444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The Indonesia digital transformation market represents one of Southeast Asia’s most dynamic and rapidly evolving technology landscapes. As the world’s fourth most populous country and largest economy in ASEAN, Indonesia has emerged as a critical hub for digital innovation and technological advancement. The market encompasses a comprehensive range of solutions including cloud computing, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and enterprise mobility solutions that are reshaping how businesses operate across various sectors.
Digital transformation initiatives in Indonesia are experiencing unprecedented momentum, driven by government support through the Indonesia Digital 2030 roadmap and increasing private sector investment in technology infrastructure. The market is characterized by robust growth in digital adoption rates, with enterprise digitalization accelerating at 15.2% annually as organizations seek to enhance operational efficiency and customer engagement capabilities.
Key market segments include banking and financial services, manufacturing, retail and e-commerce, healthcare, education, and government services. Each sector is witnessing significant digital transformation investments as organizations recognize the critical importance of technology modernization for competitive advantage and operational resilience in the post-pandemic business environment.
The Indonesia digital transformation market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of technologies, services, and solutions that enable organizations across Indonesia to modernize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and create new business models through digital technologies. This market encompasses cloud migration services, data analytics platforms, artificial intelligence implementations, IoT deployments, and digital infrastructure modernization initiatives that collectively drive organizational change and innovation.
Digital transformation in the Indonesian context involves the strategic integration of digital technologies into all areas of business operations, fundamentally changing how organizations deliver value to customers and stakeholders. The transformation process includes legacy system modernization, process automation, data-driven decision making, and the development of digital-first customer engagement strategies.
Market participants include technology vendors, system integrators, consulting firms, cloud service providers, and digital solution specialists who collaborate to deliver comprehensive transformation solutions tailored to Indonesia’s unique business environment and regulatory requirements.
Indonesia’s digital transformation market is experiencing remarkable growth momentum, positioning the country as a leading digital economy in Southeast Asia. The market benefits from strong government support, increasing digital literacy rates, and growing enterprise recognition of technology’s strategic importance for business continuity and growth.
Key growth drivers include accelerating cloud adoption, expanding e-commerce activities, increasing mobile penetration rates, and rising demand for data analytics capabilities. The market is witnessing significant investment in digital infrastructure, with cloud adoption rates increasing by 28.5% annually as organizations prioritize scalable and flexible technology solutions.
Sectoral transformation is particularly pronounced in financial services, where digital banking initiatives and fintech innovations are revolutionizing customer experiences. Manufacturing sectors are embracing Industry 4.0 technologies, while retail organizations are implementing omnichannel strategies to enhance customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Market challenges include cybersecurity concerns, digital skills gaps, and infrastructure limitations in remote areas. However, these challenges are being addressed through targeted government initiatives, private sector investments, and international partnerships that strengthen Indonesia’s digital transformation capabilities.
Strategic market insights reveal several critical trends shaping Indonesia’s digital transformation landscape:
Market maturity levels vary significantly across different sectors and regions, with urban areas and established industries leading digital adoption while rural areas and traditional sectors are experiencing gradual transformation supported by targeted government and private sector initiatives.
Primary market drivers propelling Indonesia’s digital transformation include strong government policy support, increasing digital literacy, and growing recognition of technology’s strategic importance for business competitiveness. The government’s commitment to digital infrastructure development and regulatory modernization creates favorable conditions for technology adoption and innovation.
Economic factors driving transformation include the need for operational efficiency improvements, cost reduction pressures, and demands for enhanced customer experiences. Organizations are recognizing that digital transformation is essential for maintaining competitive positioning in increasingly digital markets, with operational efficiency gains of 35-45% reported by early adopters.
Technological advancement in areas such as 5G connectivity, edge computing, and artificial intelligence is creating new opportunities for innovative digital solutions. The expanding availability of advanced technologies at competitive price points makes digital transformation more accessible to organizations of various sizes and sectors.
Consumer behavior changes are driving demand for digital services and experiences, particularly in e-commerce, digital banking, and online education. The pandemic accelerated digital adoption trends, creating lasting changes in customer expectations and business operating models that continue to drive transformation investments.
Significant market restraints include cybersecurity concerns, digital skills shortages, and infrastructure limitations in certain regions. Organizations often face challenges in finding qualified digital talent and ensuring adequate security measures for their digital transformation initiatives.
Infrastructure constraints in rural and remote areas limit the reach of digital transformation initiatives, creating digital divides that require targeted investment and policy interventions. Connectivity issues and power infrastructure limitations can impede the deployment of advanced digital solutions in certain regions.
