444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$3450
The Internet of Things in the Energy Market represents a transformative technological revolution that is fundamentally reshaping how energy systems operate, monitor, and optimize performance across global infrastructure. This rapidly expanding sector encompasses the integration of connected devices, sensors, and intelligent systems throughout the energy value chain, from generation and transmission to distribution and consumption. Smart grid technologies are driving unprecedented levels of efficiency and reliability in energy management systems worldwide.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth trajectories, with the sector experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% over the forecast period. The convergence of advanced analytics, machine learning, and IoT connectivity is creating new opportunities for energy providers to enhance operational efficiency while reducing environmental impact. Digital transformation initiatives across the energy sector are accelerating adoption rates, with utilities investing heavily in smart infrastructure and connected technologies.
Regional adoption patterns show significant variation, with North America and Europe leading in deployment rates at approximately 45% and 38% respectively of global implementations. The integration of renewable energy sources, coupled with increasing demand for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities, is driving substantial investment in IoT-enabled energy solutions across both developed and emerging markets.
The Internet of Things in the Energy Market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of interconnected devices, sensors, and intelligent systems that enable real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of energy generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption processes. This technological framework leverages advanced connectivity protocols, data analytics, and automation capabilities to create smarter, more efficient energy infrastructure that can respond dynamically to changing demand patterns and operational conditions.
Core components of this market include smart meters, grid sensors, automated control systems, predictive maintenance platforms, and energy management software that work collectively to enhance system reliability and performance. The technology enables utilities and energy companies to implement sophisticated monitoring capabilities, optimize resource allocation, and provide consumers with detailed insights into their energy consumption patterns.
Strategic market positioning reveals that IoT technologies are becoming indispensable for modern energy infrastructure, with deployment rates accelerating across all major energy sectors. The market encompasses diverse applications including smart grid management, renewable energy integration, predictive maintenance, and consumer energy management systems. Technology convergence is creating new value propositions that combine operational efficiency with environmental sustainability objectives.
Investment trends show increasing capital allocation toward IoT-enabled energy solutions, with utilities reporting efficiency improvements of up to 25% in operational costs following implementation. The sector benefits from supportive regulatory frameworks promoting smart grid development and renewable energy integration. Market consolidation is occurring as traditional energy companies partner with technology providers to accelerate digital transformation initiatives.
Competitive landscape features a mix of established energy technology companies, innovative startups, and major technology corporations developing specialized IoT solutions for energy applications. The market demonstrates strong growth potential driven by increasing energy demand, aging infrastructure replacement needs, and growing emphasis on sustainable energy practices.
Fundamental market drivers are reshaping the energy sector’s approach to infrastructure management and operational optimization. The following key insights highlight critical success factors:
Primary growth catalysts are accelerating market expansion across multiple dimensions of the energy sector. The increasing complexity of modern energy systems requires sophisticated monitoring and control capabilities that only IoT technologies can provide effectively. Grid modernization initiatives represent the largest driver, as aging infrastructure requires comprehensive upgrades to meet contemporary reliability and efficiency standards.
Renewable energy proliferation creates substantial demand for intelligent grid management systems capable of handling variable power generation sources. IoT technologies enable real-time balancing of supply and demand, facilitating higher renewable energy penetration rates. Regulatory mandates for smart meter deployment and grid modernization are compelling utilities to invest in IoT infrastructure across their service territories.
Cost reduction pressures drive adoption as utilities seek to optimize operational expenses through automated monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. The technology enables significant reductions in field service requirements and emergency response costs. Consumer demand for energy transparency and control is pushing utilities to deploy smart metering and home energy management solutions that provide detailed consumption insights.
Implementation challenges present significant barriers to widespread IoT adoption in the energy sector. High upfront capital requirements for comprehensive IoT infrastructure deployment can strain utility budgets, particularly for smaller regional providers. Technical complexity associated with integrating diverse IoT systems into existing energy infrastructure requires specialized expertise and extensive planning.
Cybersecurity concerns represent a critical restraint, as increased connectivity creates potential vulnerabilities in critical energy infrastructure. Utilities must invest heavily in security measures and protocols to protect against cyber threats. Regulatory uncertainty in some regions creates hesitation among energy companies regarding long-term IoT investment strategies.
Interoperability issues between different IoT platforms and legacy systems can complicate deployment and increase integration costs. The lack of standardized protocols across vendors creates challenges for utilities seeking to implement comprehensive IoT solutions. Skills shortages in IoT and energy technology integration limit the pace of deployment for many organizations.
Emerging opportunities are creating new revenue streams and value propositions for energy sector participants. The convergence of IoT with artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies opens possibilities for advanced predictive analytics and autonomous grid management systems. Edge computing integration enables real-time processing of sensor data at the network edge, reducing latency and improving system responsiveness.
