444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Ireland data center cooling market represents a rapidly expanding sector within the country’s thriving digital infrastructure landscape. As Ireland continues to establish itself as a premier European hub for cloud computing and data storage services, the demand for efficient cooling solutions has intensified dramatically. Major technology companies including Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook have established significant data center operations across Ireland, driving unprecedented growth in cooling technology requirements.
Market dynamics indicate that Ireland’s data center cooling sector is experiencing robust expansion, with industry analysts projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% through the forecast period. This growth trajectory reflects the country’s strategic positioning as a gateway to European markets, favorable regulatory environment, and abundant renewable energy resources. Cooling efficiency has become a critical factor in data center operations, with modern facilities achieving power usage effectiveness (PUE) ratios of 1.15 or lower.
Technological innovation continues to reshape the cooling landscape, with liquid cooling solutions gaining significant traction alongside traditional air-based systems. The market encompasses various cooling methodologies including precision air conditioning, chilled water systems, direct liquid cooling, and immersion cooling technologies. Environmental sustainability concerns have accelerated adoption of free cooling solutions, leveraging Ireland’s temperate climate to reduce energy consumption by up to 40% compared to traditional mechanical cooling.
The Ireland data center cooling market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of technologies, services, and solutions designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures within data center facilities across the Republic of Ireland. This market encompasses the design, installation, maintenance, and optimization of cooling systems that ensure reliable operation of critical IT infrastructure while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Data center cooling involves sophisticated thermal management systems that remove heat generated by servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and power distribution units. These systems must maintain precise temperature and humidity levels to prevent equipment failure, ensure optimal performance, and extend hardware lifespan. Modern cooling solutions integrate advanced monitoring, automation, and control technologies to achieve maximum efficiency and reliability.
Market participants include cooling equipment manufacturers, system integrators, maintenance service providers, and specialized consulting firms. The sector serves hyperscale data centers, colocation facilities, enterprise data centers, and edge computing installations throughout Ireland’s digital infrastructure network.
Ireland’s data center cooling market has emerged as a cornerstone of the country’s digital economy transformation, driven by substantial investments from global technology leaders and favorable business conditions. The market demonstrates exceptional resilience and growth potential, supported by Ireland’s strategic location, skilled workforce, and commitment to renewable energy adoption.
Key market drivers include the exponential growth in data generation, cloud computing adoption, and digital transformation initiatives across industries. Ireland’s position as a European data hub has attracted significant foreign direct investment, with data center capacity utilization rates exceeding 85% in major metropolitan areas. This high utilization has created sustained demand for advanced cooling solutions capable of supporting high-density computing environments.
Technological advancement remains a primary market catalyst, with next-generation cooling solutions offering improved efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced scalability. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cooling system management has enabled predictive maintenance capabilities and dynamic optimization, resulting in operational cost reductions of up to 25%.
Market challenges include increasing energy costs, stringent environmental regulations, and the need for specialized technical expertise. However, these challenges are driving innovation and creating opportunities for advanced cooling technologies that align with sustainability objectives and operational efficiency requirements.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical trends shaping Ireland’s data center cooling landscape:
Digital transformation acceleration serves as the primary driver for Ireland’s data center cooling market expansion. The unprecedented growth in data generation, cloud computing adoption, and digital service delivery has created substantial demand for data center capacity, directly translating to increased cooling requirements. Enterprise digitalization initiatives across industries including financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail continue to drive data center utilization.
Hyperscale cloud providers have established Ireland as a strategic European hub, investing billions in data center infrastructure development. These massive facilities require sophisticated cooling solutions capable of managing high-density computing environments while maintaining optimal energy efficiency. Geographic advantages including Ireland’s temperate climate, political stability, and EU membership status continue to attract international data center investments.
Regulatory support from the Irish government has created favorable conditions for data center development, including streamlined planning processes and infrastructure investment incentives. The country’s commitment to renewable energy development aligns with data center operators’ sustainability objectives, creating synergies that drive market growth.
