444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Indonesia real estate market represents one of Southeast Asia’s most dynamic and rapidly evolving property sectors, driven by robust economic growth, urbanization trends, and increasing foreign investment. Indonesia’s real estate landscape encompasses residential, commercial, industrial, and hospitality segments, with Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung emerging as primary growth centers. The market demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptability, supported by government infrastructure initiatives and demographic shifts toward urban living.
Market dynamics indicate sustained growth momentum, with the residential sector experiencing particularly strong demand from Indonesia’s expanding middle class. Commercial real estate continues to attract significant investment, particularly in office spaces and retail developments across major metropolitan areas. The market benefits from favorable demographic trends, including a young population and increasing urbanization rates of approximately 56% of the total population now residing in urban areas.
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in market development, with international developers and investors recognizing Indonesia’s potential for long-term growth. The government’s commitment to infrastructure development, including the new capital city project and transportation networks, creates substantial opportunities for real estate expansion. Digital transformation within the sector has accelerated, with PropTech solutions gaining traction among developers and consumers alike.
The Indonesia real estate market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of property development, investment, sales, and leasing activities across the Indonesian archipelago. This market encompasses all forms of real property transactions, including residential housing, commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and land development projects. Real estate activities include property development, construction, sales, leasing, property management, and related financial services that facilitate property transactions and ownership.
Market participants include property developers, construction companies, real estate agents, property consultants, financial institutions, and individual and institutional investors. The sector operates within Indonesia’s regulatory framework, which governs foreign ownership restrictions, land rights, and development permits. Property types range from affordable housing units to luxury developments, office complexes, shopping centers, industrial parks, and hospitality properties.
Geographic scope extends across Indonesia’s major islands, with concentration in Java, particularly the Greater Jakarta area, which accounts for significant market activity. The market serves both domestic and international demand, with increasing focus on sustainable development practices and smart building technologies.
Indonesia’s real estate market demonstrates robust growth potential driven by fundamental economic and demographic factors. The sector benefits from sustained GDP growth, urbanization trends, and government infrastructure investments that enhance property values and accessibility. Residential demand remains strong, supported by a growing middle class and favorable mortgage lending conditions from Indonesian banks.
Commercial real estate shows particular strength in office and retail segments, with multinational corporations expanding their presence in major Indonesian cities. The industrial real estate sector benefits from Indonesia’s position as a manufacturing hub and the government’s focus on developing industrial estates. Foreign investment regulations continue to evolve, with recent policy adjustments aimed at attracting more international capital while protecting domestic interests.
Market challenges include land acquisition complexities, regulatory compliance requirements, and infrastructure limitations in emerging markets. However, these challenges are being addressed through government initiatives and private sector innovation. Digital adoption accelerates across the sector, with online property platforms and virtual viewing technologies becoming standard practice.
Future prospects remain positive, supported by Indonesia’s young demographic profile, continued urbanization, and economic diversification efforts. The market is expected to maintain steady growth momentum, with particular opportunities in affordable housing, mixed-use developments, and sustainable building projects.

Strategic insights reveal several critical factors shaping Indonesia’s real estate landscape. The market demonstrates strong correlation between economic growth and property demand, with GDP expansion directly influencing real estate investment levels. Urbanization patterns show continued migration from rural to urban areas, creating sustained demand for residential and commercial properties in major cities.
Market maturation brings increased sophistication in development practices, financing mechanisms, and regulatory compliance. Professional property management and real estate services expand to meet growing market demands.
Primary market drivers propel Indonesia’s real estate sector forward through multiple interconnected factors. Economic growth remains the fundamental driver, with Indonesia’s GDP expansion supporting increased disposable income and property investment capacity among consumers and businesses. The country’s strategic position in Southeast Asia attracts multinational corporations seeking regional headquarters and operational bases.
Demographic trends create powerful demand dynamics, with a young, growing population driving housing needs and commercial space requirements. Urbanization acceleration continues as rural populations migrate to cities for employment opportunities, creating concentrated demand in metropolitan areas. The expanding middle class demonstrates increasing purchasing power and aspiration for property ownership.