Regulatory complexity and compliance requirements can slow digital transformation implementation, particularly in highly regulated sectors such as financial services and healthcare. Organizations must navigate evolving regulatory frameworks while implementing new technologies and processes.
Cultural resistance to change and traditional business practices can create internal barriers to digital transformation success. Organizations often struggle with change management challenges as they transition from legacy systems and processes to modern digital approaches.
Substantial market opportunities exist in emerging technology areas including artificial intelligence, blockchain, Internet of Things, and advanced analytics. These technologies offer significant potential for creating innovative solutions tailored to Indonesia’s unique market conditions and business requirements.
Sectoral opportunities are particularly strong in healthcare digitization, smart city development, and agricultural technology transformation. The government’s focus on digital health initiatives and smart city projects creates substantial opportunities for technology providers and system integrators.
Regional expansion opportunities exist as digital transformation spreads from major urban centers to secondary cities and rural areas. This geographic expansion is supported by improving infrastructure and government initiatives to reduce digital divides across the archipelago.
Partnership opportunities between local and international technology companies are creating new avenues for innovation and market development. These collaborations combine global technology expertise with local market knowledge to deliver more effective digital transformation solutions.
Market dynamics in Indonesia’s digital transformation sector are characterized by rapid technological evolution, increasing competitive intensity, and growing customer sophistication. The interplay between government policy, private sector investment, and consumer demand creates a complex but dynamic market environment.
Competitive dynamics include both established international technology companies and emerging local players who understand Indonesian market nuances. This competition drives innovation and helps ensure that digital transformation solutions are tailored to local business requirements and cultural contexts.
Technology evolution continues to reshape market dynamics, with emerging technologies creating new opportunities while potentially disrupting existing business models. Organizations must balance the adoption of proven technologies with experimentation in emerging areas to maintain competitive advantage.
Customer expectations are evolving rapidly, driven by exposure to global digital services and increasing digital literacy. This evolution creates pressure on organizations to continuously improve their digital capabilities and customer experiences, driving ongoing transformation investments.
Comprehensive research methodology employed for analyzing Indonesia’s digital transformation market includes primary research through industry interviews, surveys, and expert consultations combined with secondary research from government publications, industry reports, and technology vendor data.
Primary research activities involve structured interviews with technology executives, government officials, and industry experts to gather insights on market trends, challenges, and opportunities. Survey research captures quantitative data on adoption rates, investment levels, and technology preferences across different sectors and organization sizes.
Secondary research sources include government statistics, industry association reports, technology vendor publications, and academic research to provide comprehensive market context and validate primary research findings. This multi-source approach ensures robust and reliable market analysis.
Data validation processes include cross-referencing multiple sources, expert review panels, and statistical analysis to ensure accuracy and reliability of market insights and projections. The methodology emphasizes both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to provide comprehensive market understanding.
Regional analysis reveals significant variations in digital transformation maturity and adoption rates across Indonesia’s diverse geographic regions. Java, particularly the Jakarta metropolitan area, leads in digital transformation adoption with 65% of enterprises having implemented comprehensive digital strategies.
Jakarta and surrounding areas serve as the primary hub for digital transformation activities, benefiting from concentrated business activity, advanced infrastructure, and proximity to technology vendors and service providers. The region accounts for approximately 45% of total digital transformation investments nationwide.
Surabaya and Bandung represent important secondary markets with growing digital transformation activity driven by manufacturing, education, and service sector organizations. These cities are experiencing annual growth rates of 18-22% in digital technology adoption.
Emerging regions including Medan, Makassar, and Denpasar are showing increasing digital transformation activity supported by government infrastructure investments and growing local business sophistication. Rural and remote areas present both challenges and opportunities for digital transformation expansion.
Competitive landscape in Indonesia’s digital transformation market includes a diverse mix of international technology giants, regional specialists, and local service providers who compete across different market segments and customer categories.
Market competition is intensifying as companies expand their service offerings and develop specialized solutions for Indonesian market requirements. Partnership strategies and local market expertise are becoming increasingly important competitive differentiators.
Market segmentation analysis reveals distinct patterns across technology categories, industry verticals, and organization sizes that shape digital transformation adoption and investment patterns throughout Indonesia.
By Technology:
By Industry Vertical:
Cloud computing category dominates Indonesia’s digital transformation market, with organizations prioritizing cloud migration to achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Hybrid cloud approaches are particularly popular, allowing organizations to balance security requirements with operational flexibility.
Artificial intelligence category is experiencing rapid growth as organizations implement AI solutions for customer service automation, predictive maintenance, and business process optimization. Chatbot implementations and automated customer service solutions are showing particularly strong adoption rates.
