444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Indonesia insecticide market represents a critical component of the nation’s agricultural infrastructure, serving as the backbone for crop protection across the archipelago’s diverse farming landscapes. Indonesia’s agricultural sector relies heavily on effective pest management solutions to maintain food security and support the livelihoods of millions of farmers throughout the country. The market encompasses a comprehensive range of chemical and biological pest control products designed to combat various insect threats that pose significant risks to crop yields and agricultural productivity.
Market dynamics in Indonesia reflect the country’s unique geographical challenges, with over 17,000 islands creating diverse microclimates that support both beneficial and harmful insect populations. The tropical climate conditions provide year-round growing seasons, which simultaneously increase crop production potential and pest pressure. Agricultural modernization efforts have driven increased adoption of sophisticated insecticide formulations, with farmers increasingly recognizing the importance of integrated pest management approaches.
Growth trajectories indicate robust expansion driven by rising agricultural productivity demands and increasing awareness of crop protection benefits. The market demonstrates strong resilience, supported by government initiatives promoting food security and agricultural sustainability. Regional variations across Indonesia’s major agricultural zones create diverse market opportunities, from rice paddies in Java to palm oil plantations in Sumatra and Kalimantan.
The Indonesia insecticide market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of pest control products, services, and technologies specifically designed to manage insect populations that threaten agricultural crops throughout Indonesia’s diverse farming regions. This market encompasses various chemical formulations, biological control agents, and integrated pest management solutions that help farmers protect their crops from destructive insects while maintaining sustainable agricultural practices.
Market scope includes synthetic insecticides, bio-based alternatives, application equipment, and related services that support effective pest management strategies. The definition extends beyond simple product sales to include technical advisory services, application training, and integrated solutions that address the complex pest challenges faced by Indonesian farmers across different crop types and growing conditions.
Stakeholder involvement spans from multinational agrochemical companies to local distributors, farmers, agricultural cooperatives, and government regulatory bodies. The market operates within a framework of environmental regulations, safety standards, and agricultural policies that shape product development, registration processes, and market access strategies throughout Indonesia’s agricultural value chain.
Indonesia’s insecticide market demonstrates remarkable growth potential driven by expanding agricultural activities, increasing crop diversification, and rising awareness of integrated pest management practices. The market benefits from strong government support for agricultural modernization and food security initiatives, creating favorable conditions for sustained expansion across multiple agricultural segments.
Key market drivers include the growing need for higher crop yields to feed Indonesia’s expanding population, increasing export demands for agricultural products, and the adoption of modern farming techniques. Climate change impacts have intensified pest pressures, driving demand for more effective and environmentally sustainable pest control solutions. Technological advancement in insecticide formulations has improved efficacy while addressing environmental and safety concerns.
Market segmentation reveals strong performance across multiple categories, with synthetic insecticides maintaining dominant market positions while biological alternatives gain increasing traction. Regional distribution shows concentrated activity in major agricultural provinces, with Java, Sumatra, and Sulawesi representing primary market centers. Competitive dynamics feature both international agrochemical giants and emerging local players, creating a diverse and dynamic marketplace.
Future prospects indicate continued expansion supported by agricultural modernization trends, increasing farmer education, and growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices. The market is positioned to benefit from Indonesia’s strategic importance in global food production and the government’s commitment to achieving food security objectives through enhanced agricultural productivity.
Strategic market analysis reveals several critical insights that define the Indonesia insecticide market landscape and future development trajectory:
Population growth represents the fundamental driver behind Indonesia’s expanding insecticide market, as the country’s growing population creates increasing demand for food production and agricultural productivity enhancement. With over 270 million people requiring food security, farmers face mounting pressure to maximize crop yields while minimizing losses to pest damage. Urbanization trends have reduced available agricultural land, intensifying the need for higher productivity per hectare through effective pest management strategies.
Agricultural modernization initiatives supported by government policies have accelerated the adoption of advanced farming techniques, including sophisticated pest control methods. The Indonesian government’s commitment to achieving food self-sufficiency has resulted in substantial investments in agricultural infrastructure and farmer education programs. Technology transfer programs have introduced modern pest management concepts, driving demand for more effective insecticide solutions.