Government infrastructure initiatives significantly enhance market attractiveness through improved transportation networks, utilities, and public facilities. The development of new airports, toll roads, and mass transit systems increases property accessibility and values. Foreign investment policies that encourage international participation while maintaining domestic protections create balanced market growth.
Financial sector development improves mortgage availability and terms, making property ownership more accessible to broader population segments. Digital transformation streamlines property transactions, marketing, and management processes, reducing costs and improving efficiency. Tourism growth drives hospitality real estate demand, while manufacturing expansion supports industrial property development.
Market constraints present challenges that require strategic navigation by industry participants. Regulatory complexity creates barriers for both domestic and foreign investors, with land ownership restrictions and permit processes requiring careful legal compliance. Foreign ownership limitations in certain property types and locations restrict international investment flows.
Infrastructure limitations in emerging markets constrain development potential, particularly regarding utilities, transportation access, and telecommunications connectivity. Land acquisition challenges arise from complex ownership structures, unclear titles, and lengthy approval processes that can delay project timelines and increase costs.
Economic volatility affects market stability, with currency fluctuations impacting foreign investment attractiveness and construction material costs. Environmental concerns regarding sustainable development practices and climate change adaptation require additional investment and planning considerations.
Financing constraints limit access to development capital, particularly for smaller developers and affordable housing projects. Skills shortages in construction and property management sectors affect project quality and operational efficiency. Market oversupply risks in certain segments and locations require careful demand analysis and strategic positioning.
Significant opportunities emerge across multiple real estate segments, driven by Indonesia’s economic development trajectory and demographic advantages. Affordable housing development presents substantial potential, with government support and financing programs targeting middle and lower-income segments. The housing deficit creates sustained demand for well-planned, accessible residential projects.
Commercial real estate expansion opportunities arise from Indonesia’s growing service sector and international business presence. Office space demand increases as multinational corporations establish regional operations, while retail development benefits from rising consumer spending and modern shopping preferences.
Industrial real estate benefits from Indonesia’s manufacturing growth and strategic position in global supply chains. Logistics and warehouse facilities experience growing demand from e-commerce expansion and improved distribution networks. The development of industrial parks and special economic zones creates integrated investment opportunities.
Tourism-related properties offer growth potential as Indonesia’s hospitality sector expands to accommodate increasing domestic and international visitors. Mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and recreational components address urbanization trends and lifestyle preferences. Smart building technologies and sustainable development practices create differentiation opportunities for forward-thinking developers.
Market dynamics reflect the complex interplay of supply and demand factors, regulatory influences, and economic conditions that shape Indonesia’s real estate landscape. Supply-demand balance varies significantly across regions and property types, with urban areas generally experiencing stronger demand than supply availability.
Price dynamics show steady appreciation in prime locations, while emerging areas demonstrate more volatile pricing patterns. Rental markets remain active, particularly in commercial segments where businesses prefer leasing flexibility over ownership commitments. The relationship between property prices and rental yields influences investment decisions and market liquidity.
Seasonal patterns affect market activity, with certain periods showing increased transaction volumes and development launches. Economic cycles influence investor confidence and financing availability, creating periods of expansion and consolidation within the market.
Competitive dynamics intensify as both domestic and international developers compete for prime locations and projects. Innovation adoption accelerates as market participants seek competitive advantages through technology integration and service differentiation. According to MarkWide Research analysis, market efficiency improvements of approximately 25% in transaction processing have been achieved through digital platform adoption.
Comprehensive research methodology ensures accurate and reliable market analysis through multiple data collection and validation approaches. Primary research involves direct engagement with industry stakeholders, including property developers, real estate agents, investors, and government officials responsible for sector regulation and policy development.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of government statistics, industry reports, financial statements, and regulatory documents that provide quantitative and qualitative insights into market performance. Data triangulation methods validate findings through cross-referencing multiple sources and analytical approaches.
Market surveys capture consumer preferences, investment intentions, and satisfaction levels across different property segments and geographic regions. Expert interviews provide qualitative insights into market trends, challenges, and future prospects from experienced industry professionals.
Quantitative analysis employs statistical methods to identify patterns, correlations, and trends within market data. Qualitative assessment incorporates subjective factors such as market sentiment, regulatory impact, and competitive positioning that influence market dynamics but may not be captured in numerical data alone.