Energy storage optimization represents a significant opportunity as IoT systems can intelligently manage battery storage systems to maximize efficiency and lifespan. The growing electric vehicle market creates demand for smart charging infrastructure that can optimize grid load and integrate vehicle-to-grid capabilities. Distributed energy resources management through IoT platforms enables utilities to coordinate numerous small-scale renewable energy installations.
Data monetization opportunities allow utilities to leverage IoT-generated data for new service offerings and partnerships. Advanced analytics capabilities enable energy companies to provide consulting services and optimization solutions to industrial customers. International expansion opportunities exist in emerging markets where energy infrastructure development is accelerating rapidly.
Technological evolution continues to reshape market dynamics as IoT capabilities become more sophisticated and cost-effective. The integration of 5G connectivity is enhancing real-time communication capabilities between energy system components, enabling more responsive grid management. Artificial intelligence integration is transforming IoT data into actionable insights that optimize energy system performance automatically.
Competitive pressures are intensifying as traditional energy companies compete with technology firms entering the energy IoT space. Strategic partnerships between utilities and technology providers are becoming increasingly common to leverage complementary expertise. Market consolidation is occurring as larger players acquire specialized IoT technology companies to enhance their capabilities.
Customer expectations are evolving rapidly, with energy consumers demanding greater transparency and control over their energy usage. According to MarkWide Research analysis, consumer adoption of smart energy management systems is growing at 18% annually, driven by increasing environmental awareness and cost consciousness. Regulatory support continues to strengthen globally, with governments implementing policies that encourage smart grid development and IoT adoption.
Comprehensive research approach combines primary and secondary data collection methods to provide accurate market insights and projections. Primary research involves extensive interviews with energy industry executives, IoT technology providers, and regulatory officials to understand market dynamics and future trends. Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry reports, regulatory filings, and technology development announcements from key market participants.
Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability of market information through cross-referencing multiple sources and expert verification. Quantitative analysis includes statistical modeling of market trends and growth projections based on historical data and identified market drivers. Qualitative assessment incorporates expert opinions and industry insights to provide context for quantitative findings.
Market segmentation analysis examines different application areas, technology types, and regional markets to identify specific growth opportunities and challenges. The methodology includes assessment of competitive landscapes, regulatory environments, and technological developments that influence market evolution.
North American markets lead global adoption with approximately 42% market share, driven by substantial utility investments in smart grid infrastructure and supportive regulatory frameworks. The United States demonstrates particularly strong growth in smart meter deployment and grid modernization initiatives. Canadian markets show increasing adoption of IoT solutions for renewable energy integration and remote monitoring applications.
European markets account for roughly 35% of global deployment, with strong emphasis on renewable energy integration and energy efficiency optimization. The European Union’s digital transformation initiatives and environmental regulations drive significant investment in IoT-enabled energy solutions. Nordic countries lead in per-capita adoption rates due to advanced digital infrastructure and progressive energy policies.
Asia-Pacific regions represent the fastest-growing market segment, with adoption rates increasing at 22% annually driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization. China and India are investing heavily in smart grid infrastructure to support growing energy demand. Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa show increasing interest in IoT solutions for improving energy access and reliability in underserved areas.
Market leadership is distributed among several categories of companies, each bringing unique strengths to the IoT energy ecosystem. The competitive environment features established energy technology companies, innovative software providers, and major technology corporations developing specialized solutions.
Technology segmentation reveals diverse IoT applications across the energy value chain, each addressing specific operational requirements and market opportunities. The market encompasses multiple technology categories that work together to create comprehensive energy management ecosystems.
By Technology:
By Application:
Smart metering solutions represent the largest market segment, with deployment rates accelerating globally as utilities modernize their measurement infrastructure. These systems provide bidirectional communication capabilities that enable demand response programs and real-time pricing mechanisms. Advanced metering infrastructure serves as the foundation for broader IoT ecosystem development in the energy sector.
Grid monitoring systems constitute a rapidly growing category focused on enhancing power system reliability and efficiency. These solutions utilize distributed sensor networks to provide comprehensive visibility into grid operations and equipment performance. Predictive analytics capabilities enable utilities to identify potential issues before they cause service disruptions.
Renewable energy management systems address the unique challenges of integrating variable generation sources into traditional grid infrastructure. IoT technologies enable real-time forecasting and automated control systems that optimize renewable energy utilization. Energy storage integration through IoT platforms maximizes the value of battery systems and other storage technologies.
Utility companies benefit from significant operational improvements through IoT implementation, including reduced maintenance costs, improved system reliability, and enhanced customer service capabilities. Automated monitoring and control systems enable utilities to optimize resource allocation and respond more quickly to system disturbances. Cost savings typically range from 15-25% in operational expenses following comprehensive IoT deployment.