Climate change impacts have created new pest management challenges, with changing temperature and precipitation patterns altering insect life cycles and population dynamics. Warmer temperatures have extended growing seasons while simultaneously increasing pest reproduction rates and expanding their geographical ranges. Extreme weather events have disrupted traditional pest control timing, requiring more flexible and resilient pest management approaches.
Export market opportunities have driven quality improvements in Indonesian agricultural products, necessitating compliance with international pest management standards. Growing demand for Indonesian agricultural exports, particularly palm oil, coffee, and tropical fruits, has created incentives for farmers to adopt professional-grade pest control solutions. Global supply chain integration has introduced international quality standards that require consistent and effective pest management practices.
Environmental concerns pose significant challenges to traditional insecticide market growth, as increasing awareness of ecological impacts drives demand for more sustainable alternatives. Regulatory pressures have resulted in restrictions on certain chemical compounds, requiring manufacturers to invest in research and development of environmentally-friendly formulations. Biodiversity conservation efforts have highlighted the need for selective pest control methods that minimize impacts on beneficial insects and ecosystem health.
Economic constraints among smallholder farmers limit market expansion potential, as many producers struggle with the costs associated with modern pest control solutions. Limited access to credit and financial services restricts farmers’ ability to invest in quality insecticides and application equipment. Price sensitivity in rural markets often leads to the use of lower-quality or counterfeit products, undermining market development and farmer outcomes.
Regulatory complexity creates barriers for both domestic and international companies seeking to enter or expand within the Indonesian market. Product registration processes can be lengthy and expensive, particularly for innovative formulations or biological alternatives. Compliance requirements vary across different regions and crop types, creating additional complexity for market participants.
Knowledge gaps among farmers regarding proper insecticide selection, application techniques, and safety protocols limit market efficiency and effectiveness. Limited extension services in remote areas restrict access to technical information and training opportunities. Traditional farming practices in some regions resist adoption of modern pest management approaches, slowing market penetration and growth.
Biological insecticide development presents substantial growth opportunities as environmental awareness increases and regulatory frameworks evolve to support sustainable agriculture. The growing demand for organic and environmentally-friendly farming practices creates market space for bio-based pest control solutions. Innovation in microbial insecticides and botanical extracts offers pathways for companies to differentiate their products while addressing environmental concerns.
Digital agriculture integration creates opportunities for precision pest management solutions that optimize insecticide application timing, dosage, and targeting. Smart farming technologies, including drones, sensors, and data analytics, enable more efficient and effective pest control strategies. Mobile technology adoption among farmers provides platforms for delivering pest management advice, weather-based application recommendations, and product information.
Regional expansion opportunities exist in underserved agricultural areas, particularly in eastern Indonesia where agricultural development is accelerating. Infrastructure improvements and government development programs are opening new markets for pest control products and services. Crop diversification trends in these regions create demand for specialized insecticide formulations tailored to specific crops and growing conditions.
Value chain integration opportunities allow companies to expand beyond product sales into comprehensive pest management services, including application services, monitoring, and advisory support. Partnerships with agricultural cooperatives and input suppliers can improve market access and farmer relationships. Export-oriented agriculture growth creates demand for premium pest control solutions that meet international quality standards.
Supply chain dynamics in Indonesia’s insecticide market reflect the country’s unique geographical challenges and distribution requirements. The archipelagic nature of Indonesia creates complex logistics networks that must efficiently deliver products across thousands of islands and diverse agricultural regions. Distribution efficiency has improved through partnerships between manufacturers, distributors, and agricultural cooperatives, enabling better market penetration and farmer access to quality products.
Competitive dynamics feature intense rivalry between international agrochemical companies and emerging local manufacturers, driving innovation and competitive pricing strategies. Market leaders focus on product differentiation through advanced formulations, technical support services, and brand reputation building. Local companies compete primarily on price and regional market knowledge, while international players leverage technology and global expertise.
