444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Indonesia seeds market represents a cornerstone of the nation’s agricultural economy, serving as the foundation for food security and sustainable farming practices across the archipelago. Indonesia’s diverse agricultural landscape encompasses rice paddies, palm oil plantations, vegetable farms, and fruit orchards, all dependent on high-quality seeds for optimal productivity. The market has experienced robust growth driven by increasing population demands, government agricultural initiatives, and modernization of farming practices.
Market dynamics in Indonesia reflect the country’s position as one of the world’s largest agricultural producers, with seeds playing a crucial role in maintaining crop yields and food security. The sector encompasses various seed categories including field crops, vegetables, fruits, and ornamental plants, each contributing to the overall market expansion. Government support through subsidies and agricultural development programs has significantly boosted seed adoption rates, reaching approximately 78% penetration among commercial farmers.
Regional distribution across Indonesia’s major islands shows Java leading with 42% market share, followed by Sumatra and Sulawesi. The market benefits from Indonesia’s tropical climate, which allows for multiple growing seasons and diverse crop cultivation throughout the year. Technological advancement in seed development has introduced hybrid varieties and genetically improved seeds that offer enhanced resistance to pests, diseases, and climate variations.
The Indonesia seeds market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing the production, distribution, and commercialization of agricultural seeds across Indonesia’s diverse farming regions. This market includes conventional seeds, hybrid varieties, and genetically improved seeds designed to meet the specific agricultural needs of Indonesian farmers and support the nation’s food security objectives.
Market scope extends beyond traditional field crops to include vegetable seeds, fruit seeds, ornamental plant seeds, and specialty crops that contribute to Indonesia’s agricultural diversity. The market serves various stakeholders including smallholder farmers, commercial agricultural enterprises, government agricultural programs, and international seed companies operating within Indonesia’s regulatory framework.
Economic significance of the seeds market lies in its direct impact on agricultural productivity, rural livelihoods, and national food security. The market facilitates the introduction of improved crop varieties that enhance yield potential, nutritional content, and environmental sustainability, supporting Indonesia’s agricultural modernization goals.
Indonesia’s seeds market demonstrates exceptional growth potential driven by agricultural modernization, population growth, and government initiatives supporting food security. The market encompasses diverse seed categories with rice seeds dominating the field crop segment, while vegetable and fruit seeds show rapid expansion in commercial farming applications.
Key growth drivers include increasing adoption of hybrid seeds, which have achieved 65% acceptance rate among progressive farmers, and government subsidies that make quality seeds accessible to smallholder farmers. The market benefits from Indonesia’s strategic geographic position, favorable climate conditions, and growing domestic demand for agricultural products.
Competitive landscape features both international seed companies and domestic producers, with local companies gaining market share through region-specific seed varieties adapted to Indonesian growing conditions. The market shows strong potential for continued expansion, supported by agricultural technology adoption and sustainable farming practices.
Future prospects indicate sustained growth driven by precision agriculture adoption, climate-resilient seed varieties, and export opportunities for specialty crops. The market is positioned to benefit from Indonesia’s agricultural transformation and increasing focus on sustainable food production systems.
Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping the Indonesia seeds market landscape:
Population growth serves as a primary driver for the Indonesia seeds market, with the country’s expanding population creating increased demand for food production and agricultural output. The growing population requires enhanced agricultural productivity, driving farmers to adopt improved seed varieties that offer higher yields and better nutritional content.
Government agricultural policies significantly influence market growth through subsidies, research funding, and agricultural development programs. The Indonesian government’s commitment to food security has resulted in substantial investments in seed development and distribution systems, making quality seeds more accessible to farmers across different economic segments.
Climate change adaptation needs drive demand for climate-resilient seed varieties that can withstand extreme weather conditions, drought, and flooding. Farmers increasingly seek seeds that offer stability in unpredictable weather patterns, leading to higher adoption of specially developed varieties designed for climate resilience.
Agricultural modernization trends encourage farmers to adopt advanced farming practices, including the use of improved seeds, precision agriculture, and sustainable farming methods. This modernization drive is supported by educational programs and technology transfer initiatives that promote the benefits of quality seeds.