Technological innovation in cooling solutions enables data centers to support increasingly dense computing workloads while reducing energy consumption. Advanced cooling technologies including liquid cooling, immersion cooling, and AI-driven optimization systems are becoming essential for competitive data center operations.
Energy cost pressures represent a significant constraint for Ireland’s data center cooling market, as cooling systems typically account for 30-40% of total facility energy consumption. Rising electricity prices and carbon taxation policies create operational challenges that require careful balance between cooling performance and cost efficiency.
Infrastructure limitations in certain regions of Ireland pose challenges for large-scale data center development, particularly regarding electrical grid capacity and network connectivity. These constraints can limit cooling system deployment and require substantial infrastructure investments to overcome.
Skilled workforce shortages in specialized cooling system design, installation, and maintenance create bottlenecks for market expansion. The technical complexity of modern cooling solutions requires highly trained professionals, and competition for talent remains intense across the sector.
Environmental regulations continue to evolve, creating uncertainty around future compliance requirements and potentially restricting certain cooling technologies. Planning permission processes for new data centers have become more stringent, particularly regarding environmental impact assessments and energy efficiency standards.
Capital intensity of advanced cooling solutions can present barriers for smaller data center operators, limiting adoption of cutting-edge technologies and creating market segmentation based on facility size and investment capacity.
Renewable energy integration presents substantial opportunities for innovative cooling solutions that leverage Ireland’s abundant wind and solar resources. The development of energy storage systems and smart grid technologies creates possibilities for cooling systems that optimize energy usage based on renewable availability and pricing dynamics.
Edge computing expansion is creating new market segments for distributed cooling solutions designed for smaller, localized data centers. These edge facilities require specialized cooling approaches that balance efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in diverse deployment environments.
Waste heat recovery technologies offer opportunities to monetize thermal energy generated by data centers, creating additional revenue streams while improving overall energy efficiency. District heating systems and industrial process integration represent growing applications for data center waste heat utilization.
Liquid cooling advancement continues to create opportunities for specialized solution providers as data densities increase and traditional air cooling approaches reach practical limitations. Direct-to-chip cooling, immersion cooling, and hybrid cooling systems represent high-growth market segments.
Service sector expansion including predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and performance optimization services creates recurring revenue opportunities for cooling system providers. The integration of IoT sensors and analytics platforms enables new service delivery models and value propositions.
Competitive dynamics within Ireland’s data center cooling market reflect the interplay between established global manufacturers and specialized local service providers. Market consolidation trends are evident as larger players acquire specialized technologies and regional expertise to enhance their comprehensive solution offerings.
Technology convergence is reshaping market dynamics as cooling solutions integrate with broader data center infrastructure management systems. The boundaries between cooling, power management, and facility monitoring are becoming increasingly blurred, creating opportunities for integrated solution providers.
Customer expectations continue to evolve toward comprehensive service models that encompass design, installation, maintenance, and optimization. Data center operators increasingly prefer single-source providers capable of delivering end-to-end cooling solutions with guaranteed performance outcomes.
Innovation cycles are accelerating as market participants invest heavily in research and development to maintain competitive advantages. The rapid pace of technological advancement requires continuous adaptation and creates both opportunities and risks for market participants.
Supply chain dynamics have become increasingly important following global disruptions, with market participants focusing on supply chain resilience, local sourcing capabilities, and inventory management strategies to ensure reliable project delivery.
Comprehensive market analysis for Ireland’s data center cooling sector employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability of insights. Primary research activities include structured interviews with industry executives, technology providers, data center operators, and regulatory officials to gather firsthand market intelligence and validate trends.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, government publications, regulatory filings, company financial statements, and technical documentation to establish market baselines and identify growth patterns. Data triangulation methods ensure consistency across multiple information sources and enhance research reliability.
Market modeling techniques incorporate statistical analysis, trend extrapolation, and scenario planning to develop accurate market projections and identify potential growth trajectories. Quantitative analysis focuses on market sizing, growth rates, and competitive positioning metrics.
Qualitative assessment examines market dynamics, competitive strategies, technology trends, and regulatory impacts to provide comprehensive market understanding beyond numerical data. Expert validation processes ensure research findings align with industry expertise and market realities.
