444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Indonesia robotics market represents one of Southeast Asia’s most dynamic and rapidly expanding technological sectors, driven by the country’s ambitious digital transformation initiatives and growing industrial automation needs. Indonesia’s robotics landscape encompasses diverse applications across manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and service industries, positioning the nation as a key player in the regional automation ecosystem.
Market dynamics indicate robust growth potential, with the sector experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% as industries increasingly adopt robotic solutions to enhance productivity and competitiveness. The Indonesian government’s strong support through the Making Indonesia 4.0 initiative has accelerated robotics adoption across priority sectors, creating substantial opportunities for both domestic and international technology providers.
Industrial transformation remains the primary driver, with manufacturing companies investing heavily in robotic automation to improve operational efficiency and reduce labor costs. The automotive, electronics, and textile industries lead adoption rates, collectively accounting for approximately 68% of total robotics deployment across the archipelago. Service robotics applications are also gaining momentum, particularly in healthcare, hospitality, and retail sectors, as businesses seek innovative solutions to address evolving consumer demands and operational challenges.
The Indonesia robotics market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of robotic technologies, systems, and services deployed across various industries and applications within the Indonesian economy. This market encompasses industrial robots used in manufacturing processes, service robots designed for commercial and consumer applications, and specialized robotic solutions tailored for specific sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and logistics.
Robotics technology in Indonesia includes autonomous systems capable of performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention, ranging from traditional industrial manipulators to advanced artificial intelligence-powered robots. The market covers hardware components, software platforms, integration services, and ongoing maintenance support that collectively enable organizations to implement and optimize robotic solutions for enhanced productivity and operational excellence.
Indonesia’s robotics sector demonstrates exceptional growth trajectory, supported by favorable government policies, increasing industrial automation demand, and rising investment in advanced manufacturing technologies. The market benefits from Indonesia’s strategic position as a regional manufacturing hub and its commitment to digital transformation across key economic sectors.
Key growth drivers include the government’s Industry 4.0 roadmap, which prioritizes robotics adoption in five strategic industries: food and beverages, textiles, automotive, chemicals, and electronics. Manufacturing companies are increasingly recognizing robotics as essential for maintaining competitiveness in global markets, leading to accelerated adoption rates across diverse applications.
Market segmentation reveals strong demand across multiple categories, with industrial robotics maintaining the largest share while service robotics experiences the fastest growth rate. The healthcare robotics segment shows particular promise, driven by Indonesia’s aging population and increasing healthcare infrastructure investments. Regional distribution indicates concentration in Java and Sumatra, where major industrial centers and manufacturing facilities are located.
Strategic market analysis reveals several critical insights shaping Indonesia’s robotics landscape:
Industrial transformation serves as the primary catalyst for Indonesia’s robotics market expansion, with manufacturing companies increasingly recognizing automation as essential for global competitiveness. The government’s Making Indonesia 4.0 strategy specifically targets robotics adoption across priority industries, providing policy support and financial incentives that accelerate market growth.
Labor market dynamics contribute significantly to robotics adoption, as companies seek solutions to address skilled worker shortages and rising labor costs. The manufacturing sector faces particular challenges in maintaining consistent production quality and meeting international standards, driving demand for precision robotics systems that ensure reliable output and reduce human error.
Economic diversification efforts encourage industries to adopt advanced technologies, with robotics playing a crucial role in enhancing productivity and enabling Indonesia to move up the value chain in global manufacturing networks. The country’s strategic location and growing domestic market create attractive conditions for companies investing in robotic automation to serve both local and regional demand.
Technological advancement in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies makes robotics solutions more accessible and cost-effective for Indonesian businesses. Improved connectivity infrastructure and digital platforms enable sophisticated robotic applications that were previously unavailable or prohibitively expensive for local companies.
High initial investment requirements present significant barriers for many Indonesian companies, particularly small and medium enterprises that lack sufficient capital for comprehensive robotics implementation. The substantial upfront costs associated with robotic systems, integration services, and infrastructure modifications often deter potential adopters despite long-term benefits.
Skills shortage represents a critical constraint, as the successful deployment and operation of robotic systems require specialized technical expertise that remains limited in Indonesia’s current workforce. The gap between available skills and robotics requirements creates implementation challenges and increases operational risks for companies attempting automation projects.
Infrastructure limitations in certain regions restrict robotics deployment, particularly in areas with unreliable power supply, limited internet connectivity, or inadequate industrial facilities. These constraints affect the feasibility of advanced robotic applications and limit market expansion beyond major industrial centers.
Cultural resistance to automation exists in some sectors, where traditional manufacturing practices and concerns about job displacement create hesitation toward robotics adoption. Overcoming these perceptions requires comprehensive change management and demonstration of robotics benefits for both businesses and workers.
