444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Japan cloud computing market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving technology sectors in the Asia-Pacific region. Cloud computing adoption in Japan has accelerated significantly over the past decade, driven by digital transformation initiatives across enterprises, government modernization programs, and the increasing demand for scalable IT infrastructure solutions. The market encompasses various deployment models including public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud configurations, serving diverse industry verticals from manufacturing and finance to healthcare and retail.
Market dynamics indicate that Japanese organizations are increasingly embracing cloud-first strategies, with enterprise adoption rates reaching 78% among large corporations as of recent assessments. The shift toward remote work capabilities, enhanced by the global pandemic, has further catalyzed cloud infrastructure investments. Small and medium enterprises are also demonstrating growing interest in cloud solutions, recognizing the cost-effectiveness and operational flexibility that cloud platforms provide.
Technology advancement continues to shape the landscape, with artificial intelligence integration, edge computing capabilities, and enhanced security features driving market evolution. The Japanese government’s Society 5.0 initiative has positioned cloud computing as a fundamental enabler of digital society transformation, creating substantial opportunities for both domestic and international cloud service providers.
The Japan cloud computing market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of cloud-based services, infrastructure, and solutions delivered to Japanese organizations and consumers through internet-connected platforms. This market encompasses infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings that enable businesses to access computing resources, applications, and data storage capabilities without maintaining physical hardware infrastructure.
Cloud computing in the Japanese context involves the delivery of on-demand computing services including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the internet. Organizations can leverage these services to achieve greater operational efficiency, reduce capital expenditure, and enhance scalability while maintaining compliance with Japan’s stringent data protection and privacy regulations.
Market participants include global cloud giants, domestic technology providers, system integrators, and specialized cloud service companies that cater to the unique requirements of Japanese businesses. The market also encompasses the supporting ecosystem of consultants, managed service providers, and technology partners that facilitate cloud adoption and implementation across various industry sectors.
Japan’s cloud computing market demonstrates robust growth momentum, characterized by increasing enterprise adoption, government digitization initiatives, and evolving customer expectations for digital services. The market has experienced significant transformation as organizations recognize cloud computing as essential infrastructure for business continuity, innovation, and competitive advantage in the digital economy.
Key growth drivers include the accelerating pace of digital transformation across industries, with manufacturing companies leading adoption at 82% implementation rates among major enterprises. The financial services sector follows closely, driven by regulatory modernization and customer experience enhancement requirements. Multi-cloud strategies are gaining prominence, with approximately 65% of enterprises utilizing multiple cloud providers to optimize performance and mitigate risks.
Market segmentation reveals strong demand across all service categories, with SaaS solutions maintaining the largest market share due to their immediate business value and lower implementation barriers. IaaS and PaaS segments are experiencing rapid growth as organizations modernize their IT infrastructure and development capabilities. Regional distribution shows concentrated activity in major metropolitan areas, with Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya representing the primary growth centers.
Competitive landscape features intense rivalry among global cloud providers and domestic technology companies, driving continuous innovation in service offerings, pricing models, and localization capabilities. The market outlook remains highly positive, supported by favorable government policies, increasing digital literacy, and growing recognition of cloud computing’s strategic importance.
Strategic insights from comprehensive market analysis reveal several critical trends shaping Japan’s cloud computing landscape:
Digital transformation initiatives serve as the primary catalyst for cloud computing adoption across Japanese organizations. Companies are recognizing that traditional IT infrastructure cannot support the agility and scalability required for modern business operations. Cost optimization remains a significant driver, as organizations seek to reduce capital expenditure while improving operational efficiency through pay-as-you-use cloud models.
Remote work requirements have fundamentally altered IT infrastructure needs, with organizations requiring flexible, secure access to applications and data from distributed locations. The pandemic accelerated cloud adoption timelines by an estimated 3-5 years across many industries. Scalability demands from rapidly growing businesses and seasonal fluctuations in resource requirements make cloud computing an attractive alternative to traditional infrastructure investments.
Innovation acceleration through cloud-native technologies enables organizations to develop and deploy applications faster while leveraging advanced capabilities like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. Regulatory compliance requirements are also driving adoption, as cloud providers offer specialized compliance frameworks and security certifications that many organizations cannot achieve independently.