Dublin metropolitan area dominates Ireland’s data center cooling market, accounting for approximately 65% of total market activity due to its concentration of hyperscale facilities and superior infrastructure connectivity. The region benefits from proximity to submarine cable landing points, robust electrical grid capacity, and established technology ecosystem.
Cork region represents the second-largest market segment, with approximately 20% market share, driven by strategic investments from major cloud providers and favorable local government support. The area’s industrial heritage and skilled workforce provide advantages for data center cooling system deployment and maintenance.
Western regions including Galway and surrounding areas are experiencing emerging growth in data center development, particularly for edge computing applications and renewable energy integration projects. These regions offer cost advantages and abundant renewable energy resources that appeal to sustainability-focused operators.
Border regions near Northern Ireland present unique opportunities for cross-border data center projects and shared infrastructure development. The potential for all-island energy market integration creates additional strategic considerations for cooling system planning and deployment.
Rural areas are increasingly considered for large-scale data center development due to land availability, lower costs, and community support, though infrastructure development requirements can present challenges for cooling system implementation.
Market leadership in Ireland’s data center cooling sector is characterized by a mix of global technology providers and specialized regional players. The competitive landscape reflects the diverse requirements of different data center segments and cooling applications.
Competitive strategies focus on technological innovation, service excellence, and sustainability credentials. Market participants are investing heavily in research and development to maintain technological leadership and meet evolving customer requirements.
Technology segmentation reveals distinct market categories based on cooling methodologies and applications:
By Cooling Type:
By Application:
By Service Type:
Precision air conditioning systems continue to dominate the Irish market due to their proven reliability, established service infrastructure, and compatibility with existing data center designs. These systems offer excellent performance for traditional server configurations and provide familiar operational characteristics for facility management teams.
Chilled water systems are gaining popularity in larger facilities where centralized cooling plants can achieve superior efficiency and scalability. These systems excel in hyperscale environments where cooling loads exceed the practical limits of direct expansion systems.
Direct liquid cooling technologies are experiencing accelerated adoption as server densities increase and traditional air cooling approaches reach thermal limitations. These systems offer superior cooling efficiency and reduced energy consumption for high-performance computing applications.
Free cooling systems leverage Ireland’s temperate climate to minimize mechanical cooling requirements, achieving significant energy savings during favorable weather conditions. These systems are particularly effective in hybrid configurations that combine free cooling with mechanical backup systems.
Modular cooling solutions provide flexibility and scalability advantages for growing data center operations, enabling phased deployment and capacity expansion as requirements evolve. These systems reduce initial capital investment while maintaining upgrade pathways.
Data center operators benefit from advanced cooling solutions through reduced operational costs, improved reliability, and enhanced sustainability credentials. Modern cooling systems enable higher server densities while maintaining optimal operating conditions, maximizing facility utilization and revenue potential.
Technology providers gain access to a growing market with substantial investment requirements and recurring service opportunities. The complexity of modern cooling solutions creates barriers to entry that protect established players while rewarding innovation and technical expertise.
Service providers benefit from increasing demand for specialized maintenance, monitoring, and optimization services as cooling systems become more sophisticated and critical to data center operations. The shift toward service-based business models creates recurring revenue streams and long-term customer relationships.
Government stakeholders benefit from increased foreign direct investment, job creation, and economic development associated with data center growth. The sector contributes significantly to Ireland’s position as a European technology hub and supports broader digital economy objectives.
Environmental stakeholders benefit from improved energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions as advanced cooling technologies enable more sustainable data center operations. The integration of renewable energy and waste heat recovery creates additional environmental advantages.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Liquid cooling adoption represents the most significant trend transforming Ireland’s data center cooling landscape. As server densities continue increasing and traditional air cooling reaches practical limitations, liquid cooling solutions are becoming essential for high-performance computing environments. Direct-to-chip cooling and immersion cooling technologies are experiencing particularly rapid growth.
AI-driven optimization is revolutionizing cooling system management through predictive analytics, automated control systems, and machine learning algorithms. These technologies enable dynamic optimization of cooling performance based on real-time conditions, resulting in energy savings of 15-25% compared to traditional control methods.
