444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management market represents a rapidly evolving technological landscape that is transforming how organizations manage their mobile device ecosystems. As Indonesia continues its digital transformation journey, businesses across various sectors are increasingly adopting comprehensive mobility management solutions to secure, monitor, and optimize their mobile infrastructure. The market encompasses a wide range of solutions including mobile device management, mobile application management, mobile content management, and mobile identity management systems.
Market dynamics in Indonesia reflect the country’s position as Southeast Asia’s largest economy, with organizations recognizing the critical importance of enterprise mobility in maintaining competitive advantages. The growing adoption of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, coupled with the increasing penetration of smartphones and tablets in business environments, has created substantial demand for sophisticated mobility management platforms. MarkWide Research analysis indicates that the market is experiencing robust growth driven by digital transformation initiatives across government and private sectors.
Technology adoption rates show significant momentum, with enterprise mobility management solutions gaining traction at approximately 12.5% annually across various industry verticals. The market benefits from Indonesia’s strong telecommunications infrastructure and the government’s commitment to digital economy development through initiatives like Making Indonesia 4.0 and the Digital Indonesia roadmap.
The Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of software solutions, platforms, and services designed to enable organizations to securely manage, monitor, and control mobile devices, applications, and content within their corporate environments. This market encompasses various technological components that work together to provide seamless mobile workforce enablement while maintaining security protocols and compliance requirements.
Enterprise Mobility Management solutions in Indonesia typically include mobile device management (MDM) capabilities for device provisioning and security, mobile application management (MAM) for controlling app distribution and usage, mobile content management (MCM) for secure document sharing, and mobile identity management (MIM) for user authentication and access control. These integrated solutions enable organizations to support diverse mobile ecosystems while protecting sensitive corporate data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Strategic market positioning reveals that Indonesia’s Enterprise Mobility Management sector is experiencing unprecedented growth momentum, driven by accelerating digital transformation initiatives and evolving workplace mobility requirements. Organizations across manufacturing, financial services, healthcare, and government sectors are implementing comprehensive mobility management strategies to support remote work capabilities and enhance operational efficiency.
Key market drivers include the widespread adoption of cloud-based solutions, increasing cybersecurity concerns, and regulatory compliance requirements that mandate secure mobile device management. The market benefits from Indonesia’s robust mobile infrastructure, with mobile device penetration reaching approximately 89% of the population, creating substantial opportunities for enterprise mobility solutions.
Technology trends indicate growing demand for artificial intelligence-powered mobility management platforms, zero-trust security frameworks, and integrated endpoint management solutions. The market is characterized by increasing preference for cloud-native solutions that offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and rapid deployment capabilities across diverse organizational environments.

Market penetration analysis reveals several critical insights that define the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management landscape:
Digital transformation initiatives serve as the primary catalyst driving Indonesia’s Enterprise Mobility Management market expansion. Organizations across various sectors are implementing comprehensive digitalization strategies that require robust mobile device management capabilities to support modern workforce requirements and operational efficiency objectives.
Regulatory compliance requirements significantly influence market growth, particularly in financial services, healthcare, and government sectors where data protection and privacy regulations mandate secure mobile device management. Indonesian organizations must comply with various regulatory frameworks including the Personal Data Protection Law and sector-specific compliance requirements that drive demand for comprehensive mobility management solutions.
Cybersecurity concerns continue to escalate as organizations recognize the vulnerabilities associated with mobile device usage in corporate environments. The increasing frequency of cyber threats targeting mobile platforms has created substantial demand for advanced security features including threat detection, data encryption, and remote device management capabilities.
Workforce mobility trends reflect changing work patterns, with organizations supporting hybrid work models that require seamless mobile device integration. The growing adoption of BYOD policies and the need to support diverse mobile ecosystems drive demand for flexible and comprehensive mobility management platforms that can accommodate various device types and operating systems.
Implementation complexity presents significant challenges for organizations considering enterprise mobility management solutions. The technical complexity associated with integrating mobility management platforms with existing IT infrastructure, legacy systems, and diverse application environments can create deployment barriers and extended implementation timelines.