Export market opportunities create additional demand for high-quality seeds as Indonesian agricultural products gain recognition in international markets. The focus on export-quality production drives farmers to invest in premium seed varieties that meet international standards and quality requirements.
High seed costs present a significant barrier for smallholder farmers who constitute a large portion of Indonesia’s agricultural sector. Premium hybrid and genetically improved seeds often carry higher prices compared to traditional varieties, limiting accessibility for farmers with limited financial resources.
Limited awareness among traditional farmers about the benefits of improved seed varieties constrains market growth in rural areas. Many farmers continue to rely on saved seeds from previous harvests, lacking knowledge about the potential productivity gains from commercial seed varieties.
Infrastructure challenges in remote agricultural areas affect seed distribution and storage capabilities. Poor transportation networks and inadequate storage facilities can compromise seed quality and limit market reach to distant farming communities.
Regulatory complexities surrounding seed certification, import procedures, and quality standards create barriers for both domestic and international seed companies. Complex approval processes can delay the introduction of new seed varieties and increase operational costs.
Climate variability poses challenges for seed performance and farmer confidence in new varieties. Unpredictable weather patterns can affect seed germination rates and crop performance, leading to farmer reluctance to invest in new seed technologies.
Precision agriculture adoption presents significant opportunities for advanced seed varieties designed to work with modern farming technologies. The integration of GPS-guided planting, soil sensors, and data analytics creates demand for seeds optimized for precision farming applications.
Organic farming expansion opens new market segments for organic and naturally produced seeds. Growing consumer demand for organic products drives farmers to seek certified organic seeds, creating opportunities for specialized seed producers.
Export market development offers potential for Indonesian seed companies to expand beyond domestic markets. The country’s expertise in tropical agriculture and seed production positions it well for exports to other tropical regions globally.
Research and development partnerships between international seed companies and local institutions create opportunities for developing region-specific varieties. These collaborations can produce seeds better adapted to Indonesian growing conditions and farmer needs.
Digital agriculture integration enables new approaches to seed selection, planting recommendations, and crop management. Digital platforms can connect farmers with appropriate seed varieties based on their specific location, soil conditions, and farming objectives.
Supply chain dynamics in the Indonesia seeds market involve complex interactions between seed producers, distributors, retailers, and farmers. The market operates through multiple channels including government distribution programs, private retailers, and direct sales from producers to large-scale farmers.
Seasonal demand patterns significantly influence market dynamics, with peak demand periods coinciding with major planting seasons. Rice planting seasons create the highest demand volumes, while vegetable and fruit seeds show more consistent year-round demand patterns.
Price dynamics reflect the balance between seed production costs, government subsidies, and farmer purchasing power. Market prices are influenced by production volumes, import costs, and government policy changes affecting agricultural subsidies.
Technology adoption rates vary significantly across different farmer segments, with commercial farmers showing 85% adoption of improved varieties compared to 45% adoption among smallholder farmers. This disparity creates different market dynamics for various seed categories and price points.
Competitive dynamics involve both price competition and innovation-based differentiation. Companies compete on seed performance, local adaptation, technical support services, and distribution network coverage across Indonesia’s diverse agricultural regions.
Primary research methodology employed comprehensive data collection through structured interviews with key market participants including seed producers, distributors, farmers, and agricultural experts across Indonesia’s major agricultural regions. The research covered diverse stakeholders to ensure representative market insights.
Secondary research involved extensive analysis of government agricultural statistics, industry reports, trade publications, and academic research related to Indonesia’s agricultural sector and seed market dynamics. Data sources included the Indonesian Ministry of Agriculture, agricultural research institutions, and industry associations.
Market segmentation analysis utilized both quantitative and qualitative approaches to categorize the market by seed type, application, distribution channel, and geographic region. This segmentation provides detailed insights into market structure and growth opportunities.
Data validation processes ensured accuracy and reliability through cross-referencing multiple sources, expert consultations, and statistical verification methods. The methodology incorporated feedback from industry experts to validate findings and conclusions.