Sustainability integration continues gaining momentum as data center operators prioritize environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that sustainability considerations influence cooling system selection in over 85% of new data center projects.
Modular deployment strategies are becoming standard practice for data center cooling systems, enabling flexible capacity scaling and reduced initial capital investment. These approaches support rapid deployment timelines and accommodate evolving cooling requirements as facilities expand.
Edge computing proliferation is creating demand for distributed cooling solutions designed for smaller, unmanned facilities. These applications require highly reliable, low-maintenance cooling systems with remote monitoring capabilities.
Major infrastructure investments continue reshaping Ireland’s data center cooling market, with several hyperscale operators announcing significant facility expansions requiring advanced cooling solutions. These projects drive demand for cutting-edge cooling technologies and create opportunities for innovative solution providers.
Technology partnerships between cooling system manufacturers and data center operators are becoming increasingly common, enabling collaborative development of customized solutions that address specific operational requirements and performance objectives.
Regulatory developments including updated energy efficiency standards and environmental impact requirements are influencing cooling system design and selection criteria. The introduction of stricter PUE targets is accelerating adoption of high-efficiency cooling technologies.
Service model evolution toward comprehensive managed services and performance-based contracts is changing how cooling solutions are delivered and maintained. These models transfer operational risk to service providers while ensuring optimal performance outcomes for data center operators.
Research and development investments in next-generation cooling technologies continue accelerating, with particular focus on liquid cooling advancement, waste heat recovery, and integration with renewable energy systems.
Strategic positioning recommendations for market participants emphasize the importance of developing comprehensive solution portfolios that address diverse customer requirements across different data center segments. MWR analysis suggests that companies offering integrated cooling, monitoring, and service capabilities will achieve superior market positioning.
Technology investment priorities should focus on liquid cooling capabilities, AI-driven optimization systems, and sustainability-focused solutions that align with evolving market demands. Companies that fail to invest in these areas risk losing competitive relevance as market requirements evolve.
Service capability development represents a critical success factor as customers increasingly prefer comprehensive service models over equipment-only relationships. Building strong local service capabilities and remote monitoring platforms will be essential for long-term market success.
Partnership strategies should emphasize collaboration with data center operators, renewable energy providers, and technology integrators to create comprehensive value propositions that address complex customer requirements.
Market expansion opportunities exist in edge computing applications, waste heat recovery systems, and specialized cooling solutions for emerging technologies including quantum computing and high-performance computing applications.
Long-term market prospects for Ireland’s data center cooling sector remain exceptionally positive, driven by continued digital transformation, cloud computing growth, and Ireland’s strategic position in the global data center ecosystem. Market expansion is expected to continue at robust rates, with particular strength in advanced cooling technologies and comprehensive service offerings.
Technology evolution will continue driving market transformation, with liquid cooling solutions expected to achieve mainstream adoption rates exceeding 50% within the next five years. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT technologies will become standard features in cooling system design and operation.
Sustainability requirements will intensify, creating opportunities for innovative cooling solutions that minimize environmental impact while maximizing operational efficiency. The integration of renewable energy sources and waste heat recovery systems will become increasingly important for competitive positioning.
Market consolidation trends are likely to continue as larger players acquire specialized technologies and regional expertise to enhance their comprehensive solution offerings. This consolidation will create opportunities for innovative companies with differentiated technologies or specialized market focus.
Regulatory evolution will continue shaping market dynamics, with increasing emphasis on energy efficiency, environmental impact, and sustainability reporting requirements. Companies that proactively address these requirements will achieve competitive advantages in customer selection processes.
Ireland’s data center cooling market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector with exceptional growth prospects driven by digital transformation, technological innovation, and strategic geographic advantages. The market’s trajectory reflects the broader expansion of Ireland’s digital infrastructure ecosystem and its position as a premier European data center hub.
Key success factors for market participants include technological innovation, comprehensive service capabilities, sustainability focus, and strategic partnerships that address evolving customer requirements. The shift toward liquid cooling technologies, AI-driven optimization, and integrated service models creates both opportunities and challenges for industry participants.