Cost considerations influence adoption decisions, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises that may find comprehensive mobility management solutions financially challenging. The total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, ongoing maintenance, and staff training requirements, can represent substantial investments for organizations with limited IT budgets.
Skills shortage in the Indonesian market creates challenges for organizations seeking to implement and manage sophisticated mobility management platforms. The limited availability of qualified IT professionals with expertise in enterprise mobility management technologies can impact deployment success and ongoing solution optimization.
Privacy concerns among employees regarding device monitoring and data collection capabilities can create resistance to mobility management implementation. Organizations must balance security requirements with employee privacy expectations, which can complicate solution deployment and user acceptance.
Government digitalization initiatives present substantial opportunities for Enterprise Mobility Management solution providers in Indonesia. The government’s commitment to digital transformation through various national programs creates demand for secure and scalable mobility management platforms across public sector organizations and government agencies.
SME market expansion represents a significant growth opportunity as small and medium-sized enterprises increasingly recognize the importance of mobile device management. The development of cost-effective, cloud-based solutions specifically designed for SME requirements can unlock substantial market potential in this underserved segment.
Industry-specific solutions offer opportunities for specialized mobility management platforms tailored to specific sector requirements. Industries such as healthcare, education, and logistics present unique mobility management challenges that can be addressed through customized solutions and vertical-specific features.
Artificial intelligence integration creates opportunities for next-generation mobility management platforms that leverage AI and machine learning capabilities for predictive analytics, automated threat detection, and intelligent device management. These advanced capabilities can differentiate solutions and create competitive advantages in the evolving market landscape.
Technology evolution continues to reshape the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management market, with emerging technologies such as 5G connectivity, edge computing, and artificial intelligence creating new possibilities for mobile device management and optimization. These technological advances enable more sophisticated mobility management capabilities while improving performance and user experience.
Competitive landscape dynamics reflect increasing market consolidation as established technology vendors acquire specialized mobility management providers to expand their solution portfolios. This consolidation trend creates opportunities for comprehensive platform providers while challenging standalone solution vendors to differentiate their offerings.
Customer expectations continue to evolve, with organizations demanding more intuitive, automated, and intelligent mobility management solutions. The shift toward user-centric design and simplified management interfaces drives innovation in solution development and influences vendor product roadmaps.
Partnership ecosystems play increasingly important roles in market dynamics, with solution providers collaborating with system integrators, telecommunications providers, and technology vendors to deliver comprehensive mobility management solutions. These strategic partnerships enable broader market reach and enhanced solution capabilities.
Comprehensive market analysis for the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management market employed a multi-faceted research approach combining primary and secondary research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable market insights. The research framework incorporated quantitative and qualitative analysis techniques to provide comprehensive market understanding.
Primary research activities included structured interviews with key market participants, including enterprise mobility management solution providers, system integrators, end-user organizations, and industry experts. These interviews provided valuable insights into market trends, challenges, opportunities, and competitive dynamics from multiple stakeholder perspectives.
Secondary research encompassed extensive analysis of industry reports, company financial statements, government publications, regulatory documents, and technology trend analyses. This comprehensive secondary research provided foundational market data and contextual information supporting primary research findings.
Data validation processes ensured research accuracy through triangulation of information sources, cross-verification of market data, and validation of findings with industry experts. The research methodology incorporated statistical analysis techniques to identify market trends and growth patterns while maintaining data integrity and reliability.
Jakarta metropolitan area dominates the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management market, accounting for approximately 42% of total market activity. The capital region’s concentration of multinational corporations, financial institutions, and government agencies creates substantial demand for sophisticated mobility management solutions. Jakarta’s advanced telecommunications infrastructure and high smartphone penetration rates support robust market growth.
Surabaya and surrounding East Java region represents the second-largest market segment, driven by significant manufacturing and industrial activity that requires comprehensive mobile device management capabilities. The region’s growing technology sector and increasing digitalization initiatives among local businesses contribute to steady market expansion.
Bandung and West Java demonstrate strong growth potential, particularly in the technology and education sectors. The region’s emerging startup ecosystem and increasing adoption of digital technologies among educational institutions create opportunities for mobility management solution providers.
