444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
Market Overview
Japan Fuel Cell Market refers to the growing industry within Japan that focuses on fuel cell technologies and applications. Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that convert the chemical energy of a fuel, typically hydrogen, into electricity. These clean and efficient energy systems have gained significant attention due to their potential to address environmental concerns and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Japan, being a country committed to sustainability and renewable energy solutions, has been actively promoting and investing in fuel cell technologies.
Meaning
Fuel cells are a form of clean energy technology that can provide a reliable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional power sources. Japan, as a leading technological hub, has been at the forefront of fuel cell research and development, recognizing its significance in achieving energy security and a low-carbon future.
Executive Summary
The Japan Fuel Cell Market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the country’s efforts to adopt cleaner energy sources and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The government’s supportive policies and financial incentives have spurred investments in fuel cell infrastructure and applications. As a result, various industries and sectors have embraced fuel cells for power generation, transportation, and backup power solutions. However, challenges such as high initial costs and limited hydrogen infrastructure remain as hindrances to widespread adoption.
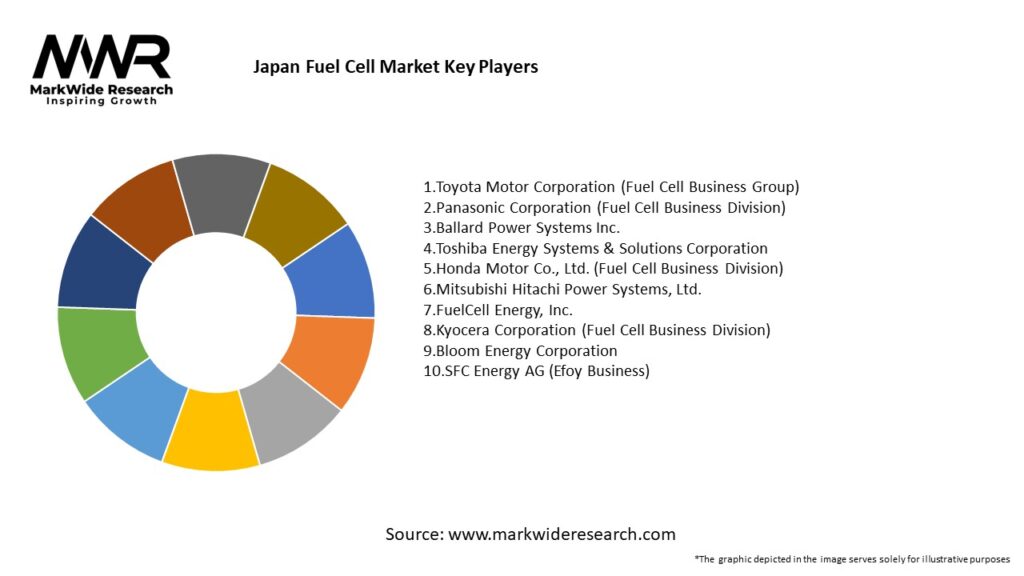
Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
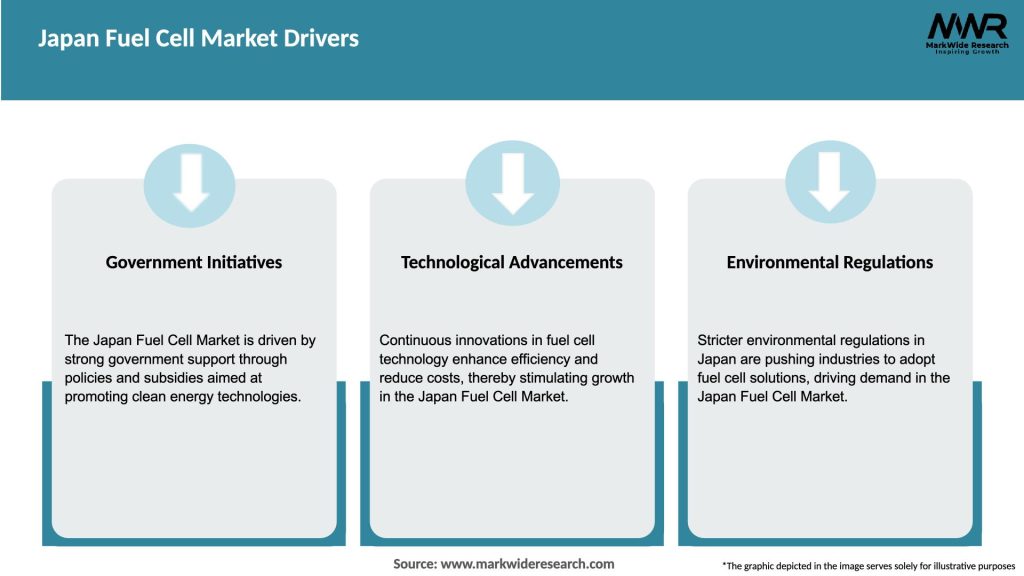
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The Japan Fuel Cell Market is dynamic and constantly evolving. Technological advancements, government policies, and consumer demand heavily influence its growth trajectory. While the market has witnessed steady progress, certain challenges still need to be addressed to unlock its full potential.