Healthcare robotics presents exceptional growth opportunities as Indonesia’s healthcare system modernizes and addresses increasing demand from an aging population. Surgical robots, rehabilitation devices, and automated pharmacy systems offer significant potential for improving healthcare delivery while addressing workforce constraints in medical facilities.
Agricultural automation represents a transformative opportunity for Indonesia’s large agricultural sector, where robotics can address labor shortages, improve crop yields, and enhance food security. Precision farming robots, automated harvesting systems, and livestock monitoring solutions align with government priorities for agricultural modernization and sustainability.
Smart city initiatives across major Indonesian urban centers create demand for service robotics in public safety, waste management, and infrastructure maintenance. These applications offer opportunities for local robotics companies to develop specialized solutions tailored to Indonesia’s unique urban challenges and environmental conditions.
Export manufacturing growth drives demand for industrial robotics as companies seek to meet international quality standards and production efficiency requirements. Indonesia’s position in global supply chains creates opportunities for robotics providers to support export-oriented industries with advanced automation solutions.
Supply chain evolution significantly influences Indonesia’s robotics market dynamics, with increasing emphasis on local assembly and component manufacturing to reduce costs and improve service support. International robotics companies are establishing regional operations and partnerships with Indonesian firms to better serve the growing market demand.
Technology adoption patterns reveal a preference for proven, reliable robotic solutions over cutting-edge but unproven technologies. Indonesian companies typically prioritize robotics systems with demonstrated return on investment and strong local support capabilities, influencing product development and market positioning strategies.
Competitive landscape dynamics show increasing participation from both international and domestic players, with collaboration models becoming more prevalent than direct competition. Joint ventures, technology transfer agreements, and local partnerships enable knowledge sharing while addressing market-specific requirements and regulatory considerations.
Investment flows indicate growing confidence in Indonesia’s robotics potential, with both venture capital and government funding supporting startups and established companies developing innovative robotic solutions. According to MarkWide Research analysis, investment activity has increased by 34% annually over the past three years, reflecting strong market fundamentals and growth prospects.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into Indonesia’s robotics market. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, government officials, technology providers, and end-users across various sectors to gather firsthand perspectives on market trends and challenges.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government publications, industry reports, academic studies, and company financial statements to validate primary findings and provide broader market context. Statistical analysis of trade data, investment flows, and adoption rates supports quantitative market assessments and growth projections.
Field studies conducted at manufacturing facilities, research institutions, and technology centers provide practical insights into robotics implementation challenges and success factors. These on-site investigations help identify emerging trends and validate theoretical market models with real-world observations.
Expert consultations with robotics engineers, industry analysts, and policy makers ensure comprehensive understanding of technical, commercial, and regulatory factors affecting market development. This multi-stakeholder approach provides balanced perspectives on market opportunities and constraints.
Java region dominates Indonesia’s robotics market, accounting for approximately 72% of total robotics deployment due to its concentration of manufacturing facilities, automotive plants, and electronics assembly operations. The region benefits from superior infrastructure, skilled workforce availability, and proximity to major ports facilitating international trade and technology transfer.
Sumatra’s industrial corridor represents the second-largest robotics market, driven by palm oil processing, petrochemicals, and pulp and paper industries seeking automation solutions for improved efficiency and environmental compliance. The region shows 18% market share with growing adoption rates in resource-based manufacturing sectors.
Kalimantan and Sulawesi demonstrate emerging robotics adoption, particularly in mining, agriculture, and food processing applications. These regions collectively represent 7% of current market activity but show strong growth potential as infrastructure development and industrial diversification programs advance.
Eastern Indonesia remains an underdeveloped robotics market due to infrastructure constraints and limited industrial activity. However, government development programs and natural resource projects create future opportunities for specialized robotic applications in remote and challenging environments.
Market leadership in Indonesia’s robotics sector features a mix of international technology giants and emerging local players, each contributing unique strengths to the evolving competitive landscape:
Strategic partnerships between international robotics companies and local firms have become increasingly important for market success, enabling technology transfer while addressing specific Indonesian market requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
By Robot Type:
By Application:
By End-User Industry:
Industrial Robotics Category maintains market leadership with strong demand from manufacturing sectors seeking productivity improvements and quality enhancement. Articulated robots dominate this segment, offering versatility for diverse applications including welding, assembly, and material handling. Collaborative robots show the fastest growth rate at 28% annually, driven by SME adoption and safety considerations in human-robot interaction environments.
Service Robotics Category demonstrates exceptional growth potential, particularly in healthcare applications where surgical robots and rehabilitation devices address critical needs in Indonesia’s expanding medical infrastructure. Professional cleaning robots and hospitality service robots gain traction as businesses seek automation solutions for labor-intensive service operations.