Medan and North Sumatra show growing market interest, primarily driven by agricultural and commodity trading businesses that require mobile workforce management capabilities. The region’s economic development and increasing business digitalization efforts support market growth prospects.
Other regional markets including Central Java, South Sumatra, and Bali contribute to overall market expansion, with local businesses and government organizations increasingly recognizing the importance of enterprise mobility management for operational efficiency and security.
Market leadership in Indonesia’s Enterprise Mobility Management sector is characterized by a mix of international technology giants and specialized regional solution providers. The competitive landscape reflects diverse approaches to mobility management, ranging from comprehensive platform providers to niche solution specialists.
Competitive strategies focus on solution differentiation through advanced security features, artificial intelligence integration, and industry-specific customization capabilities. Vendors increasingly emphasize cloud-native architectures, simplified deployment processes, and comprehensive support services to gain competitive advantages.
By Solution Type:
By Deployment Model:
By Organization Size:
By Industry Vertical:
Mobile Device Management solutions continue to dominate the Indonesia market, representing approximately 55% of total solution deployments. Organizations prioritize comprehensive device control capabilities including remote configuration, security policy enforcement, and device lifecycle management. The segment benefits from increasing BYOD adoption and the need for centralized device management across diverse mobile ecosystems.
Mobile Application Management demonstrates strong growth momentum as organizations seek granular control over application distribution and usage. The segment addresses critical requirements for application security, data protection, and compliance management while supporting diverse application environments and development frameworks.
Cloud-based deployment models achieve dominant market position, with 76% of new implementations choosing cloud solutions over traditional on-premises alternatives. Organizations value the scalability, cost-effectiveness, and rapid deployment capabilities offered by cloud-native mobility management platforms.
Large enterprise segment maintains market leadership through substantial investments in comprehensive mobility management platforms. However, the SME segment shows accelerating growth as cost-effective solutions become more accessible and small businesses recognize the importance of mobile device security and management.
Financial services vertical leads market adoption driven by stringent regulatory requirements and the critical importance of data security in mobile banking and financial applications. The sector’s sophisticated security requirements drive demand for advanced threat protection and compliance management capabilities.
Enhanced Security Posture: Organizations implementing enterprise mobility management solutions achieve significantly improved security capabilities through comprehensive device monitoring, threat detection, and data protection features. These security enhancements protect against mobile-specific threats while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Operational Efficiency Gains: MWR analysis indicates that organizations experience substantial operational efficiency improvements through centralized device management, automated policy enforcement, and streamlined mobile application deployment processes. These efficiency gains translate to reduced IT administrative overhead and improved workforce productivity.
Cost Optimization: Enterprise mobility management solutions enable organizations to optimize mobile-related costs through better device lifecycle management, reduced support requirements, and improved resource utilization. Cloud-based solutions particularly offer cost advantages through subscription-based pricing models and reduced infrastructure requirements.
Compliance Assurance: Solutions provide comprehensive compliance management capabilities that help organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards. Automated compliance reporting and policy enforcement reduce compliance risks while simplifying audit processes.
Workforce Enablement: Modern mobility management platforms support flexible work arrangements and diverse device preferences while maintaining security and control. This workforce enablement capability improves employee satisfaction and supports organizational agility in responding to changing business requirements.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Zero Trust Security Architecture emerges as a dominant trend in Indonesia’s Enterprise Mobility Management market, with organizations implementing comprehensive security frameworks that verify every device and user before granting network access. This approach addresses evolving cybersecurity threats while supporting distributed workforce models and diverse device ecosystems.
Artificial Intelligence Integration transforms mobility management capabilities through intelligent threat detection, predictive analytics, and automated policy enforcement. AI-powered solutions provide enhanced security insights, proactive threat prevention, and optimized device performance management that improves overall solution effectiveness.
Unified Endpoint Management gains traction as organizations seek comprehensive platforms that manage diverse endpoint types including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and IoT devices through single management interfaces. This unified approach simplifies IT administration while providing consistent security and policy enforcement across all endpoint categories.
Cloud-Native Architectures dominate new solution deployments, with organizations preferring solutions built specifically for cloud environments rather than traditional on-premises solutions migrated to cloud platforms. Cloud-native solutions offer superior scalability, performance, and integration capabilities that align with modern IT infrastructure requirements.
