444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Solar energy has gained significant momentum in Japan in recent years, emerging as a key source of renewable energy. The country’s commitment to reducing its dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change has propelled the growth of the solar energy market. Japan’s unique geographic location and favorable government policies have contributed to the rapid expansion of solar power installations across the nation.
Solar energy refers to the conversion of sunlight into usable electricity through the utilization of photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated solar power (CSP) systems. The sunlight is harnessed and converted into direct current (DC), which is then transformed into alternating current (AC) through inverters for consumption.
Executive Summary
The Japan solar energy market has experienced remarkable growth over the past decade. The increasing demand for clean energy, government incentives, and technological advancements have played pivotal roles in shaping the market. With a focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving energy security, Japan has established itself as one of the leading solar energy markets globally.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Japan solar energy market is characterized by dynamic factors that shape its growth trajectory. Government policies, technological advancements, market competition, and environmental concerns contribute to the evolving landscape of the industry. Continued innovation, research, and collaboration between stakeholders are essential for driving sustainable development in the market.
Regional Analysis
The Japan solar energy market exhibits regional variations in terms of solar irradiance, land availability, and government support. Southern regions of Japan, such as Kyushu and Okinawa, receive higher solar irradiation and have favorable conditions for solar power generation. However, solar installations can be found throughout the country, with varying capacities depending on regional factors.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the Japan Solar Energy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
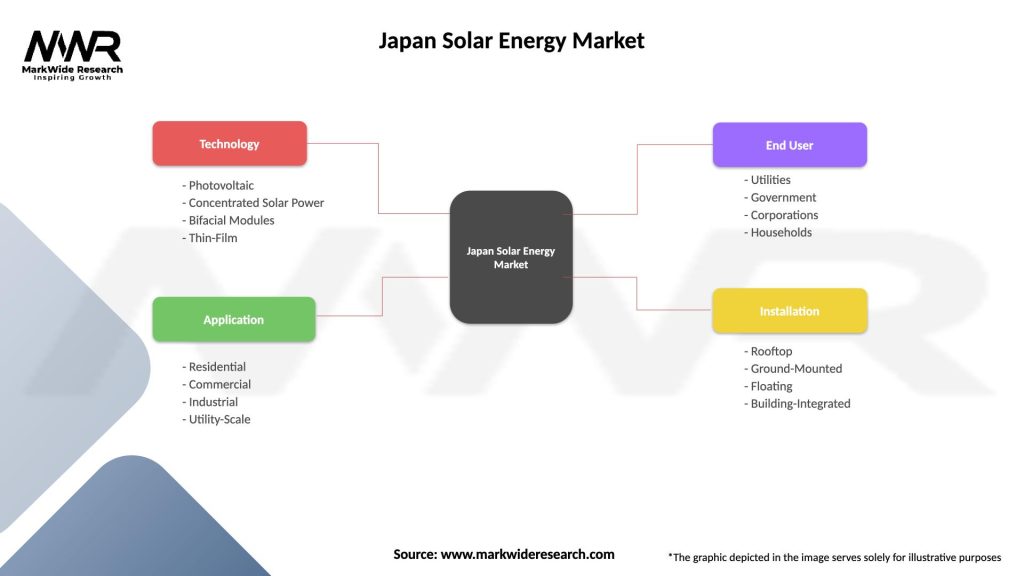
The Japan solar energy market can be segmented based on technology, application, and end-user.
Based on technology, the market can be categorized into:
On the basis of application, the market segments include:
Based on end-user, the market can be divided into:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
The Japan solar energy market offers numerous benefits for industry participants and stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had a temporary impact on the Japan solar energy market. Supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and delays in project installations were experienced. However, the market has shown resilience and is expected to recover as economic activities normalize and government support continues.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the Japan solar energy market looks promising, with significant growth opportunities. The government’s commitment to renewable energy, technological advancements, and increasing public awareness about environmental sustainability will continue to drive the market forward. Continued investments, research, and innovation will contribute to the expansion of solar power capacity and the integration of solar energy into the country’s energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
The Japan solar energy market has experienced remarkable growth and presents a promising outlook for the future. With favorable government policies, technological advancements, and increasing environmental concerns, solar power has emerged as a key player in the country’s energy transition. Collaborative efforts, innovation, and continued investments will pave the way for a sustainable and clean energy future in Japan.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy refers to the energy harnessed from the sun’s rays, which can be converted into electricity or heat. It is a renewable energy source that plays a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability.
What are the key players in the Japan Solar Energy Market?
Key players in the Japan Solar Energy Market include companies like Sharp Corporation, Kyocera Corporation, and Panasonic Corporation, which are known for their solar panel manufacturing and technology development, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Japan Solar Energy Market?
The Japan Solar Energy Market is driven by factors such as government incentives for renewable energy adoption, increasing energy demand, and advancements in solar technology that enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
What challenges does the Japan Solar Energy Market face?
Challenges in the Japan Solar Energy Market include regulatory hurdles, competition from other energy sources, and the need for significant investment in infrastructure to support solar energy integration.
What opportunities exist in the Japan Solar Energy Market?
Opportunities in the Japan Solar Energy Market include the expansion of solar farms, innovations in energy storage solutions, and the potential for increased residential solar installations as consumers seek energy independence.
What trends are shaping the Japan Solar Energy Market?
Trends in the Japan Solar Energy Market include the growing adoption of smart grid technologies, increased focus on energy efficiency, and the rise of community solar projects that allow shared access to solar energy among local residents.
Japan Solar Energy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Photovoltaic, Concentrated Solar Power, Bifacial Modules, Thin-Film |
| Application | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Utility-Scale |
| End User | Utilities, Government, Corporations, Households |
| Installation | Rooftop, Ground-Mounted, Floating, Building-Integrated |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the Japan Solar Energy Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at