Energy consumers gain access to detailed consumption information and control capabilities that enable more informed energy usage decisions. Smart home energy management systems provide real-time feedback and automated optimization features that reduce energy costs. Commercial and industrial customers benefit from sophisticated energy management platforms that optimize consumption patterns and reduce demand charges.
Technology providers find expanding opportunities in the growing energy IoT market, with increasing demand for specialized solutions and services. The market offers potential for recurring revenue through software-as-a-service models and ongoing support contracts. System integrators benefit from growing demand for expertise in connecting IoT technologies with existing energy infrastructure.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial intelligence integration represents the most significant trend reshaping the IoT energy landscape, with machine learning algorithms enabling autonomous grid management and predictive maintenance capabilities. AI-powered systems can process vast amounts of IoT sensor data to identify patterns and optimize energy system performance automatically. Edge computing adoption is accelerating as utilities seek to reduce latency and improve real-time decision-making capabilities.
Blockchain technology integration is emerging as a solution for secure energy trading and peer-to-peer energy transactions in distributed energy systems. This trend enables new business models for renewable energy sharing and microgrid operations. Digital twin technology is gaining traction for creating virtual replicas of energy infrastructure that enable advanced simulation and optimization capabilities.
Sustainability focus is driving increased adoption of IoT solutions that optimize renewable energy integration and reduce carbon emissions. Energy companies are leveraging IoT data to demonstrate environmental performance and meet sustainability targets. Customer-centric solutions are evolving to provide more personalized energy management services and enhanced user experiences.
Strategic partnerships between traditional utilities and technology companies are accelerating IoT deployment across the energy sector. Major utilities are forming alliances with cloud computing providers to develop scalable IoT platforms that can handle massive data volumes. Acquisition activity continues as established energy companies acquire specialized IoT technology firms to enhance their digital capabilities.
Regulatory developments are creating new requirements and incentives for IoT adoption in energy infrastructure. Grid modernization mandates and smart meter deployment requirements are driving substantial investment in IoT technologies. MWR research indicates that regulatory support is contributing to accelerated adoption rates of 28% in regions with supportive policy frameworks.
Technology innovations continue to expand IoT capabilities in energy applications, with advances in sensor technology, wireless communication, and data analytics platforms. New low-power wide-area network technologies are enabling cost-effective IoT deployment in remote energy infrastructure locations. Standardization efforts are progressing to improve interoperability between different IoT systems and vendors.
Investment prioritization should focus on IoT solutions that deliver measurable operational improvements and strong return on investment. Energy companies should develop comprehensive IoT strategies that align with long-term business objectives and regulatory requirements. Pilot project approaches enable organizations to test IoT technologies on a smaller scale before committing to large-scale deployments.
Partnership strategies are essential for successful IoT implementation, as few organizations possess all the necessary expertise internally. Utilities should seek technology partners with proven experience in energy sector applications and strong cybersecurity capabilities. Skills development programs should be implemented to build internal IoT expertise and reduce dependence on external consultants.
Cybersecurity investment must be prioritized from the beginning of IoT deployment to protect critical energy infrastructure. Organizations should implement comprehensive security frameworks that address both technical and operational aspects of IoT security. Data governance strategies should be established to maximize the value of IoT-generated data while ensuring privacy and regulatory compliance.
Market evolution will be characterized by increasing sophistication of IoT applications and deeper integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. The next five years will see widespread deployment of autonomous grid management systems that can optimize energy distribution without human intervention. MarkWide Research projects that autonomous system adoption will reach 35% penetration rates in developed markets by the end of the forecast period.
Technology convergence will create new opportunities for integrated energy management platforms that combine IoT, AI, blockchain, and edge computing capabilities. These comprehensive solutions will enable new business models and revenue streams for energy companies. Sustainability integration will become increasingly important as IoT systems help organizations meet ambitious carbon reduction targets.
Global expansion will accelerate as IoT technologies become more cost-effective and easier to deploy in emerging markets. Developing regions will benefit from leapfrogging traditional energy infrastructure limitations through IoT-enabled solutions. Innovation acceleration will continue as the energy sector attracts increasing investment from technology companies and venture capital firms focused on clean energy solutions.
The Internet of Things in the Energy Market represents a fundamental transformation of how energy systems operate, monitor, and optimize performance across the entire value chain. The convergence of advanced connectivity, intelligent analytics, and automated control systems is creating unprecedented opportunities for efficiency improvements and cost reductions throughout the energy sector. Market growth continues to accelerate as utilities and energy companies recognize the strategic importance of IoT technologies for maintaining competitive advantage and meeting evolving customer expectations.