Forecasting methodology combined historical trend analysis, market driver assessment, and expert opinions to project future market developments. The approach considered various scenarios and factors that could influence market growth trajectories.
Java region dominates the Indonesia seeds market with 42% market share, driven by its dense population, intensive agriculture, and proximity to major distribution centers. The region benefits from well-developed infrastructure, government agricultural programs, and high farmer adoption rates of improved seed varieties.
Sumatra region represents the second-largest market segment, focusing primarily on palm oil seeds, rice, and plantation crops. The region’s extensive agricultural land and favorable climate conditions support diverse crop production and create substantial demand for various seed categories.
Sulawesi region shows rapid growth in vegetable and fruit seeds, driven by increasing commercial farming activities and export-oriented agriculture. The region’s strategic location and growing agricultural investments contribute to expanding seed market opportunities.
Kalimantan region demonstrates strong potential for plantation crop seeds, particularly palm oil and rubber. The region’s vast agricultural land availability and government development programs support continued market expansion.
Eastern Indonesia regions including Papua and Maluku show emerging opportunities for specialty crops and sustainable agriculture initiatives. These regions benefit from unique growing conditions suitable for specific crop varieties and organic farming practices.
Market leadership in the Indonesia seeds market involves both international companies and domestic producers, each bringing distinct advantages to the competitive landscape:
Competitive strategies focus on local adaptation, farmer education, distribution network expansion, and research and development investments. Companies compete through product innovation, technical support services, and strategic partnerships with local agricultural institutions.
Market positioning varies among competitors, with some focusing on premium hybrid varieties while others target cost-effective solutions for smallholder farmers. This diverse positioning creates multiple market segments and opportunities for different competitive approaches.
By Crop Type:
By Technology:
By Distribution Channel:
Rice Seeds Category dominates the market with consistent demand driven by Indonesia’s position as a major rice consumer. This category benefits from government support, research investments, and farmer familiarity with rice cultivation practices. Hybrid rice varieties show increasing adoption rates, reaching 35% penetration among commercial rice farmers.
Vegetable Seeds Category demonstrates rapid growth driven by urbanization, changing dietary preferences, and commercial horticulture expansion. The category benefits from higher profit margins and shorter crop cycles, making it attractive for farmers seeking quick returns on investment.
Corn Seeds Category shows steady growth supported by livestock feed demand and industrial applications. The category benefits from mechanization trends and government programs promoting corn production for food security and economic diversification.
Specialty Crops Category including spices, medicinal plants, and export-oriented crops presents emerging opportunities. This category benefits from premium pricing, export potential, and growing demand for value-added agricultural products.
Fruit Seeds Category demonstrates potential for expansion driven by domestic consumption growth and export opportunities. The category benefits from Indonesia’s tropical climate advantages and increasing investment in commercial fruit production.
Farmers benefit from access to improved seed varieties that offer higher yields, disease resistance, and better adaptation to local growing conditions. Quality seeds enable farmers to increase productivity, reduce production risks, and improve farm profitability through enhanced crop performance.
Seed companies benefit from Indonesia’s large agricultural market, government support for agricultural development, and growing demand for improved varieties. The market offers opportunities for product innovation, market expansion, and long-term business growth in a stable agricultural economy.
Government stakeholders benefit from enhanced food security, rural economic development, and agricultural productivity improvements. Investment in the seeds market supports national agricultural objectives and contributes to sustainable rural development.
Consumers benefit from improved food quality, nutritional content, and food security resulting from enhanced agricultural productivity. Better seeds contribute to stable food supplies and affordable prices for essential agricultural products.
Research institutions benefit from collaboration opportunities, funding for agricultural research, and practical applications for scientific innovations. The seeds market provides a platform for translating research into commercial applications that benefit farmers and society.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital agriculture integration represents a transformative trend reshaping how farmers select, purchase, and utilize seeds. Mobile applications and digital platforms provide farmers with access to seed information, planting recommendations, and crop management advice, improving decision-making and agricultural outcomes.
