the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market?
Trends shaping the LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market include increasing investments in renewable energy sources, the development of hybrid systems combining hydrogen and battery technologies, and a focus on reducing the carbon footprint of public transportation. These trends reflect a broader shift towards sustainable mobility solutions.
LAMEA Hydrogen Fuel Cell Train Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Passenger Trains, Freight Trains, Light Rail, High-Speed Trains |
| End User | Public Transport Authorities, Private Operators, Freight Companies, Government Agencies |
| Technology | Proton Exchange Membrane, Solid Oxide, Alkaline, Hybrid Systems |
| Application | Urban Transit, Intercity Transport, Cargo Transport, Tourism |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at