444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview:
Japan’s insurance market is one of the largest and most dynamic in the world, comprising both life and non-life insurance sectors. With a population of over 126 million and a robust economy, Japan presents a significant opportunity for insurance providers. The country’s unique cultural and economic characteristics have shaped the insurance landscape, making it a compelling market for both domestic and international insurers.
Meaning
Japan’s insurance market encompasses both life insurance and non-life insurance segments. Life insurance covers policies that provide financial protection and support to individuals and their families in the event of death, disability, or critical illness. Non-life insurance, on the other hand, offers coverage for property, health, liability, travel, and other risks that individuals and businesses may face. These insurance policies play a crucial role in safeguarding the economic well-being of individuals and organizations, making them an integral part of Japan’s financial landscape.
Executive Summary:
The Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market have witnessed significant growth and development over the years. The market has been shaped by various factors, including changing demographics, economic conditions, regulatory developments, and technological advancements. Both life and non-life insurance segments have been impacted by the evolving needs and preferences of consumers and businesses. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the key market insights, drivers, restraints, opportunities, and market dynamics that have influenced the growth of the insurance industry in Japan.
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights:
Market Drivers:
Market Restraints:
Market Opportunities:
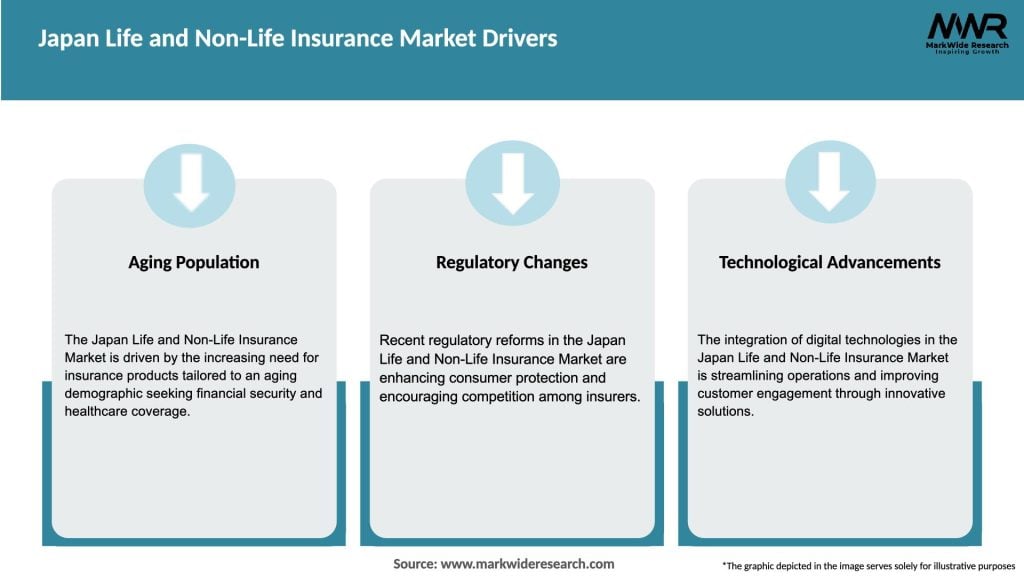
Market Dynamics:
The Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including demographic trends, economic conditions, regulatory landscape, technological advancements, and consumer behavior. Insurance companies need to adapt and innovate to stay competitive in this dynamic market. Factors such as the aging population, changes in consumer preferences, and advancements in digital technology will continue to shape the market’s trajectory.
Regional Analysis:
The insurance market in Japan is well-established across all regions of the country. While urban centers like Tokyo and Osaka remain the major contributors to insurance premium revenue, there is significant potential for growth in rural areas. As the population ages, regions with a higher concentration of elderly individuals present opportunities for life insurance providers. On the other hand, densely populated urban areas offer prospects for non-life insurance products, such as property and liability coverage.