Regional market analysis reveals significant variations in real estate performance, opportunities, and challenges across Indonesia’s diverse geographic landscape. Greater Jakarta Area dominates market activity, accounting for approximately 40% of total real estate investment and demonstrating the highest property values and transaction volumes.
Java Island concentrates the majority of real estate development, with cities like Surabaya, Bandung, and Semarang showing strong growth potential. Surabaya emerges as a significant secondary market, benefiting from its position as East Java’s economic center and improved infrastructure connectivity.
Bali maintains its position as a premium destination for tourism-related real estate, with international investors particularly active in hospitality and luxury residential segments. Sumatra shows growing potential, particularly in Medan and Palembang, driven by natural resource industries and agricultural development.
Emerging regions including Kalimantan and Sulawesi present long-term opportunities as infrastructure development improves accessibility and economic activity expands. Regional development policies aim to distribute economic growth more evenly across the archipelago, creating new real estate investment opportunities outside traditional centers.
Urban-rural dynamics show continued concentration of high-value developments in major cities, while rural areas focus on agricultural and industrial land use. Coastal areas attract tourism and logistics developments, while inland regions emphasize manufacturing and residential projects.
Competitive landscape features a diverse mix of domestic and international players operating across various real estate segments and geographic markets. Market leadership is distributed among several major developers, each with distinct strengths and market positioning strategies.
International developers increasingly participate through joint ventures and partnerships with local companies, bringing global expertise and capital to Indonesian projects. Competitive strategies emphasize location selection, product differentiation, and customer service excellence to maintain market position.
Market segmentation reveals distinct characteristics and performance patterns across different property types, price ranges, and target markets. Residential segment dominates overall market activity, with subsegments including luxury, middle-class, and affordable housing categories serving different demographic groups.
By Property Type:
By Price Segment:
By Geographic Focus:
Residential category demonstrates robust performance across multiple subsegments, with condominiums and apartments showing particular strength in urban markets. Luxury residential attracts both domestic high-net-worth individuals and international buyers seeking Indonesian property exposure. The segment benefits from exclusive locations, premium amenities, and professional property management services.
Middle-class housing represents the largest market opportunity, supported by improving mortgage availability and rising incomes. Affordable housing initiatives receive government support through subsidies and financing programs, creating opportunities for developers focused on this segment.
Commercial real estate shows strong performance in office and retail categories. Office space demand grows with multinational corporation expansion and domestic business development. Retail properties benefit from rising consumer spending and modern shopping preferences, though e-commerce growth creates challenges for traditional retail formats.
Industrial properties experience sustained demand from manufacturing expansion and logistics development. Warehouse facilities particularly benefit from e-commerce growth and improved distribution networks. Industrial parks offer integrated solutions for manufacturing companies seeking operational efficiency.
Hospitality properties show recovery and growth potential as tourism rebounds and domestic travel increases. Hotel developments focus on both business and leisure segments, while serviced apartments cater to extended-stay and corporate housing needs.
Industry participants realize substantial benefits from Indonesia’s dynamic real estate market environment. Property developers benefit from strong demand fundamentals, government infrastructure support, and access to diverse financing options. The market offers opportunities for both large-scale integrated developments and specialized niche projects.
Investors gain exposure to Indonesia’s economic growth through real estate appreciation and rental income opportunities. Portfolio diversification benefits arise from property investments that often demonstrate different risk-return profiles compared to financial assets. Inflation hedging characteristics of real estate provide protection against currency devaluation and economic volatility.
Financial institutions expand business opportunities through mortgage lending, development financing, and real estate investment products. Construction companies benefit from sustained development activity and infrastructure projects that support market growth.
Government stakeholders achieve economic development objectives through real estate sector growth that creates employment, generates tax revenue, and supports related industries. Urban planning benefits from private sector development that contributes to city infrastructure and amenities.
End users benefit from improved housing options, modern commercial facilities, and enhanced property management services. Quality of life improvements result from better-planned developments that incorporate amenities and sustainable design practices.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Emerging trends reshape Indonesia’s real estate landscape through technological innovation, changing consumer preferences, and evolving business models. Digital transformation accelerates across all market segments, with online property platforms, virtual tours, and digital transaction processing becoming standard practice.