Regulatory dynamics continue evolving as Indonesian authorities strengthen oversight of pesticide registration, quality control, and environmental impact assessment. Recent regulatory changes have emphasized safety standards, environmental protection, and farmer education requirements. Policy alignment with international standards has improved market access for global companies while raising quality expectations across the industry.
Technology dynamics drive continuous innovation in insecticide formulations, application methods, and integrated pest management approaches. According to MarkWide Research analysis, technological advancement has improved application efficiency by approximately 25% over recent years. Research and development investments focus on developing more selective, environmentally-friendly, and cost-effective pest control solutions that meet evolving market demands.
Comprehensive market research methodology employed for analyzing Indonesia’s insecticide market incorporates multiple data collection and analysis approaches to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings. Primary research activities include extensive field surveys, farmer interviews, distributor consultations, and industry expert discussions across major agricultural regions throughout Indonesia. Data collection protocols ensure representative sampling across different farm sizes, crop types, and geographical locations.
Secondary research components involve analysis of government agricultural statistics, trade data, regulatory documents, and industry publications to establish market context and validate primary findings. International databases and agricultural research institutions provide comparative analysis and trend identification capabilities. Market intelligence gathering includes monitoring of competitor activities, pricing trends, and product launch patterns across the Indonesian market.
Analytical frameworks employ both quantitative and qualitative research methods to develop comprehensive market insights. Statistical analysis techniques identify market trends, growth patterns, and correlation factors affecting market development. Qualitative analysis explores farmer behavior, decision-making processes, and market perception factors that influence purchasing patterns and product adoption rates.
Validation processes include cross-referencing multiple data sources, expert review panels, and field verification activities to ensure research accuracy and reliability. Market projections undergo sensitivity analysis and scenario modeling to account for various market development possibilities. Quality assurance measures maintain research standards and ensure findings accurately represent market conditions and future prospects.
Java region dominates Indonesia’s insecticide market, accounting for approximately 40% of national consumption due to its intensive agricultural activities and high population density. The region’s advanced agricultural infrastructure, extensive irrigation systems, and proximity to major ports create favorable conditions for market development. West Java and Central Java provinces lead in rice production and vegetable cultivation, driving consistent demand for various insecticide categories throughout the year.
Sumatra region represents the second-largest market segment, with 25% market share driven primarily by plantation agriculture including palm oil, rubber, and coffee production. The region’s large-scale agricultural operations require substantial quantities of insecticides for crop protection across extensive plantation areas. North Sumatra and South Sumatra provinces show particularly strong market activity due to their diverse agricultural portfolios and commercial farming operations.
Sulawesi region demonstrates rapid market growth, with increasing agricultural development and crop diversification driving demand for specialized pest control solutions. The region’s expanding cocoa, coffee, and rice production creates opportunities for both traditional and innovative insecticide products. South Sulawesi leads regional market activity, supported by government agricultural development programs and improving infrastructure.
Eastern Indonesia regions, including Kalimantan, Papua, and smaller islands, represent emerging market opportunities with significant growth potential. Infrastructure development and agricultural expansion programs are opening new markets for insecticide products and services. Kalimantan’s palm oil industry creates substantial demand for plantation-specific pest control solutions, while Papua’s agricultural development initiatives drive market expansion in previously underserved areas.
Market leadership in Indonesia’s insecticide sector features a diverse mix of international agrochemical giants and established local companies, creating a dynamic competitive environment that benefits farmers through product innovation and competitive pricing. The competitive landscape reflects both global expertise and local market knowledge, with companies competing on product efficacy, technical support, and distribution network strength.
International players maintain strong market positions through advanced product portfolios and comprehensive technical support services:
Local companies compete effectively through regional market knowledge, competitive pricing, and tailored product offerings:
Product-based segmentation reveals distinct market categories with varying growth trajectories and application characteristics across Indonesia’s diverse agricultural landscape:
By Chemical Class:
By Crop Application:
By Formulation Type:
Synthetic insecticides continue dominating the Indonesian market through proven efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and farmer familiarity. This category benefits from extensive distribution networks, technical support infrastructure, and established application practices among farming communities. Innovation within synthetic categories focuses on improved selectivity, reduced environmental impact, and resistance management strategies that extend product lifecycle and effectiveness.