Competitive pressure from digitally native companies is forcing traditional enterprises to modernize their technology infrastructure rapidly. Customer experience expectations for always-available, responsive digital services require the reliability and performance that cloud platforms provide.
Security concerns continue to represent the most significant barrier to cloud adoption among Japanese organizations, particularly those handling sensitive customer data or intellectual property. Data sovereignty requirements and concerns about data location and control create hesitation among enterprises considering public cloud deployment. Many organizations worry about losing direct control over their critical business data and applications.
Integration complexity with existing legacy systems poses substantial challenges for organizations with established IT infrastructure. The cost and complexity of migrating legacy applications to cloud environments can be prohibitive for some organizations. Skills shortage in cloud technologies creates implementation and management challenges, with many organizations lacking the internal expertise required for successful cloud adoption.
Regulatory uncertainty regarding data protection, privacy, and cross-border data transfer requirements creates compliance concerns for organizations considering cloud deployment. Network dependency and concerns about internet connectivity reliability affect organizations in regions with less robust telecommunications infrastructure.
Cultural resistance to change within traditional Japanese organizations can slow cloud adoption, particularly in companies with established IT practices and risk-averse cultures. Vendor lock-in concerns and worries about long-term dependency on cloud service providers influence decision-making processes.
Small and medium enterprise adoption represents a substantial growth opportunity, as these organizations increasingly recognize cloud computing’s potential to level the playing field with larger competitors. SME cloud adoption rates currently stand at approximately 45%, indicating significant room for expansion. Simplified cloud solutions and competitive pricing models specifically designed for smaller organizations are driving this segment’s growth.
Industry-specific cloud solutions present significant opportunities for specialized providers. Manufacturing companies require cloud platforms optimized for IoT integration, supply chain management, and production optimization. Healthcare cloud services are experiencing growing demand for electronic health records, telemedicine, and medical imaging solutions that comply with strict privacy regulations.
Edge computing integration creates opportunities for hybrid cloud solutions that combine centralized cloud processing with distributed edge capabilities. This is particularly relevant for applications requiring low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing, and real-time analytics. Artificial intelligence services delivered through cloud platforms represent a rapidly expanding opportunity as organizations seek to implement AI capabilities without substantial infrastructure investments.
Government digitization initiatives offer substantial opportunities for cloud service providers, as public sector organizations modernize their IT infrastructure and citizen services. Disaster recovery and business continuity services present growing opportunities, particularly given Japan’s exposure to natural disasters and the increasing importance of operational resilience.
Competitive intensity in Japan’s cloud computing market continues to escalate as global providers expand their local presence while domestic companies strengthen their cloud offerings. Price competition has intensified, with providers offering increasingly attractive pricing models and value-added services to differentiate their offerings. This competitive pressure benefits customers through improved service quality and reduced costs.
Technology evolution drives continuous market transformation, with emerging technologies like quantum computing, advanced AI services, and enhanced security capabilities creating new market segments and opportunities. Customer expectations are evolving rapidly, with organizations demanding more sophisticated, integrated cloud solutions that address specific business requirements rather than generic infrastructure services.
Regulatory developments significantly influence market dynamics, with government policies on data protection, cybersecurity, and digital transformation creating both opportunities and challenges for market participants. Partnership strategies are becoming increasingly important, with cloud providers forming alliances with system integrators, consultants, and industry specialists to expand their market reach and capabilities.
Market consolidation trends are emerging as smaller cloud providers either partner with larger companies or focus on specialized niche markets. Innovation cycles are accelerating, with new services and capabilities being introduced at an unprecedented pace to meet evolving customer demands and maintain competitive advantage.
Comprehensive market analysis was conducted through a multi-faceted research approach combining primary and secondary research methodologies. Primary research involved extensive interviews with cloud service providers, enterprise customers, system integrators, and industry experts across various sectors to gather firsthand insights into market trends, challenges, and opportunities.
Secondary research encompassed analysis of industry reports, government publications, company financial statements, and technology trend analyses to validate primary findings and provide comprehensive market context. Quantitative analysis included statistical modeling of market trends, adoption rates, and growth projections based on historical data and current market indicators.
Industry surveys were conducted among enterprise decision-makers, IT professionals, and cloud service users to understand adoption patterns, satisfaction levels, and future requirements. Expert interviews with technology analysts, consultants, and industry thought leaders provided strategic insights into market evolution and competitive dynamics.