Sustainable development gains prominence as environmental awareness increases and green building standards become more widely adopted. Energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction materials attract environmentally conscious buyers and tenants while reducing operational costs.
Mixed-use development trend reflects urbanization patterns and lifestyle preferences for integrated living, working, and recreational spaces. Transit-oriented development aligns with government infrastructure investments and addresses urban mobility challenges.
Co-living and co-working concepts gain traction among younger demographics seeking flexible, community-oriented spaces. Smart building technologies including IoT integration, automated systems, and enhanced security features become competitive differentiators.
Affordable housing innovation incorporates new construction methods, financing mechanisms, and design approaches to address housing accessibility challenges. Regional expansion beyond traditional centers creates opportunities in emerging cities and suburban areas with improved infrastructure connectivity.
Recent industry developments demonstrate the dynamic nature of Indonesia’s real estate sector and its adaptation to changing market conditions. Government policy initiatives include new regulations aimed at streamlining permit processes and encouraging affordable housing development through tax incentives and financing support.
Infrastructure projects significantly impact real estate markets, with new transportation networks, airports, and utilities enhancing property accessibility and values. The development of Indonesia’s new capital city represents a major long-term opportunity for real estate investment and development.
Technology adoption accelerates across the sector, with major developers implementing PropTech solutions for marketing, sales, and property management. Digital platforms transform property search and transaction processes, improving efficiency and customer experience.
International partnerships increase as Indonesian developers collaborate with foreign companies to access capital, expertise, and global best practices. Sustainability initiatives gain momentum with green building certifications and environmentally responsible development practices becoming more common.
Financial innovation includes new mortgage products, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and crowdfunding platforms that expand investment access and financing options. Market consolidation trends show larger developers acquiring smaller companies to achieve scale and market presence.
Strategic recommendations for market participants emphasize the importance of adapting to evolving market conditions while capitalizing on Indonesia’s fundamental growth drivers. Location strategy remains critical, with focus on areas benefiting from infrastructure development and demographic trends.
Product diversification helps developers and investors manage risk while capturing opportunities across different market segments. Technology integration becomes essential for competitive positioning and operational efficiency. Companies should invest in digital platforms, smart building features, and data analytics capabilities.
Partnership strategies can help overcome regulatory challenges and access specialized expertise or capital. Joint ventures with local partners benefit foreign investors, while domestic companies can gain from international collaboration.
Sustainability focus addresses both regulatory requirements and market demand for environmentally responsible developments. Financial planning should account for economic volatility and ensure adequate capital reserves for project completion and market downturns.
Market research and customer analysis become increasingly important as competition intensifies and consumer preferences evolve. MWR analysis suggests that companies investing in market intelligence and customer relationship management achieve superior performance compared to industry averages.
Future prospects for Indonesia’s real estate market remain positive, supported by fundamental economic and demographic drivers that create sustained demand across multiple property segments. Long-term growth expectations reflect Indonesia’s position as one of Southeast Asia’s largest and most dynamic economies.
Demographic advantages continue to support market expansion, with a young population and ongoing urbanization creating sustained demand for residential and commercial properties. Economic diversification efforts reduce dependence on commodity exports while strengthening service and manufacturing sectors that drive real estate demand.
Infrastructure development programs enhance market accessibility and create new development opportunities across previously underserved regions. Government commitment to housing accessibility and urban development supports continued sector growth.
Technology integration will accelerate, transforming property development, marketing, and management practices. Sustainability requirements will become more stringent, driving innovation in construction methods and building operations.
Market maturation brings increased sophistication in development practices, financing mechanisms, and regulatory compliance. Regional expansion beyond traditional centers offers growth opportunities as infrastructure and economic development spread across the archipelago. According to MarkWide Research projections, the market is expected to maintain steady growth momentum with annual expansion rates exceeding regional averages over the next decade.
Indonesia’s real estate market presents compelling opportunities for developers, investors, and industry participants seeking exposure to one of Southeast Asia’s most dynamic property sectors. The market benefits from fundamental strengths including a large domestic population, sustained economic growth, and government support for infrastructure and housing development.