Privacy-Preserving Technologies become increasingly important as organizations balance security requirements with employee privacy expectations. Solutions incorporating privacy-by-design principles and granular privacy controls help organizations maintain security while respecting individual privacy rights and preferences.
Strategic partnerships between international mobility management vendors and local system integrators accelerate market expansion and solution accessibility. These partnerships combine global technology expertise with local market knowledge and implementation capabilities, creating more effective go-to-market strategies for enterprise customers.
Government digitalization programs drive significant market development through large-scale mobility management implementations across public sector organizations. These government initiatives create market momentum while demonstrating the value and effectiveness of comprehensive mobility management solutions.
Industry-specific solution development addresses unique requirements in key vertical markets such as healthcare, financial services, and manufacturing. Vendors increasingly develop specialized features and compliance capabilities tailored to specific industry needs and regulatory requirements.
Technology integration initiatives focus on seamless connectivity between mobility management platforms and other enterprise systems including identity management, security information and event management (SIEM), and business applications. These integration capabilities improve solution value and organizational efficiency.
Skills development programs launched by vendors and industry associations address the critical shortage of qualified mobility management professionals. These training initiatives support market growth by developing local expertise and implementation capabilities.
Solution providers should focus on developing cost-effective, cloud-native platforms specifically designed for the Indonesian market’s unique requirements and price sensitivity. Emphasis on simplified deployment, intuitive management interfaces, and comprehensive support services will differentiate offerings in the competitive landscape.
Organizations evaluating enterprise mobility management solutions should prioritize platforms offering strong security capabilities, seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure, and scalable architectures that can accommodate future growth. Pilot implementations and phased deployment approaches can minimize risks while demonstrating solution value.
Government agencies should consider mobility management as a critical component of digital transformation initiatives, ensuring adequate budget allocation and skills development for successful implementation. Collaboration with experienced system integrators can accelerate deployment and maximize solution benefits.
SME market participants should explore cloud-based solutions that offer enterprise-grade capabilities at accessible price points. Focus on solutions providing immediate security benefits and operational efficiency improvements that justify investment costs and support business growth objectives.
Industry stakeholders should collaborate on skills development initiatives, best practice sharing, and market education programs that accelerate overall market maturity and adoption rates. These collaborative efforts benefit the entire ecosystem while addressing common challenges and barriers to adoption.
Market expansion prospects remain highly positive for Indonesia’s Enterprise Mobility Management sector, with continued growth expected across all market segments and industry verticals. The combination of ongoing digital transformation initiatives, increasing cybersecurity awareness, and evolving workforce mobility requirements creates sustainable demand for comprehensive mobility management solutions.
Technology evolution will drive next-generation mobility management capabilities incorporating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics for predictive threat detection and automated policy optimization. These technological advances will enhance solution effectiveness while reducing administrative complexity and improving user experience.
Market maturation is expected to accelerate over the next five years, with projected growth rates of approximately 14.2% annually driven by increasing solution sophistication and broader market adoption. The SME segment particularly shows strong growth potential as cost-effective solutions become more accessible and small businesses recognize mobility management importance.
Regulatory environment evolution will continue influencing market development, with enhanced data protection requirements and cybersecurity regulations driving demand for comprehensive compliance management capabilities. Organizations will increasingly view mobility management as essential infrastructure for regulatory compliance and risk management.
Competitive landscape consolidation is anticipated as larger technology vendors acquire specialized providers to expand their mobility management portfolios. This consolidation will create opportunities for comprehensive platform providers while challenging standalone solution vendors to differentiate through specialized capabilities or vertical focus.
The Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management market represents a dynamic and rapidly expanding sector that plays a crucial role in the country’s ongoing digital transformation journey. As organizations across various industries recognize the critical importance of secure and efficient mobile device management, the market continues to demonstrate robust growth potential and increasing sophistication in solution offerings.
Market fundamentals remain strong, supported by Indonesia’s substantial economic base, growing digital infrastructure, and government commitment to digitalization initiatives. The combination of increasing cybersecurity awareness, evolving workforce mobility requirements, and regulatory compliance needs creates sustainable demand for comprehensive enterprise mobility management solutions across all organizational sizes and industry verticals.
