444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
The Kenya mobile money market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, revolutionizing the country’s financial landscape. Mobile money refers to the use of mobile phones to conduct financial transactions, such as payments, transfers, and savings. Kenya has emerged as a global leader in mobile money adoption, with its success story often attributed to the introduction of M-Pesa in 2007.
Meaning
Mobile money provides a convenient and accessible platform for individuals to manage their financial transactions without the need for a traditional bank account. It enables users to deposit money into a virtual wallet linked to their mobile number and perform various financial activities using their mobile phones. This technology has proven to be a game-changer, especially in developing countries like Kenya, where traditional banking services are limited.
Executive Summary
The Kenya mobile money market has experienced exponential growth over the years, driven by factors such as increasing smartphone penetration, a large unbanked population, and a robust telecommunications infrastructure. The market has become highly competitive, with numerous mobile money service providers vying for a significant share. Key players in the market include M-Pesa, Airtel Money, Equitel, and T-Kash.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
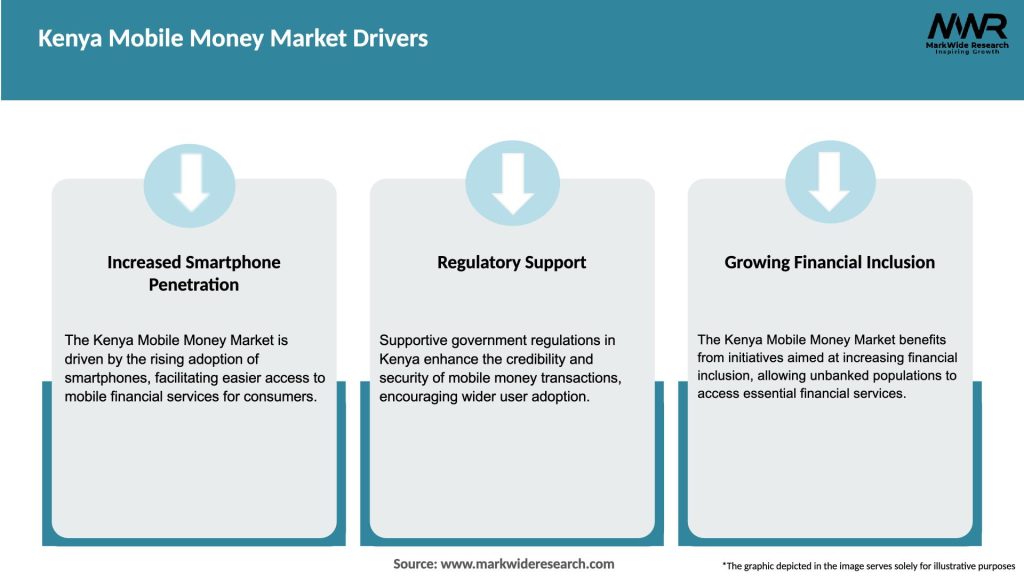
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities

Market Dynamics
The Kenya mobile money market is characterized by intense competition, rapid technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. Service providers are continuously innovating to offer new features and improve the user experience. Partnerships between mobile money providers, financial institutions, and other stakeholders are also driving market growth.
Regional Analysis
The mobile money market in Kenya is not limited to urban areas but has expanded to rural regions as well. The increased accessibility of mobile phones and network coverage has facilitated the adoption of mobile money services across the country. Rural areas, with their largely unbanked populations, offer untapped potential for further market expansion.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Kenya Mobile Money Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Segmentation
The Kenya mobile money market can be segmented based on user type, service type, and application.
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of mobile money services in Kenya. The need for contactless transactions and the closure of physical payment channels during lockdowns prompted more individuals and businesses to rely on mobile money for their financial needs. The pandemic also highlighted the importance of financial inclusion and the role of mobile money in providing access to essential services.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the Kenya mobile money market looks promising, with continued growth expected. Factors such as increasing smartphone penetration, government support for financial inclusion, and advancements in technology will fuel market expansion. The integration of mobile money with other sectors and the introduction of innovative services will further drive market growth and create new opportunities.
Conclusion
The Kenya mobile money market has transformed the financial landscape by providing convenient and accessible financial services to individuals and businesses. With its high adoption rates, the market offers immense opportunities for revenue generation and financial inclusion. Despite challenges such as security concerns and regulatory compliance, the market’s future looks promising, driven by technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and evolving consumer preferences. Mobile money providers must continue to innovate, expand their service offerings, and collaborate to unlock the full potential of this thriving market.
What is Kenya Mobile Money?
Kenya Mobile Money refers to the digital financial services that allow users to send, receive, and manage money through mobile devices. This system has transformed financial transactions in Kenya, enabling access to banking services for many who were previously unbanked.
Who are the key players in the Kenya Mobile Money Market?
Key players in the Kenya Mobile Money Market include Safaricom’s M-Pesa, Airtel Money, and Equitel. These companies have established significant market presence and offer various mobile financial services, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Kenya Mobile Money Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Kenya Mobile Money Market include the increasing smartphone penetration, the need for convenient financial transactions, and the growing acceptance of digital payments among consumers and businesses.
What challenges does the Kenya Mobile Money Market face?
Challenges in the Kenya Mobile Money Market include regulatory hurdles, security concerns regarding fraud and data breaches, and competition from emerging fintech solutions that may disrupt traditional mobile money services.
What opportunities exist for the future of the Kenya Mobile Money Market?
Opportunities for the future of the Kenya Mobile Money Market include expanding services to rural areas, integrating with e-commerce platforms, and leveraging blockchain technology to enhance security and transparency in transactions.
What trends are shaping the Kenya Mobile Money Market?
Trends shaping the Kenya Mobile Money Market include the rise of agent networks, increased collaboration between mobile operators and banks, and the growing use of mobile money for international remittances and cross-border transactions.
Kenya Mobile Money Market
| Segmentation | Details |
|---|---|
| Transaction Mode | Mobile Wallets, Mobile Money Apps |
| Transaction Type | Person-to-Person (P2P) Transfers, Bill Payments, Airtime Top-ups, Others |
| Country | Kenya |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Kenya Mobile Money Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at