Market segmentation analysis involved detailed examination of different service categories, deployment models, industry verticals, and geographic regions to identify specific growth opportunities and market dynamics. Competitive intelligence gathering included analysis of major market participants’ strategies, service offerings, pricing models, and market positioning to understand competitive landscape dynamics.
Tokyo metropolitan area dominates Japan’s cloud computing market, accounting for approximately 55% of total market activity due to its concentration of large enterprises, financial institutions, and technology companies. The region benefits from advanced telecommunications infrastructure, skilled workforce availability, and proximity to major cloud service provider data centers. Enterprise adoption rates in Tokyo exceed national averages, driven by competitive pressure and digital transformation initiatives.
Osaka region represents the second-largest market segment, with strong manufacturing and trading company presence driving cloud adoption for supply chain optimization and business process automation. The region’s strategic location and industrial base create substantial opportunities for industry-specific cloud solutions. Kansai area adoption rates have grown significantly, reaching 68% among medium to large enterprises.
Nagoya and surrounding areas demonstrate strong growth potential, particularly in manufacturing and automotive sectors where cloud computing supports Industry 4.0 initiatives and smart manufacturing implementations. Regional government initiatives promoting digital transformation and smart city development are accelerating cloud adoption across smaller cities and rural areas.
Northern regions including Sendai and Sapporo are experiencing growing cloud adoption, supported by government digitization programs and increasing recognition of cloud computing’s benefits for business continuity and disaster recovery. Rural area adoption remains lower but is growing steadily as telecommunications infrastructure improves and cloud services become more accessible to smaller organizations.
Market leadership is contested among several major players, each bringing unique strengths and capabilities to the Japanese cloud computing market:
Competitive strategies vary significantly among market participants, with global providers focusing on scale, innovation, and comprehensive service portfolios while domestic companies emphasize local market knowledge, regulatory compliance, and specialized industry solutions. Partnership approaches are becoming increasingly important as companies seek to combine their strengths and expand market reach through strategic alliances.
By Service Type:
By Deployment Model:
By Organization Size:
By Industry Vertical:
SaaS Solutions continue to dominate the Japanese cloud computing market due to their immediate business value and low implementation barriers. Business productivity applications including email, collaboration tools, and document management systems represent the largest SaaS segment. Customer relationship management and enterprise resource planning solutions are experiencing strong growth as organizations digitize their business processes.
IaaS Adoption is accelerating among organizations modernizing their IT infrastructure and seeking scalable computing resources. Virtual machine services and storage solutions represent the core IaaS offerings, while specialized services like disaster recovery and backup are gaining traction. Organizations appreciate the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand fluctuations.
PaaS Platforms are gaining popularity among development teams building cloud-native applications and organizations seeking to accelerate their digital transformation initiatives. Application development platforms and database services are the primary PaaS categories, with growing interest in artificial intelligence and machine learning platforms.
Industry-Specific Solutions are emerging as a significant growth category, with cloud providers developing specialized offerings for manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, and government sectors. These solutions address specific regulatory requirements, industry workflows, and integration needs that generic cloud services cannot adequately address.
Enterprise Organizations benefit from reduced capital expenditure, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced scalability through cloud computing adoption. Cost optimization occurs through elimination of hardware procurement and maintenance costs, while operational flexibility enables rapid response to changing business requirements. Enhanced security capabilities and disaster recovery options provide improved business continuity and risk management.
Small and Medium Enterprises gain access to enterprise-grade technology capabilities without substantial upfront investments. Competitive advantage emerges through access to advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and collaboration tools previously available only to larger organizations. Simplified IT management reduces the burden on internal resources while improving system reliability and performance.
Cloud Service Providers benefit from growing market demand and opportunities for service expansion and differentiation. Revenue growth potential exists through both market expansion and increased service adoption per customer. Strategic partnerships and specialized service offerings create competitive advantages and market positioning opportunities.