Competitive Landscape:
Leading Companies in Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
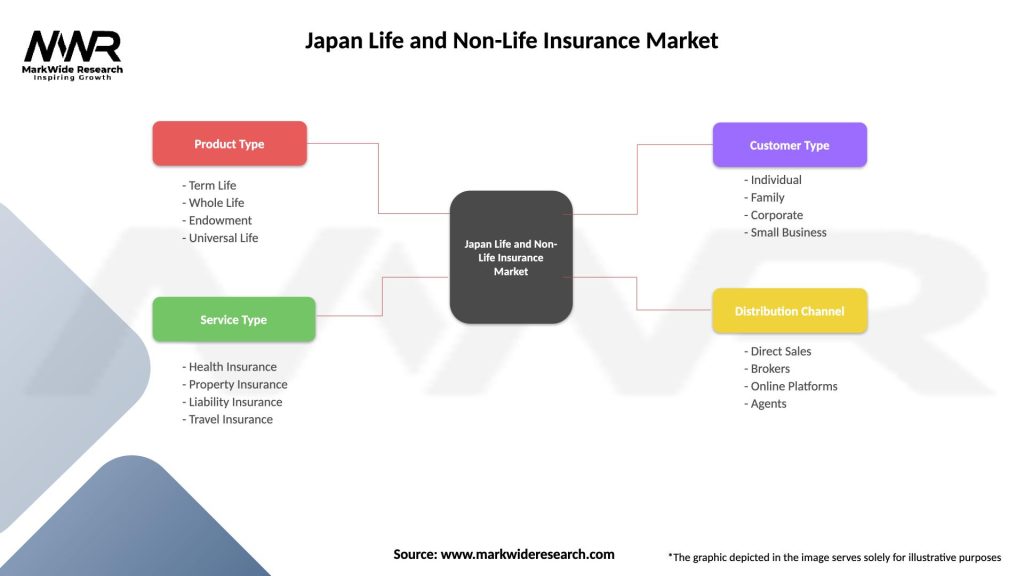
Segmentation:
The insurance market in Japan can be segmented based on various factors, including insurance type, customer demographics, distribution channel, and region. The life insurance segment includes individual life, group life, and pension products. The non-life insurance segment comprises property and casualty insurance, health insurance, travel insurance, and liability insurance. Furthermore, insurers target different customer segments, such as individuals, families, SMEs, and large corporations.
Category-wise Insights:
a. Life Insurance:
b. Non-Life Insurance:
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders:
SWOT Analysis:
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends:
Covid-19 Impact:
The Covid-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the insurance industry in Japan. While the life insurance segment experienced a surge in demand for protection products, the non-life insurance segment faced challenges related to travel insurance claims and business interruptions. The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital processes and contactless interactions, driving insurers to innovate and adapt to changing customer preferences.
Key Industry Developments:
Analyst Suggestions:
Future Outlook:
The Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market are expected to continue growing, driven by factors such as an aging population, rising healthcare costs, and increasing awareness about insurance protection. The industry’s future will be shaped by advancements in technology, changing customer preferences, and regulatory developments.
Conclusion:
The Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market play a vital role in providing financial security and support to individuals, families, and businesses. With a wide range of insurance products and robust distribution networks, the insurance industry has established a strong presence in the Japanese financial landscape. As the market continues to evolve, insurers must adapt to changing consumer needs, embrace technology, and innovate to remain competitive and meet the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By focusing on customer-centricity, product diversification, and technological integration, insurance companies can build a sustainable and thriving future in Japan’s insurance market.
What is Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance?
html,
body,
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) *,
html body.ds *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) div *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) span *,
html body p *,
html body h1 *,
html body h2 *,
html body h3 *,
html body h4 *,
html body h5 *,
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
),
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*[class]:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
),
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*[id]:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
) {
user-select: text !important;
pointer-events: initial !important;
}
html body *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
body *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body div *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body span *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body p *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h1 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h2 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h3 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h4 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h5 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection {
background-color: #3297fd !important;
color: #ffffff !important;
}
/* linkedin */
/* squize */
.www_linkedin_com
.sa-assessment-flow__card.sa-assessment-quiz
.sa-assessment-quiz__scroll-content
.sa-assessment-quiz__response
.sa-question-multichoice__item.sa-question-basic-multichoice__item
.sa-question-multichoice__input.sa-question-basic-multichoice__input.ember-checkbox.ember-view {
width: 40px;
}
/*linkedin*/
/*instagram*/
/*wall*/
.www_instagram_com ._aagw {
display: none;
}
/*developer.box.com*/
.bp-doc .pdfViewer .page:not(.bp-is-invisible):before {
}
/*telegram*/
.web_telegram_org .emoji-animation-container {
display: none;
}
html
body.web_telegram_org
.bubbles-group
> .bubbles-group-avatar-container:not(input):not(textarea):not(
[contenteditable=””]
):not([contenteditable=”true”]),
html
body.web_telegram_org
.custom-emoji-renderer:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
) {
pointer-events: none !important;
}
/*ladno_ru*/
.ladno_ru [style*=”position: absolute; left: 0; right: 0; top: 0; bottom: 0;”] {
display: none !important;
}
/*mycomfyshoes.fr */
.mycomfyshoes_fr #fader.fade-out {
display: none !important;
}
/*www_mindmeister_com*/
.www_mindmeister_com .kr-view {
z-index: -1 !important;
}
/*www_newvision_co_ug*/
.www_newvision_co_ug .v-snack:not(.v-snack–absolute) {
z-index: -1 !important;
}
/*derstarih_com*/
.derstarih_com .bs-sks {
z-index: -1;
}
Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance refers to the insurance services provided in Japan that cover life-related risks and non-life risks, including health, property, and casualty insurance. This sector plays a crucial role in financial security and risk management for individuals and businesses.