Sustainability focus drives increasing demand for environmentally friendly seed varieties that support sustainable farming practices. Farmers and consumers show growing interest in seeds that reduce chemical inputs, improve soil health, and support biodiversity conservation.
Climate-smart agriculture adoption accelerates demand for seeds designed to withstand climate variability, drought conditions, and extreme weather events. MarkWide Research indicates that climate-resilient varieties show 25% higher adoption rates in climate-vulnerable regions.
Precision breeding techniques enable development of seeds with specific traits tailored to Indonesian growing conditions and farmer needs. Advanced breeding methods accelerate variety development and improve seed performance characteristics.
Supply chain digitization improves seed traceability, quality assurance, and distribution efficiency. Digital technologies enable better inventory management, demand forecasting, and customer service throughout the seed value chain.
Government policy initiatives have introduced new agricultural development programs focusing on seed quality improvement and farmer education. Recent policy changes emphasize food security, sustainable agriculture, and rural economic development through enhanced seed systems.
Research and development investments by both public and private sectors have accelerated the development of locally adapted seed varieties. New research facilities and breeding programs focus on developing seeds suitable for Indonesian growing conditions and farmer requirements.
International partnerships between Indonesian institutions and global seed companies have facilitated technology transfer and knowledge sharing. These collaborations bring advanced seed technologies and breeding expertise to the Indonesian market.
Infrastructure development projects improve seed storage, processing, and distribution capabilities across Indonesia’s agricultural regions. New facilities enhance seed quality maintenance and market access for farmers in remote areas.
Digital platform launches provide farmers with online access to seed information, purchasing options, and agricultural advisory services. These platforms improve market efficiency and farmer access to quality seeds and technical support.
Market expansion strategies should focus on developing distribution networks in underserved regions and improving farmer education programs. Companies should invest in local partnerships and extension services to increase market penetration and seed adoption rates.
Product development priorities should emphasize climate-resilient varieties, locally adapted seeds, and affordable options for smallholder farmers. MWR analysis suggests that region-specific varieties show 40% higher farmer satisfaction compared to generic varieties.
Technology integration recommendations include developing digital platforms for seed selection, implementing precision agriculture solutions, and creating data-driven farming advisory services. These technologies can improve seed performance and farmer outcomes.
Partnership strategies should focus on collaborations with government agencies, research institutions, and farmer organizations. Strategic partnerships can facilitate market access, technology development, and farmer education initiatives.
Investment priorities should include research and development, distribution infrastructure, and farmer education programs. Long-term investments in these areas will support sustainable market growth and competitive positioning.
Market growth prospects remain positive driven by Indonesia’s expanding population, agricultural modernization trends, and government support for food security initiatives. The market is expected to benefit from continued investment in agricultural development and rural infrastructure improvements.
Technology advancement will play an increasingly important role in market development, with precision agriculture, digital platforms, and advanced breeding techniques transforming seed selection and utilization practices. These technologies will improve seed performance and farmer productivity.
Sustainability trends will drive demand for environmentally friendly seed varieties and sustainable farming practices. The market will benefit from growing consumer awareness and government policies supporting sustainable agriculture development.
Regional expansion opportunities exist in underserved areas and emerging agricultural regions. Companies that successfully develop distribution networks and farmer relationships in these areas will capture significant market share and growth opportunities.
Export market development presents long-term opportunities for Indonesian seed companies to expand beyond domestic markets. The country’s tropical agriculture expertise positions it well for regional and global market expansion in specialty seed categories.
Indonesia’s seeds market represents a dynamic and essential component of the nation’s agricultural economy, offering substantial opportunities for growth and development. The market benefits from strong fundamentals including a large agricultural sector, government support, favorable climate conditions, and growing demand for food security solutions.
Key success factors for market participants include developing locally adapted varieties, building strong distribution networks, investing in farmer education, and embracing technological innovations. Companies that focus on these areas will be well-positioned to capture market opportunities and achieve sustainable growth.