System Integrators and Consultants experience increased demand for cloud migration, implementation, and management services. Business expansion opportunities arise from helping organizations navigate cloud adoption challenges and optimize their cloud investments. Specialized expertise in cloud technologies creates premium service opportunities and long-term customer relationships.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Multi-cloud strategies are becoming increasingly prevalent as organizations seek to avoid vendor lock-in while optimizing performance and costs across different cloud platforms. Hybrid cloud adoption continues to grow, with approximately 72% of enterprises implementing some form of hybrid deployment to balance security, performance, and cost considerations.
Edge computing integration represents a significant trend as organizations require low-latency processing for IoT applications, autonomous systems, and real-time analytics. Artificial intelligence services are experiencing rapid adoption, with cloud-based AI and machine learning platforms enabling organizations to implement intelligent capabilities without substantial infrastructure investments.
Industry-specific cloud solutions are gaining traction as providers develop specialized offerings for manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, and government sectors. Security-first approaches are becoming standard, with enhanced encryption, identity management, and compliance capabilities being primary differentiators among cloud providers.
Sustainability initiatives are influencing cloud adoption decisions, with organizations seeking environmentally responsible technology solutions. Low-code and no-code platforms are expanding rapidly, enabling business users to develop applications without extensive programming knowledge. Container technologies and microservices architectures are becoming mainstream approaches for cloud application development and deployment.
Major cloud providers have significantly expanded their data center presence in Japan, with new facilities in Tokyo, Osaka, and other key regions to improve service performance and data sovereignty compliance. Strategic partnerships between global cloud companies and Japanese system integrators are accelerating market penetration and localization of cloud services.
Government initiatives including the Digital Agency establishment and national digitization programs are creating substantial opportunities for cloud service adoption across public sector organizations. Regulatory developments in data protection and cybersecurity are shaping cloud service requirements and compliance capabilities.
Technology innovations in quantum computing, advanced AI services, and edge computing are being introduced by major cloud providers to differentiate their offerings and capture emerging market opportunities. Industry consolidation is occurring as smaller cloud providers either partner with larger companies or focus on specialized market niches.
Investment activities in cloud infrastructure, technology development, and market expansion continue at high levels as companies position themselves for long-term growth. Talent acquisition and skills development programs are expanding as organizations address the cloud expertise shortage through training and recruitment initiatives.
MarkWide Research analysis suggests that organizations should prioritize hybrid cloud strategies to balance security, performance, and cost considerations while maintaining operational flexibility. Security investment should be a primary focus, with organizations implementing comprehensive security frameworks and compliance capabilities to address data protection requirements.
Skills development initiatives are critical for successful cloud adoption, with organizations needing to invest in training programs and talent acquisition to build internal cloud expertise. Vendor selection should consider not only technical capabilities but also local support, compliance features, and long-term strategic alignment with business objectives.
Gradual migration approaches are recommended for organizations with complex legacy systems, allowing for careful planning and risk mitigation during cloud transition processes. Industry-specific solutions should be prioritized when available, as they offer better alignment with business requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Partnership strategies with experienced system integrators and cloud consultants can accelerate adoption and reduce implementation risks. Continuous monitoring and optimization of cloud investments are essential to maximize value and maintain cost-effectiveness as business requirements evolve.
Market growth is expected to continue at a robust pace, driven by accelerating digital transformation initiatives and increasing recognition of cloud computing’s strategic importance. Enterprise adoption rates are projected to reach 85% among large corporations within the next three years, while SME adoption is expected to grow significantly as cloud services become more accessible and affordable.
Technology evolution will continue to drive market expansion, with artificial intelligence, edge computing, and quantum computing services creating new growth opportunities. Industry specialization is expected to increase, with cloud providers developing more sophisticated sector-specific solutions to address unique business requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Competitive dynamics will intensify as market participants seek to differentiate their offerings through innovation, specialized services, and strategic partnerships. Pricing models are likely to become more sophisticated, with outcome-based and value-driven pricing approaches gaining popularity alongside traditional consumption-based models.
Regulatory environment evolution will continue to shape market development, with data protection, cybersecurity, and cross-border data transfer requirements influencing cloud service design and delivery. Sustainability considerations are expected to become increasingly important in cloud adoption decisions, with environmental impact becoming a key evaluation criterion for organizations selecting cloud providers.
Japan’s cloud computing market stands at a pivotal point in its evolution, characterized by accelerating adoption rates, increasing sophistication in deployment strategies, and growing recognition of cloud computing’s strategic importance for business success. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals with robust demand across all segments, supportive government policies, and continuous technology innovation driving expansion opportunities.