html,
body,
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) *,
html body.ds *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) div *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) span *,
html body p *,
html body h1 *,
html body h2 *,
html body h3 *,
html body h4 *,
html body h5 *,
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
),
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*[class]:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
),
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*[id]:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
) {
user-select: text !important;
pointer-events: initial !important;
}
html body *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
body *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body div *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body span *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body p *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h1 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h2 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h3 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h4 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h5 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection {
background-color: #3297fd !important;
color: #ffffff !important;
}
/* linkedin */
/* squize */
.www_linkedin_com
.sa-assessment-flow__card.sa-assessment-quiz
.sa-assessment-quiz__scroll-content
.sa-assessment-quiz__response
.sa-question-multichoice__item.sa-question-basic-multichoice__item
.sa-question-multichoice__input.sa-question-basic-multichoice__input.ember-checkbox.ember-view {
width: 40px;
}
/*linkedin*/
/*instagram*/
/*wall*/
.www_instagram_com ._aagw {
display: none;
}
/*developer.box.com*/
.bp-doc .pdfViewer .page:not(.bp-is-invisible):before {
}
/*telegram*/
.web_telegram_org .emoji-animation-container {
display: none;
}
html
body.web_telegram_org
.bubbles-group
> .bubbles-group-avatar-container:not(input):not(textarea):not(
[contenteditable=””]
):not([contenteditable=”true”]),
html
body.web_telegram_org
.custom-emoji-renderer:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
) {
pointer-events: none !important;
}
/*ladno_ru*/
.ladno_ru [style*=”position: absolute; left: 0; right: 0; top: 0; bottom: 0;”] {
display: none !important;
}
/*mycomfyshoes.fr */
.mycomfyshoes_fr #fader.fade-out {
display: none !important;
}
/*www_mindmeister_com*/
.www_mindmeister_com .kr-view {
z-index: -1 !important;
}
/*www_newvision_co_ug*/
.www_newvision_co_ug .v-snack:not(.v-snack–absolute) {
z-index: -1 !important;
}
/*derstarih_com*/
.derstarih_com .bs-sks {
z-index: -1;
}
What are the key companies in the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market?
Key companies in the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market include Nippon Life Insurance, Tokio Marine Holdings, and Dai-ichi Life Holdings, among others. These companies offer a range of products from life insurance policies to property and casualty coverage.
What are the growth factors driving the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market?
The growth of the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market is driven by an aging population, increasing awareness of insurance products, and the rising demand for health and property insurance. Additionally, advancements in technology are enhancing service delivery and customer engagement.
What challenges does the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market face?
The Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market faces challenges such as low interest rates affecting profitability, intense competition among insurers, and regulatory changes. These factors can impact the sustainability and growth of insurance providers in the region.
What opportunities exist in the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market?
Opportunities in the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market include the development of innovative insurance products tailored to consumer needs, the integration of digital technologies for better customer service, and expanding coverage options for emerging risks such as cyber threats.
What trends are shaping the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market?
Trends shaping the Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market include the increasing adoption of insurtech solutions, a focus on personalized insurance offerings, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and ESG factors in underwriting practices. These trends are influencing how insurers operate and engage with customers.
Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Term Life, Whole Life, Endowment, Universal Life |
| Service Type | Health Insurance, Property Insurance, Liability Insurance, Travel Insurance |
| Customer Type | Individual, Family, Corporate, Small Business |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Brokers, Online Platforms, Agents |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Japan Life and Non-Life Insurance Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at