Biological insecticides represent the fastest-growing market category, with annual growth rates exceeding 15% driven by environmental awareness and regulatory support for sustainable agriculture. This segment includes microbial insecticides, botanical extracts, and pheromone-based products that offer environmentally-friendly alternatives to synthetic chemicals. Market adoption is accelerating among export-oriented farmers and organic producers seeking certification compliance.
Systemic insecticides demonstrate strong performance in plantation and perennial crop applications where long-lasting protection is essential. These products offer efficient pest control through plant uptake and translocation, providing extended protection periods and reduced application frequency. Technology advancement in systemic formulations has improved plant safety and environmental fate characteristics.
Contact insecticides maintain important market positions for immediate pest control needs and resistance management programs. These products offer rapid knockdown effects and visible pest control results that farmers value for immediate problem resolution. Application versatility makes contact insecticides suitable for various crop types and pest situations across Indonesia’s diverse agricultural systems.
Farmers benefit significantly from Indonesia’s expanding insecticide market through improved crop protection options, higher yields, and enhanced profitability. Access to effective pest control solutions enables farmers to reduce crop losses, improve product quality, and meet market requirements for both domestic and export sales. Technical support services accompanying modern insecticide products provide farmers with valuable knowledge and application guidance that improves overall farm management practices.
Manufacturers and distributors benefit from Indonesia’s large and growing agricultural market, which provides substantial revenue opportunities and market expansion potential. The country’s diverse agricultural landscape creates demand for various product categories and formulations, enabling companies to optimize their product portfolios. Local partnerships with distributors and cooperatives provide market access and customer relationship advantages that support long-term business development.
Agricultural cooperatives gain value through bulk purchasing power, technical expertise access, and member service enhancement capabilities. Cooperative involvement in insecticide distribution creates revenue streams while providing members with quality products and technical support. Training programs delivered through cooperatives improve farmer knowledge and application practices, leading to better pest control outcomes and member satisfaction.
Government stakeholders benefit from improved food security, agricultural productivity, and rural economic development supported by effective pest management. Enhanced crop protection contributes to national food security objectives and agricultural export competitiveness. Regulatory oversight of insecticide markets ensures product quality, environmental protection, and farmer safety while supporting sustainable agricultural development goals.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainable agriculture adoption represents the most significant trend shaping Indonesia’s insecticide market, with increasing emphasis on environmentally-responsible pest management practices. Farmers are gradually shifting toward integrated pest management approaches that combine biological, cultural, and chemical control methods. Organic farming growth has accelerated demand for biological insecticides and natural pest control alternatives that meet organic certification requirements.
Digital technology integration is transforming pest management practices through smartphone applications, weather monitoring systems, and precision agriculture tools. MWR data indicates that 22% of commercial farmers now use digital tools for pest management decision-making. Mobile applications providing pest identification, treatment recommendations, and application timing guidance are gaining widespread adoption among tech-savvy farmers.
Resistance management has become a critical focus area as pest populations develop resistance to commonly-used insecticides. Farmers and advisors are implementing rotation strategies, tank mixing approaches, and integrated pest management practices to preserve product effectiveness. Industry collaboration on resistance monitoring and management strategies has improved through farmer education programs and technical support initiatives.
Premium product adoption is increasing among commercial farmers and export-oriented producers who recognize the value of advanced formulations and technical support services. Quality-conscious farmers are willing to invest in higher-priced products that offer superior efficacy, environmental safety, and technical support. Brand loyalty is strengthening as farmers experience the benefits of consistent product performance and reliable technical service.
Regulatory modernization has significantly impacted Indonesia’s insecticide market through updated registration requirements, safety standards, and environmental impact assessments. Recent regulatory changes have streamlined approval processes for biological products while strengthening oversight of synthetic chemicals. International harmonization efforts have aligned Indonesian standards with global best practices, improving market access for international companies.