Key success factors for market participants include developing comprehensive security and compliance capabilities, building strong local partnerships, and creating specialized solutions that address specific industry requirements. Organizations considering cloud adoption should focus on strategic planning, skills development, and gradual implementation approaches to maximize value while minimizing risks.
Future prospects remain highly positive, with continued growth expected across all market segments and deployment models. The convergence of cloud computing with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, edge computing, and IoT will create new opportunities for innovation and market expansion. MWR analysis indicates that organizations embracing cloud computing strategically will be best positioned to compete effectively in Japan’s increasingly digital economy.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, including storage, processing power, and applications. It allows users to access and manage data remotely, enhancing flexibility and scalability for businesses.
What are the key players in the Japan Cloud Computing Market?
Key players in the Japan Cloud Computing Market include companies like Fujitsu, NEC Corporation, and NTT Communications. These companies provide a range of cloud services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and software as a service (SaaS), among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Japan Cloud Computing Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Japan Cloud Computing Market include the increasing demand for digital transformation, the rise of remote work, and the need for scalable IT solutions. Additionally, businesses are adopting cloud services to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
What challenges does the Japan Cloud Computing Market face?
The Japan Cloud Computing Market faces challenges such as data security concerns, regulatory compliance issues, and the complexity of migrating existing systems to the cloud. These factors can hinder the adoption of cloud solutions among businesses.
What opportunities exist in the Japan Cloud Computing Market?
Opportunities in the Japan Cloud Computing Market include the growing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, as well as the expansion of cloud services in sectors like healthcare and finance. These trends are expected to drive innovation and new service offerings.
What trends are shaping the Japan Cloud Computing Market?
Trends shaping the Japan Cloud Computing Market include the increasing use of hybrid cloud solutions, the rise of edge computing, and a focus on sustainability in cloud operations. These trends reflect the evolving needs of businesses and the push for more efficient resource management.
Japan Cloud Computing Market
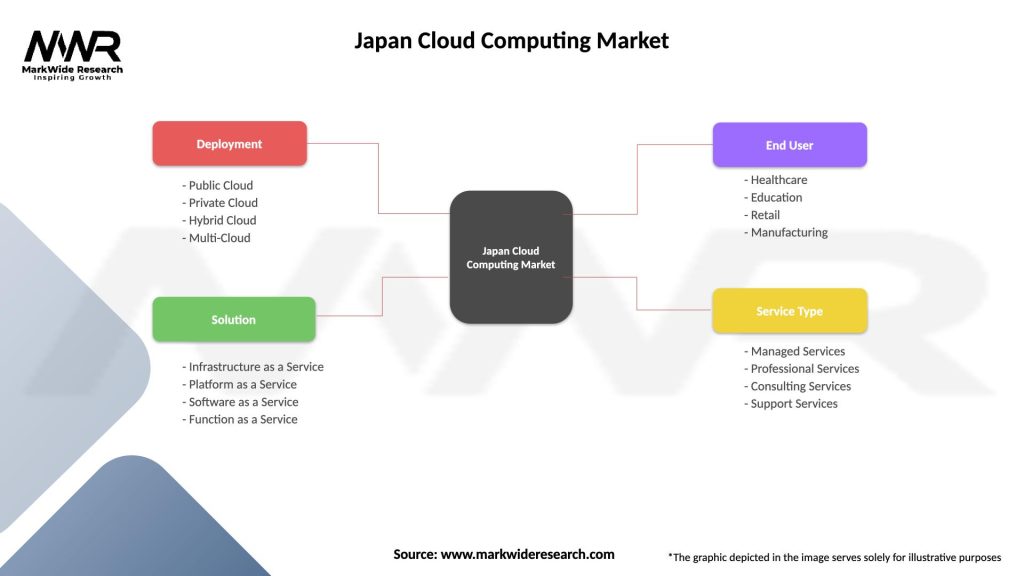
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Deployment | Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, Multi-Cloud |
| Solution | Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, Software as a Service, Function as a Service |
| End User | Healthcare, Education, Retail, Manufacturing |
| Service Type | Managed Services, Professional Services, Consulting Services, Support Services |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Japan Cloud Computing Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at