Regional Analysis
The adoption of fuel cell technology varies across different regions in Japan. Urban centers, such as Tokyo and Osaka, have witnessed higher uptake due to better infrastructure and government support. However, rural areas are yet to see significant developments in fuel cell adoption, mainly due to the lack of hydrogen infrastructure and awareness.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in Japan Fuel Cell Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
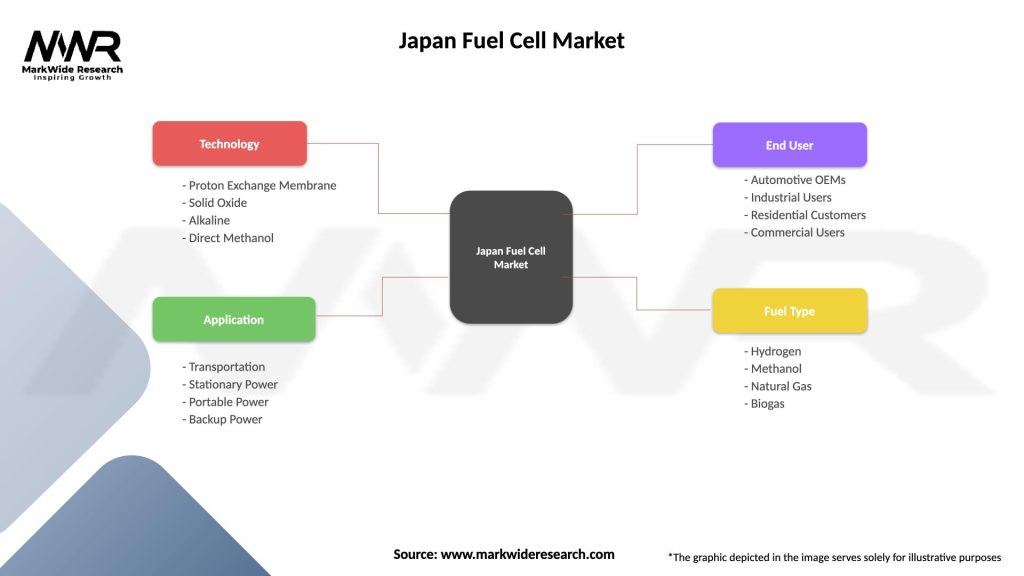
Segmentation
The Japan Fuel Cell Market can be segmented based on application areas:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had some short-term disruptions on the Japan Fuel Cell Market, mainly due to supply chain disruptions and reduced economic activities. However, the crisis also highlighted the importance of resilient and sustainable energy solutions, creating an opportunity for the fuel cell industry to contribute to future energy strategies.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the Japan Fuel Cell Market looks promising. With continued government support, technological advancements, and growing environmental awareness, fuel cells are likely to become a prominent player in Japan’s energy landscape. The market is expected to witness significant growth in various sectors, including stationary power generation, transportation, and portable electronics. As the country continues to shift towards sustainable energy solutions, fuel cells will play a crucial role in achieving Japan’s carbon reduction targets. In the transportation sector, fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are anticipated to gain greater prominence. Automakers are expected to introduce more FCEV models with improved driving range and faster refueling times. The development of an extensive hydrogen refueling infrastructure across Japan will be a critical factor in promoting the widespread adoption of FCEVs.
Moreover, fuel cells are likely to find increasing applications in industrial settings for stationary power generation. Businesses are recognizing the benefits of fuel cells in reducing their carbon footprint while ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. This trend is expected to continue as businesses seek to align with sustainability goals and explore cleaner energy alternatives.
Conclusion
The Japan Fuel Cell Market has emerged as a vital player in the country’s pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. Fuel cells offer a clean, efficient, and versatile energy source, making them an attractive option for various sectors, including transportation, stationary power generation, and portable electronics. The government’s supportive policies and financial incentives have been instrumental in driving market growth and encouraging private sector involvement. However, challenges such as high initial costs and limited hydrogen infrastructure need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of fuel cells in Japan.