Future market development will be shaped by sustainability trends, technology adoption, climate change adaptation, and evolving farmer needs. The market offers significant potential for companies that can effectively address these trends while maintaining focus on farmer value creation and agricultural productivity improvement.
Strategic recommendations emphasize the importance of long-term investment in research and development, infrastructure development, and stakeholder partnerships. Success in the Indonesia seeds market requires commitment to serving farmer needs, supporting agricultural development, and contributing to national food security objectives through innovative seed solutions and sustainable business practices.
What is Seeds?
Seeds are the reproductive units of flowering plants, capable of developing into another such plant. In the context of the Indonesia Seeds Market, they play a crucial role in agriculture, horticulture, and forestry, providing the foundation for crop production and biodiversity.
What are the key players in the Indonesia Seeds Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Seeds Market include companies like PT Bisi International Tbk, Syngenta, and Monsanto, which are involved in the development and distribution of various seed types, including hybrid and genetically modified seeds, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Indonesia Seeds Market?
The Indonesia Seeds Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for high-yield crops, advancements in seed technology, and the growing focus on sustainable agricultural practices to enhance food security.
What challenges does the Indonesia Seeds Market face?
Challenges in the Indonesia Seeds Market include regulatory hurdles related to genetically modified organisms, climate change impacts on crop viability, and competition from informal seed systems that may offer lower-quality alternatives.
What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Seeds Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia Seeds Market include the potential for innovation in seed breeding techniques, the expansion of organic seed production, and increasing investments in agricultural research and development.
What trends are shaping the Indonesia Seeds Market?
Trends in the Indonesia Seeds Market include the rise of precision agriculture, the integration of digital technologies in seed production, and a growing consumer preference for sustainable and organic seed varieties.
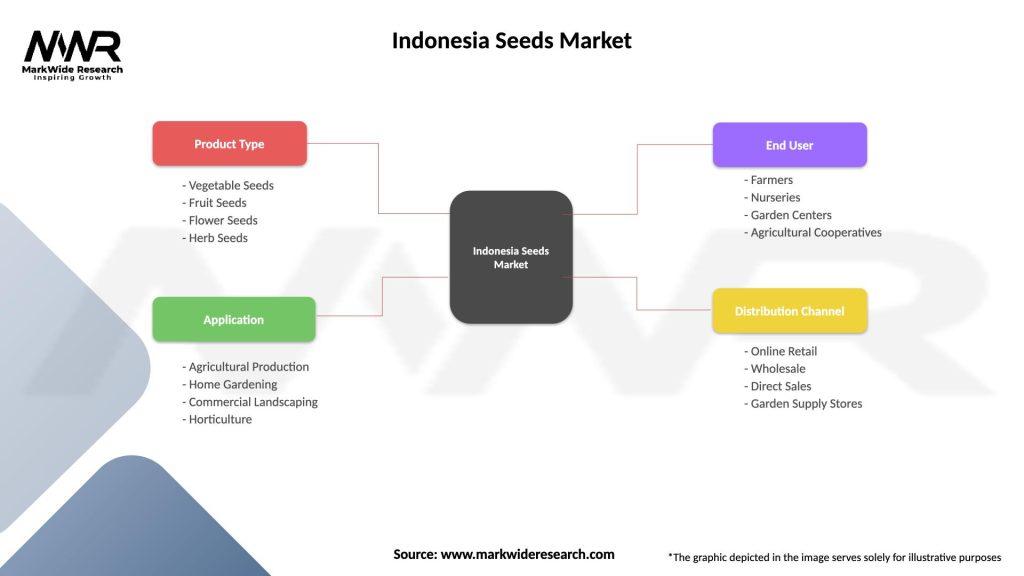
Indonesia Seeds Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Vegetable Seeds, Fruit Seeds, Flower Seeds, Herb Seeds |
| Application | Agricultural Production, Home Gardening, Commercial Landscaping, Horticulture |
| End User | Farmers, Nurseries, Garden Centers, Agricultural Cooperatives |
| Distribution Channel | Online Retail, Wholesale, Direct Sales, Garden Supply Stores |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indonesia Seeds Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at