Strategic implementation of IoT solutions requires careful planning, substantial investment, and strong partnerships between energy companies and technology providers. Organizations that successfully navigate the challenges of IoT deployment will benefit from significant operational improvements, enhanced customer service capabilities, and new revenue opportunities. The future energy landscape will be increasingly defined by intelligent, connected systems that optimize performance automatically while supporting sustainability objectives and regulatory compliance requirements.
What is Internet of Things in the Energy?
The Internet of Things in the Energy refers to the integration of smart devices and sensors in energy systems to enhance efficiency, monitoring, and management. This includes applications such as smart grids, energy management systems, and predictive maintenance.
What are the key companies involved in the Internet of Things in the Energy Market?
Key companies in the Internet of Things in the Energy Market include Siemens, General Electric, Schneider Electric, and IBM, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Internet of Things in the Energy Market?
The growth of the Internet of Things in the Energy Market is driven by the increasing demand for energy efficiency, the rise of renewable energy sources, and advancements in smart technology. These factors contribute to improved energy management and reduced operational costs.
What challenges does the Internet of Things in the Energy Market face?
Challenges in the Internet of Things in the Energy Market include cybersecurity risks, high implementation costs, and the need for standardization across devices. These issues can hinder widespread adoption and integration of IoT solutions.
What future opportunities exist for the Internet of Things in the Energy Market?
Future opportunities for the Internet of Things in the Energy Market include the expansion of smart cities, enhanced grid resilience, and the integration of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics. These developments can lead to more sustainable energy practices.
What trends are shaping the Internet of Things in the Energy Market?
Trends shaping the Internet of Things in the Energy Market include the increasing use of edge computing, the rise of decentralized energy systems, and the growing importance of data analytics. These trends are transforming how energy is produced, distributed, and consumed.
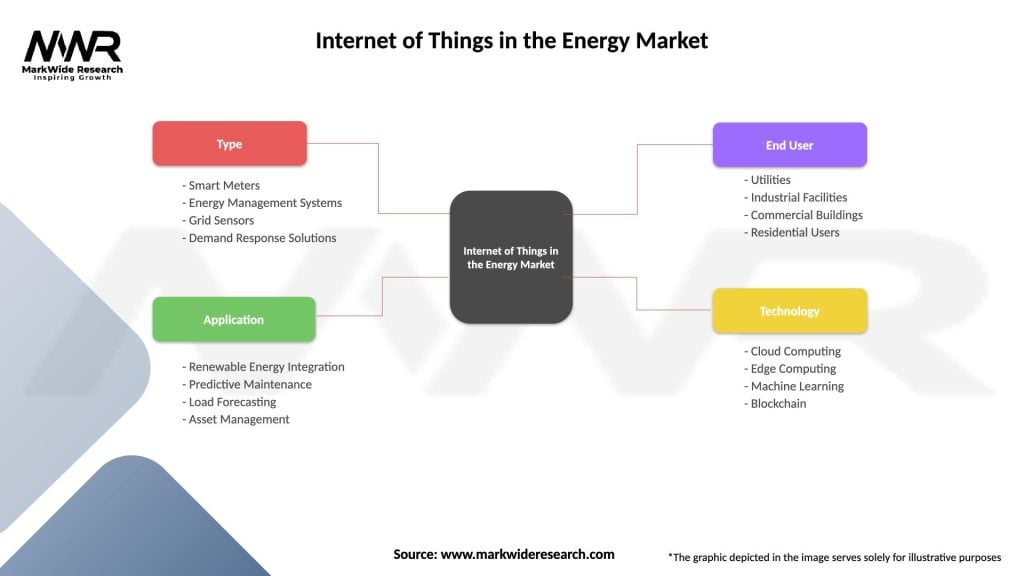
Internet of Things in the Energy Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Smart Meters, Energy Management Systems, Grid Sensors, Demand Response Solutions |
| Application | Renewable Energy Integration, Predictive Maintenance, Load Forecasting, Asset Management |
| End User | Utilities, Industrial Facilities, Commercial Buildings, Residential Users |
| Technology | Cloud Computing, Edge Computing, Machine Learning, Blockchain |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Internet of Things in the Energy Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
North America
o US
o Canada
o Mexico
Europe
o Germany
o Italy
o France
o UK
o Spain
o Denmark
o Sweden
o Austria
o Belgium
o Finland
o Turkey
o Poland
o Russia
o Greece
o Switzerland
o Netherlands
o Norway
o Portugal
o Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o South Korea
o Indonesia
o Malaysia
o Kazakhstan
o Taiwan
o Vietnam
o Thailand
o Philippines
o Singapore
o Australia
o New Zealand
o Rest of Asia Pacific
South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Chile
o Peru
o Rest of South America
The Middle East & Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Qatar
o South Africa
o Israel
o Kuwait
o Oman
o North Africa
o West Africa
o Rest of MEA
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at