Agricultural Robotics Category represents significant untapped potential, with precision farming robots and automated harvesting systems offering solutions to Indonesia’s agricultural productivity challenges. Government support for agricultural modernization and food security initiatives creates favorable conditions for robotics adoption in farming operations.
Consumer Robotics Category remains nascent but shows growing interest, particularly in urban areas where household automation and personal assistance robots appeal to tech-savvy consumers. Educational robots also gain popularity as schools and universities integrate robotics into STEM curricula.
Manufacturing Companies benefit from robotics adoption through improved production efficiency, consistent quality output, and reduced operational costs. Robotic systems enable 24/7 operations, minimize human error, and provide precise control over manufacturing processes, resulting in enhanced competitiveness in global markets.
Technology Providers gain access to a rapidly expanding market with strong government support and growing industrial demand. Indonesia’s large population and diverse economy create opportunities for both standard and customized robotic solutions across multiple sectors and applications.
Workers and Society benefit from robotics through job creation in high-skill technical roles, improved workplace safety by removing humans from dangerous tasks, and enhanced product quality leading to better consumer experiences. Robotics also enables Indonesian companies to compete globally, supporting overall economic growth.
Government and Policymakers achieve strategic objectives including industrial modernization, export competitiveness, and technology transfer through robotics adoption. The sector supports Indonesia’s transition to higher value-added manufacturing and contributes to the country’s digital transformation goals.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Collaborative Robotics emerges as a dominant trend, with Indonesian manufacturers increasingly adopting cobots that work safely alongside human workers. This trend addresses both productivity needs and workforce concerns, enabling gradual automation while maintaining employment opportunities in modified roles requiring human creativity and problem-solving skills.
Artificial Intelligence Integration transforms robotics capabilities, enabling more sophisticated applications in quality control, predictive maintenance, and adaptive manufacturing processes. AI-powered robots demonstrate improved decision-making capabilities and reduced programming complexity, making advanced automation more accessible to Indonesian companies.
Mobile Robotics gains momentum in logistics and warehouse applications, with autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) providing flexible material handling solutions. This trend particularly benefits e-commerce and distribution centers seeking efficient order fulfillment and inventory management capabilities.
Robotics-as-a-Service models emerge as alternative deployment approaches, allowing companies to access robotic capabilities without large capital investments. This trend democratizes robotics access for SMEs while providing predictable operational costs and reduced technical risks.
Government Initiatives include the establishment of robotics research centers and technology incubators to support domestic innovation and skills development. The Ministry of Industry launched comprehensive programs for robotics adoption in priority sectors, providing technical assistance and financial incentives for qualifying companies.
Educational Partnerships between universities and robotics companies create specialized training programs addressing the skills gap in robotics engineering and maintenance. These collaborations produce graduates with practical experience in robotics implementation and operation, supporting market growth and technology adoption.
International Collaborations expand through joint ventures and technology transfer agreements between Indonesian companies and global robotics leaders. These partnerships enable knowledge sharing while developing solutions tailored to local market requirements and operating conditions.
Infrastructure Investments in digital connectivity and industrial facilities support advanced robotics deployment across Indonesia. Improved internet infrastructure enables cloud-based robotics applications and remote monitoring capabilities essential for sophisticated automation systems.
Investment Strategy recommendations emphasize focusing on sectors with strong government support and clear automation benefits, particularly automotive, electronics, and food processing industries. Companies should prioritize partnerships with local system integrators to ensure effective implementation and ongoing support capabilities.
Technology Adoption should follow a phased approach, beginning with proven applications and gradually expanding to more complex robotics solutions as expertise and confidence develop. MWR analysis suggests starting with collaborative robots and material handling applications before advancing to sophisticated manufacturing automation.
Skills Development requires immediate attention through comprehensive training programs and partnerships with educational institutions. Companies investing in robotics should allocate significant resources to workforce development to ensure successful implementation and optimal system utilization.
Market Entry strategies should emphasize local partnerships and gradual market penetration rather than aggressive expansion. Understanding Indonesian business culture and regulatory requirements proves essential for long-term success in the robotics market.
Market trajectory indicates sustained growth driven by continued industrial expansion and government support for automation initiatives. The robotics sector is projected to maintain strong momentum with expanding applications across healthcare, agriculture, and service industries complementing traditional manufacturing demand.
Technology evolution will bring more sophisticated and affordable robotic solutions to Indonesian markets, with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities becoming standard features. These advances will enable broader adoption across small and medium enterprises while supporting more complex applications in established industries.