Manufacturing capacity expansion by both domestic and international companies has improved product availability and reduced import dependence. Several major players have established or expanded local production facilities to serve the Indonesian market more effectively. Local production has reduced costs, improved supply chain reliability, and created employment opportunities in the agricultural sector.
Distribution network enhancement has improved farmer access to quality products and technical support services across Indonesia’s diverse agricultural regions. Companies have invested in rural distribution centers, mobile sales units, and cooperative partnerships to reach smallholder farmers. Digital distribution platforms are emerging to complement traditional channels and provide farmers with convenient product access and information.
Research and development investments have accelerated innovation in insecticide formulations, application technologies, and integrated pest management solutions. Collaborative research programs between companies, universities, and government institutions have advanced understanding of local pest dynamics and control strategies. Innovation focus emphasizes developing products specifically adapted to Indonesian agricultural conditions and pest challenges.
Market participants should prioritize development of environmentally-sustainable product portfolios that align with evolving regulatory requirements and farmer preferences for responsible pest management solutions. Investment in biological insecticides, reduced-risk formulations, and integrated pest management systems will position companies favorably for long-term market success. Innovation strategies should focus on products that address specific Indonesian pest challenges while meeting international environmental and safety standards.
Distribution strategy optimization requires enhanced focus on reaching smallholder farmers through cooperative partnerships, mobile distribution units, and digital platforms. Companies should invest in rural infrastructure development and farmer education programs that build long-term customer relationships. Technical support services should be expanded to include application training, pest monitoring assistance, and integrated pest management guidance.
Digital transformation initiatives should be accelerated to capitalize on growing smartphone adoption and farmer interest in precision agriculture tools. Development of user-friendly mobile applications, weather-based advisory services, and pest identification tools can differentiate companies and improve farmer outcomes. Data analytics capabilities should be developed to provide personalized recommendations and optimize pest management strategies for individual farms.
Regional expansion strategies should target underserved agricultural areas in eastern Indonesia where infrastructure development and agricultural modernization create new market opportunities. Companies should adapt their product portfolios and distribution approaches to local conditions and farmer needs. Partnership development with local distributors, cooperatives, and government agencies can accelerate market penetration and build sustainable competitive advantages.
Long-term market prospects for Indonesia’s insecticide sector remain highly positive, supported by fundamental drivers including population growth, agricultural modernization, and increasing food security requirements. The market is expected to maintain robust growth trajectories driven by expanding agricultural activities, crop diversification, and rising farmer awareness of professional pest management benefits. Structural changes in Indonesian agriculture, including consolidation trends and commercialization, will create opportunities for advanced pest control solutions.
Technology evolution will significantly reshape market dynamics through precision agriculture adoption, biological product development, and digital integration of pest management services. According to MarkWide Research projections, biological insecticides could capture 20% market share within the next decade as environmental awareness and regulatory support continue growing. Innovation acceleration in sustainable pest control technologies will create new market categories and competitive advantages.
Regulatory development will continue influencing market evolution through strengthened environmental standards, safety requirements, and sustainable agriculture promotion. Future regulations are expected to favor biological products, integrated pest management approaches, and reduced-risk formulations. Policy alignment with international standards will improve market access for global companies while raising quality expectations across the industry.
Market consolidation trends may emerge as smaller players seek partnerships or acquisition opportunities to compete effectively with larger companies. Successful market participants will be those that combine product innovation, technical expertise, and strong distribution capabilities. Sustainable competitive advantages will increasingly depend on environmental stewardship, farmer education, and integrated service offerings that go beyond traditional product sales.
Indonesia’s insecticide market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector that plays a crucial role in supporting the country’s agricultural development and food security objectives. The market demonstrates strong fundamentals driven by expanding agricultural activities, increasing pest management awareness, and growing demand for crop protection solutions across diverse agricultural systems. Market evolution reflects the balance between traditional pest control approaches and emerging sustainable alternatives that address environmental and safety concerns.