Market outlook remains highly positive, with continued growth expected across all major segments and applications. The increasing importance of edge computing, sustainability requirements, and advanced cooling technologies will drive ongoing market evolution and create new opportunities for innovative solution providers. Companies that successfully navigate these trends while building strong local capabilities and customer relationships will achieve sustainable competitive advantages in this dynamic market environment.
What is Data Center Cooling?
Data Center Cooling refers to the methods and technologies used to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels in data centers, ensuring the efficient operation of servers and IT equipment. Effective cooling is crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring reliability in data center operations.
What are the key players in the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market?
Key players in the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market include companies like Schneider Electric, Vertiv, and Airedale International. These companies provide various cooling solutions, including precision air conditioning and liquid cooling systems, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market?
The main drivers of the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market include the increasing demand for data storage and processing, the growth of cloud computing, and the need for energy-efficient cooling solutions. These factors contribute to the expansion of data centers and the technologies used to cool them.
What challenges does the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market face?
The Ireland Data Center Cooling Market faces challenges such as high energy consumption and the environmental impact of cooling technologies. Additionally, the need for continuous innovation to keep up with evolving data center designs poses a significant challenge.
What opportunities exist in the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market?
Opportunities in the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market include the adoption of sustainable cooling technologies and the integration of AI for optimizing cooling efficiency. As data centers evolve, there is potential for innovative solutions that reduce energy costs and environmental impact.
What trends are shaping the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market?
Trends shaping the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market include the shift towards liquid cooling solutions and the increasing use of renewable energy sources for cooling operations. Additionally, advancements in cooling technologies are leading to more efficient and compact systems.
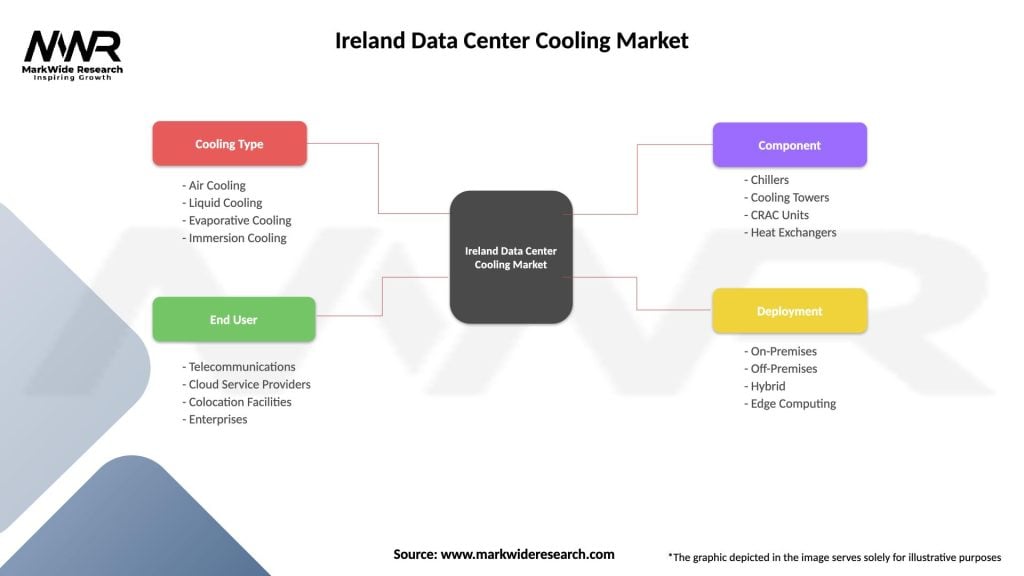
Ireland Data Center Cooling Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Cooling Type | Air Cooling, Liquid Cooling, Evaporative Cooling, Immersion Cooling |
| End User | Telecommunications, Cloud Service Providers, Colocation Facilities, Enterprises |
| Component | Chillers, Cooling Towers, CRAC Units, Heat Exchangers |
| Deployment | On-Premises, Off-Premises, Hybrid, Edge Computing |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Ireland Data Center Cooling Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at