IoT category insights reveal strong growth in manufacturing and smart city applications, with organizations implementing connected device solutions for operational monitoring, predictive maintenance, and resource optimization. The category benefits from improving connectivity infrastructure and declining sensor costs.
Cybersecurity category is gaining critical importance as digital transformation increases organizational exposure to cyber threats. Investment in security solutions is growing at 25% annually as organizations recognize the need for comprehensive security frameworks to protect their digital assets and customer data.
Technology vendors benefit from Indonesia’s large and growing market opportunity, with increasing demand for digital transformation solutions across multiple sectors. The market offers opportunities for both established international companies and emerging local players to develop specialized solutions for Indonesian business requirements.
System integrators gain from the complexity of digital transformation projects, which require specialized expertise in solution design, implementation, and ongoing support. The growing market creates opportunities for service providers to develop deep industry expertise and long-term customer relationships.
Enterprise customers benefit from improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and new business model opportunities enabled by digital transformation investments. Organizations report significant improvements in productivity, cost reduction, and competitive positioning following successful transformation initiatives.
Government stakeholders benefit from digital transformation through improved public service delivery, enhanced economic competitiveness, and progress toward national digitalization goals. Digital transformation supports broader economic development objectives and helps position Indonesia as a regional technology leader.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Artificial intelligence integration represents a dominant trend as organizations implement AI solutions for customer service, operations optimization, and predictive analytics. Machine learning applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated and accessible to organizations of various sizes.
Cloud-first strategies are becoming standard practice as organizations prioritize cloud migration for improved scalability, flexibility, and cost management. Multi-cloud approaches are gaining popularity as organizations seek to avoid vendor lock-in while optimizing performance and costs.
Edge computing adoption is accelerating as organizations require real-time processing capabilities for IoT applications, autonomous systems, and latency-sensitive operations. This trend is particularly strong in manufacturing and smart city implementations.
Sustainability focus is driving demand for green technology solutions and energy-efficient digital infrastructure. Organizations are increasingly considering environmental impact in their digital transformation decisions, creating opportunities for sustainable technology solutions.
Low-code and no-code platforms are gaining traction as organizations seek to accelerate application development and reduce dependence on specialized programming skills. These platforms enable faster digital transformation implementation and greater business user involvement in solution development.
Government initiatives continue to shape market development, with the launch of comprehensive digital transformation programs and regulatory frameworks supporting technology adoption across public and private sectors. The Indonesia Digital 2030 roadmap provides clear direction for national digitalization efforts.
Infrastructure investments in 5G networks, data centers, and fiber optic connectivity are creating foundations for advanced digital transformation implementations. These investments support more sophisticated technology deployments and enable new use cases for digital solutions.
Partnership announcements between international technology companies and local partners are expanding market capabilities and creating new solution offerings tailored to Indonesian business requirements. These partnerships combine global expertise with local market knowledge.
Startup ecosystem development is contributing to innovation in digital transformation solutions, with emerging companies developing specialized technologies and services for specific industry verticals and use cases. According to MarkWide Research analysis, startup activity in the digital transformation space has increased significantly over the past two years.
Strategic recommendations for market participants include focusing on local market expertise, developing industry-specific solutions, and building strong partnership networks to navigate Indonesia’s complex and diverse business environment effectively.
Technology vendors should prioritize local presence development, cultural adaptation of solutions, and partnerships with local system integrators to enhance market penetration and customer success rates. Understanding Indonesian business practices and regulatory requirements is essential for long-term success.
Organizations considering digital transformation should develop comprehensive strategies that address both technology implementation and change management requirements. Successful transformation requires strong leadership commitment, employee training programs, and phased implementation approaches that minimize business disruption.
Investment priorities should focus on cloud infrastructure, cybersecurity capabilities, and data analytics platforms as foundational elements for successful digital transformation. Organizations should also invest in digital skills development and change management capabilities to ensure transformation success.
Future market prospects for Indonesia’s digital transformation sector remain highly positive, with continued growth expected across all major technology categories and industry verticals. The market is projected to maintain robust growth momentum driven by ongoing government support, increasing business digitalization needs, and expanding technology accessibility.
Emerging technology adoption will accelerate as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and advanced analytics solutions become more mature and accessible. MWR projects that AI adoption rates will increase by 40-50% over the next three years as organizations recognize the competitive advantages of intelligent automation.
Geographic expansion of digital transformation activities will continue as infrastructure improvements and government initiatives extend advanced technology access to secondary cities and rural areas. This expansion will create new market opportunities while helping reduce digital divides across the archipelago.