Regional development patterns suggest gradual expansion beyond Java and Sumatra as infrastructure improvements and industrial diversification programs advance. Eastern Indonesia regions show potential for specialized robotics applications in natural resource industries and remote operations.
Investment climate remains favorable with continued government support and growing private sector confidence in robotics benefits. According to MarkWide Research projections, the sector will experience accelerating growth rates reaching 15.2% CAGR over the next five years, driven by expanding applications and improved technology accessibility.
Indonesia’s robotics market represents a compelling growth opportunity supported by strong fundamentals including government policy support, expanding industrial base, and growing recognition of automation benefits across diverse sectors. The market demonstrates resilience and adaptability, with increasing adoption rates across both traditional manufacturing and emerging service applications.
Strategic positioning of Indonesia as a regional manufacturing hub creates sustained demand for robotics solutions while government initiatives provide policy framework and incentives supporting market development. The combination of domestic market growth and export manufacturing requirements ensures continued expansion opportunities for robotics providers.
Future success in Indonesia’s robotics market will depend on addressing key challenges including skills development, infrastructure improvement, and technology accessibility for smaller enterprises. Companies that invest in local partnerships, workforce training, and tailored solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on the market’s substantial growth potential and contribute to Indonesia’s industrial transformation objectives.
What is Robotics?
Robotics refers to the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots. It encompasses various fields including automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, which are increasingly being integrated into various industries.
What are the key players in the Indonesia Robotics Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Robotics Market include companies like PT. Astra International, PT. Jaya Konstruksi, and PT. Schneider Electric, which are involved in manufacturing and deploying robotic solutions across sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Indonesia Robotics Market?
The Indonesia Robotics Market is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes, the rise of e-commerce requiring advanced logistics solutions, and the growing focus on improving operational efficiency in various industries.
What challenges does the Indonesia Robotics Market face?
Challenges in the Indonesia Robotics Market include high initial investment costs for robotic systems, a shortage of skilled workforce to operate and maintain these technologies, and concerns regarding job displacement in traditional sectors.
What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Robotics Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia Robotics Market include the potential for growth in sectors like agriculture through automation, advancements in AI and machine learning enhancing robotic capabilities, and increasing government support for technology adoption in various industries.
What trends are shaping the Indonesia Robotics Market?
Trends in the Indonesia Robotics Market include the rise of collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside humans, the integration of IoT technologies for smarter operations, and the increasing use of robotics in healthcare for tasks such as surgery and patient care.
Indonesia Robotics Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
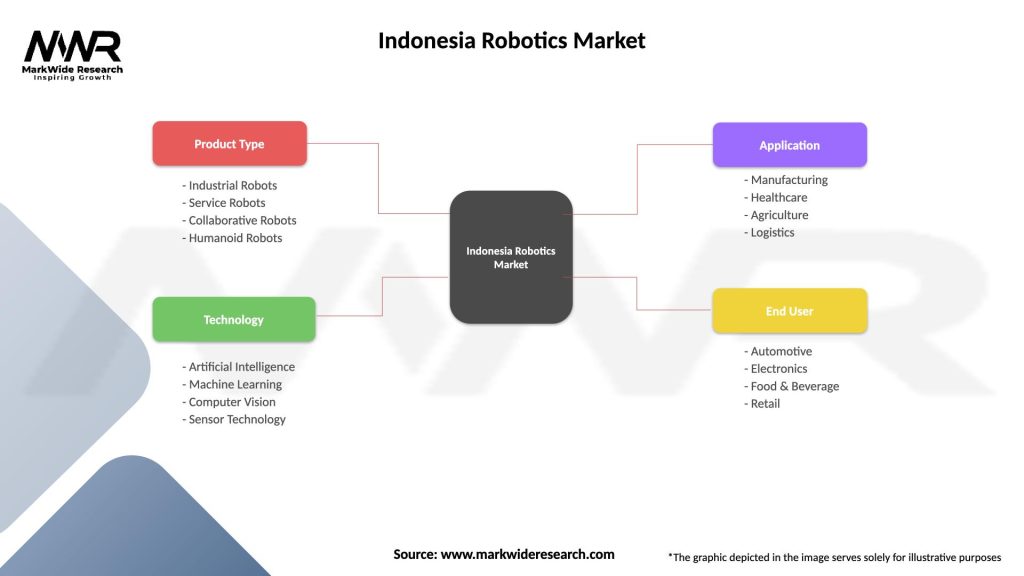
| Product Type | Industrial Robots, Service Robots, Collaborative Robots, Humanoid Robots |
| Technology | Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Computer Vision, Sensor Technology |
| Application | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Agriculture, Logistics |
| End User | Automotive, Electronics, Food & Beverage, Retail |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indonesia Robotics Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at