Strategic opportunities abound for companies that can effectively navigate the complex Indonesian market landscape while delivering value to farmers through innovative products, technical support, and distribution excellence. The shift toward sustainable agriculture practices creates significant opportunities for biological products, integrated pest management solutions, and environmentally-responsible formulations. Success factors include understanding local market conditions, building strong farmer relationships, and adapting to evolving regulatory requirements.
Future market development will be characterized by continued growth, technological advancement, and increasing sophistication in pest management approaches. Companies that invest in innovation, sustainability, and farmer education will be best positioned to capitalize on Indonesia’s substantial market potential. The Indonesia insecticide market remains an attractive opportunity for both established players and new entrants willing to commit to long-term market development and farmer success.
What is Insecticide?
Insecticide refers to substances used to kill or control insects that are harmful to crops, livestock, and human health. They are essential in agriculture for protecting plants from pests and ensuring food security.
What are the key players in the Indonesia Insecticide Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Insecticide Market include Syngenta, Bayer CropScience, and BASF, which are known for their innovative pest control solutions and extensive product portfolios, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Indonesia Insecticide Market?
The growth of the Indonesia Insecticide Market is driven by increasing agricultural production, rising pest resistance to traditional methods, and the growing demand for sustainable farming practices.
What challenges does the Indonesia Insecticide Market face?
The Indonesia Insecticide Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns regarding chemical usage, and the need for effective pest management strategies that minimize harm to non-target species.
What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Insecticide Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia Insecticide Market include the development of biopesticides, advancements in precision agriculture technologies, and increasing awareness of integrated pest management practices among farmers.
What trends are shaping the Indonesia Insecticide Market?
Trends in the Indonesia Insecticide Market include a shift towards organic and environmentally friendly products, the use of digital tools for pest monitoring, and the integration of AI in pest control solutions.
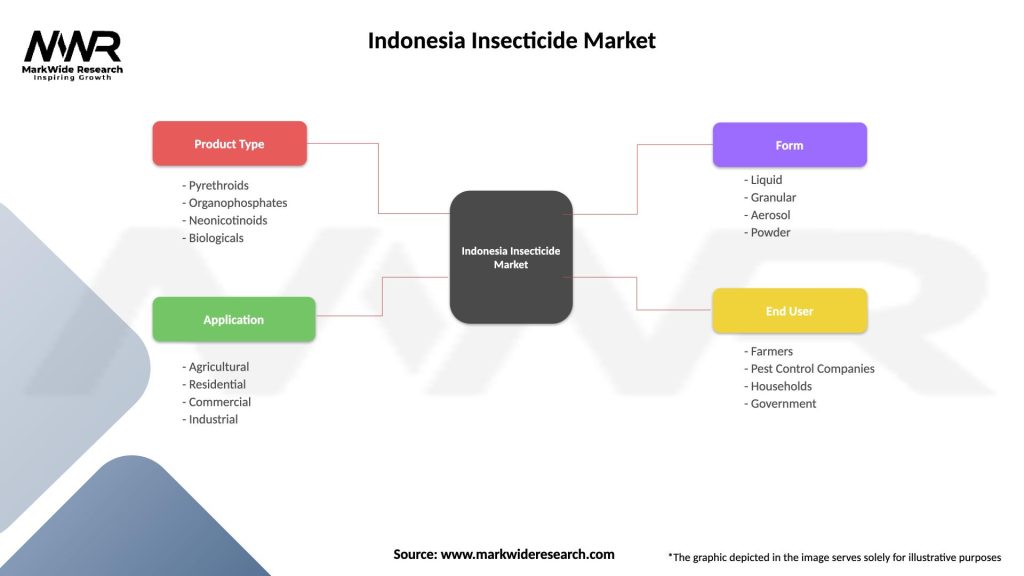
Indonesia Insecticide Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Pyrethroids, Organophosphates, Neonicotinoids, Biologicals |
| Application | Agricultural, Residential, Commercial, Industrial |
| Form | Liquid, Granular, Aerosol, Powder |
| End User | Farmers, Pest Control Companies, Households, Government |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indonesia Insecticide Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at