Market dynamics reflect the complex interplay of urbanization trends, demographic advantages, and evolving consumer preferences that create sustained demand across residential, commercial, and industrial property segments. Technological transformation and sustainability focus reshape industry practices while creating competitive differentiation opportunities.
Strategic success in this market requires careful attention to location selection, product positioning, regulatory compliance, and customer needs. Partnership strategies and technology adoption become increasingly important for competitive positioning and operational efficiency.
Future growth prospects remain positive, supported by Indonesia’s economic development trajectory and demographic advantages that create long-term demand fundamentals. The Indonesia real estate market continues to evolve and mature, offering substantial opportunities for well-positioned market participants who understand local conditions and adapt to changing market dynamics.
What is Indonesia Real Estate?
Indonesia Real Estate refers to the buying, selling, and leasing of land and properties in Indonesia, encompassing residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
What are the key players in the Indonesia Real Estate Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Real Estate Market include companies like Agung Podomoro Land, Ciputra Development, and Summarecon Agung, among others.
What are the main drivers of growth in the Indonesia Real Estate Market?
The main drivers of growth in the Indonesia Real Estate Market include urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and government infrastructure projects that enhance connectivity.
What challenges does the Indonesia Real Estate Market face?
Challenges in the Indonesia Real Estate Market include regulatory hurdles, fluctuating property prices, and issues related to land ownership and title disputes.
What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Real Estate Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia Real Estate Market include the growing demand for affordable housing, the rise of smart city developments, and increased foreign investment in property.
What trends are shaping the Indonesia Real Estate Market?
Trends shaping the Indonesia Real Estate Market include the shift towards sustainable building practices, the integration of technology in property management, and the increasing popularity of mixed-use developments.
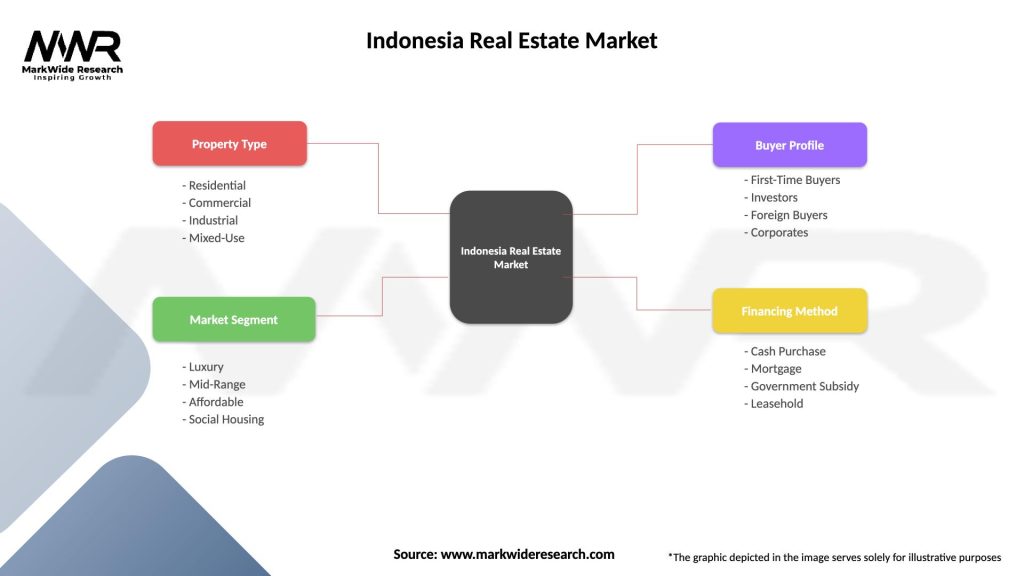
Indonesia Real Estate Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Property Type | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Mixed-Use |
| Market Segment | Luxury, Mid-Range, Affordable, Social Housing |
| Buyer Profile | First-Time Buyers, Investors, Foreign Buyers, Corporates |
| Financing Method | Cash Purchase, Mortgage, Government Subsidy, Leasehold |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indonesia Real Estate Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at