Future success in this market will depend on solution providers’ ability to deliver cost-effective, secure, and user-friendly platforms that address Indonesia’s unique market requirements while maintaining global technology standards. Organizations that strategically implement enterprise mobility management solutions will gain significant competitive advantages through enhanced security, improved operational efficiency, and better workforce enablement capabilities. The market’s continued evolution toward cloud-native, AI-powered, and industry-specific solutions positions Indonesia as a key growth market for enterprise mobility management technologies in the Southeast Asian region.
What is Enterprise Mobility Management?
Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) refers to the set of technologies and strategies that organizations use to manage and secure mobile devices, applications, and data within the workplace. It encompasses various solutions that facilitate mobile device management, application management, and security policies.
What are the key players in the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market include VMware, IBM, Microsoft, and Citrix, among others. These companies provide a range of solutions that help businesses manage mobile devices and applications effectively.
What are the main drivers of the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market?
The main drivers of the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market include the increasing adoption of mobile devices in enterprises, the need for enhanced security measures, and the growing trend of remote work. These factors are pushing organizations to implement EMM solutions to protect sensitive data.
What challenges does the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market face?
The Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market faces challenges such as data privacy concerns, the complexity of managing diverse mobile platforms, and the rapid pace of technological change. These issues can hinder the effective implementation of EMM solutions.
What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market include the rising demand for cloud-based EMM solutions and the integration of artificial intelligence in mobile management. These trends can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of EMM strategies.
What trends are shaping the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market?
Trends shaping the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market include the increasing focus on mobile application security, the rise of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, and the growing importance of user experience in mobile management solutions. These trends are influencing how organizations approach EMM.
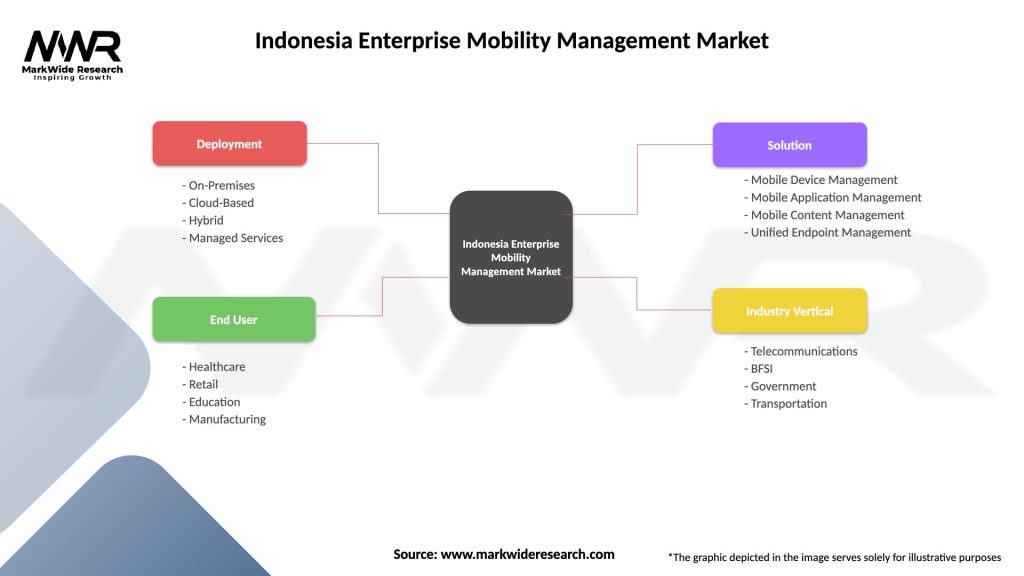
Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Deployment | On-Premises, Cloud-Based, Hybrid, Managed Services |
| End User | Healthcare, Retail, Education, Manufacturing |
| Solution | Mobile Device Management, Mobile Application Management, Mobile Content Management, Unified Endpoint Management |
| Industry Vertical | Telecommunications, BFSI, Government, Transportation |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indonesia Enterprise Mobility Management Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at