Collaborations between industry players, government bodies, and energy companies can pave the way for the development of a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure. This will not only support the adoption of fuel cell vehicles but also bolster fuel cell applications in various sectors. The Covid-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of resilient and sustainable energy solutions, creating an opportunity for the fuel cell industry to play a more significant role in future energy strategies.
What is Fuel Cell?
html,
body,
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) *,
html body.ds *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) div *,
html body:not(.web_whatsapp_com) span *,
html body p *,
html body h1 *,
html body h2 *,
html body h3 *,
html body h4 *,
html body h5 *,
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
),
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*[class]:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
),
html
body:not(.web_whatsapp_com)
*[id]:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
) {
user-select: text !important;
pointer-events: initial !important;
}
html body *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
body *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body div *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body span *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body p *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h1 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h2 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h3 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h4 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection,
html body h5 *:not(input):not(textarea)::selection {
background-color: #3297fd !important;
color: #ffffff !important;
}
/* linkedin */
/* squize */
.www_linkedin_com
.sa-assessment-flow__card.sa-assessment-quiz
.sa-assessment-quiz__scroll-content
.sa-assessment-quiz__response
.sa-question-multichoice__item.sa-question-basic-multichoice__item
.sa-question-multichoice__input.sa-question-basic-multichoice__input.ember-checkbox.ember-view {
width: 40px;
}
/*linkedin*/
/*instagram*/
/*wall*/
.www_instagram_com ._aagw {
display: none;
}
/*developer.box.com*/
.bp-doc .pdfViewer .page:not(.bp-is-invisible):before {
}
/*telegram*/
.web_telegram_org .emoji-animation-container {
display: none;
}
html
body.web_telegram_org
.bubbles-group
> .bubbles-group-avatar-container:not(input):not(textarea):not(
[contenteditable=””]
):not([contenteditable=”true”]),
html
body.web_telegram_org
.custom-emoji-renderer:not(input):not(textarea):not([contenteditable=””]):not(
[contenteditable=”true”]
) {
pointer-events: none !important;
}
/*ladno_ru*/
.ladno_ru [style*=”position: absolute; left: 0; right: 0; top: 0; bottom: 0;”] {
display: none !important;
}
/*mycomfyshoes.fr */
.mycomfyshoes_fr #fader.fade-out {
display: none !important;
}
/*www_mindmeister_com*/
.www_mindmeister_com .kr-view {
z-index: -1 !important;
}
/*www_newvision_co_ug*/
.www_newvision_co_ug .v-snack:not(.v-snack–absolute) {
z-index: -1 !important;
}
/*derstarih_com*/
.derstarih_com .bs-sks {
z-index: -1;
}
Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy from fuels, such as hydrogen, into electricity through a reaction with oxygen. They are known for their efficiency and low emissions, making them a key technology in the transition to cleaner energy sources.
What are the key players in the Japan Fuel Cell Market?
Key players in the Japan Fuel Cell Market include companies like Toyota, Honda, and Panasonic, which are actively involved in the development and commercialization of fuel cell technologies. These companies focus on various applications, including transportation and stationary power generation, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Japan Fuel Cell Market?
The Japan Fuel Cell Market is driven by factors such as government support for clean energy initiatives, increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions, and advancements in fuel cell technology. Additionally, the push for energy security and reduced greenhouse gas emissions contributes to market growth.
What challenges does the Japan Fuel Cell Market face?
Challenges in the Japan Fuel Cell Market include high production costs, limited hydrogen infrastructure, and competition from alternative energy sources. These factors can hinder widespread adoption and commercialization of fuel cell technologies.
What opportunities exist in the Japan Fuel Cell Market?
Opportunities in the Japan Fuel Cell Market include the potential for innovation in hydrogen production and storage technologies, as well as expanding applications in various sectors such as automotive, residential, and industrial. The growing interest in renewable energy sources also presents new avenues for development.
What trends are shaping the Japan Fuel Cell Market?
Trends in the Japan Fuel Cell Market include increasing collaboration between public and private sectors to enhance hydrogen infrastructure, advancements in fuel cell efficiency, and a growing focus on integrating fuel cells with renewable energy sources. These trends are expected to drive further innovation and adoption.
Japan Fuel Cell Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Proton Exchange Membrane, Solid Oxide, Alkaline, Direct Methanol |
| Application | Transportation, Stationary Power, Portable Power, Backup Power |
| End User | Automotive OEMs, Industrial Users, Residential Customers, Commercial Users |
| Fuel Type | Hydrogen, Methanol, Natural Gas, Biogas |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in Japan Fuel Cell Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at