Sector-specific solutions will become increasingly important as digital transformation matures and organizations seek specialized capabilities for their unique business requirements. Healthcare, education, and agricultural technology sectors are expected to show particularly strong growth in digital transformation investments.
Indonesia’s digital transformation market represents one of Southeast Asia’s most dynamic and promising technology sectors, characterized by strong government support, growing business adoption, and significant opportunities for innovation and growth. The market benefits from Indonesia’s large economy, increasing digital literacy, and comprehensive policy frameworks supporting nationwide digitalization efforts.
Key success factors for market participants include developing deep understanding of local business requirements, building strong partnership networks, and maintaining focus on security, scalability, and cultural adaptation in solution development. The market rewards organizations that combine global technology expertise with local market knowledge and cultural sensitivity.
Future growth prospects remain highly favorable, with continued expansion expected across all major technology categories and industry verticals. The combination of government support, private sector investment, and growing customer sophistication creates a sustainable foundation for long-term market development and innovation in Indonesia’s digital transformation landscape.
What is Digital Transformation?
Digital Transformation refers to the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value to customers. It encompasses various aspects such as process automation, data analytics, and customer engagement strategies.
What are the key players in the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market?
Key players in the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market include companies like Gojek, Tokopedia, and Bukalapak, which are leveraging technology to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. Other notable companies include Telkom Indonesia and Grab, among others.
What are the main drivers of the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market?
The main drivers of the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market include the increasing internet penetration, the growing demand for mobile services, and the need for businesses to improve operational efficiency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and digital payment solutions is significantly contributing to this growth.
What challenges does the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market face?
Challenges in the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market include a lack of digital skills among the workforce, cybersecurity concerns, and resistance to change within organizations. Additionally, infrastructure limitations in certain regions can hinder the adoption of digital technologies.
What opportunities exist in the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market?
Opportunities in the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market include the potential for startups to innovate in sectors like fintech and healthtech, as well as the expansion of smart city initiatives. Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainability and green technologies presents new avenues for digital solutions.
What trends are shaping the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market?
Trends shaping the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market include the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning applications, the growth of cloud computing services, and the increasing importance of data privacy regulations. Additionally, the shift towards remote work and digital collaboration tools is influencing business strategies.
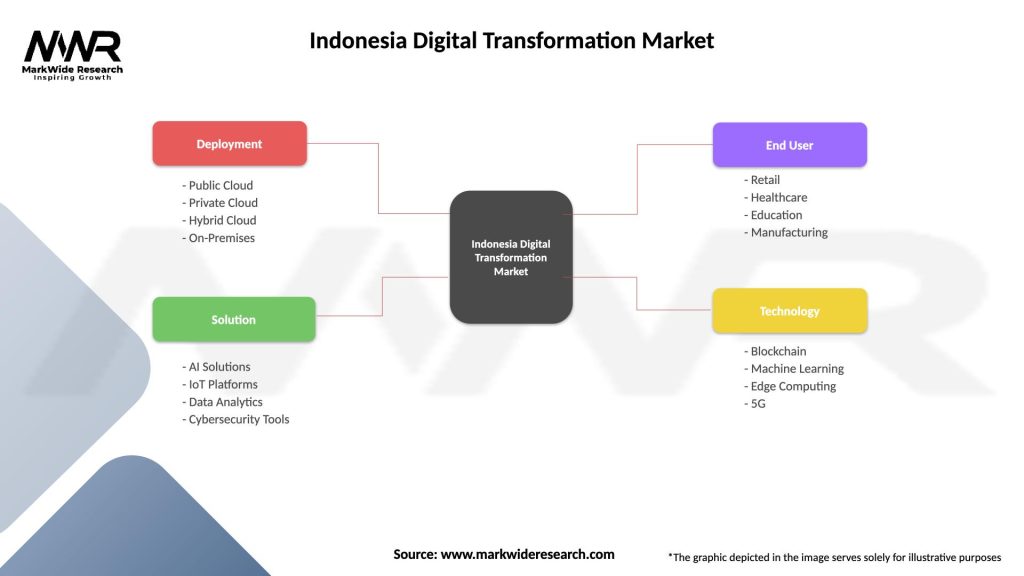
Indonesia Digital Transformation Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Deployment | Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, On-Premises |
| Solution | AI Solutions, IoT Platforms, Data Analytics, Cybersecurity Tools |
| End User | Retail, Healthcare, Education, Manufacturing |
| Technology | Blockchain, Machine Learning, Edge Computing, 5G |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indonesia Digital Transformation Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at