444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2150
The Indian rice market represents one of the most significant agricultural sectors in the global food industry, serving as the backbone of food security for over 1.4 billion people. India stands as the world’s largest rice-producing nation, accounting for approximately 22% of global rice production and maintaining its position as a leading exporter. The market encompasses diverse varieties including basmati, non-basmati, organic, and specialty rice segments that cater to both domestic consumption and international trade requirements.
Market dynamics in the Indian rice sector are influenced by monsoon patterns, government policies, technological advancements in farming practices, and evolving consumer preferences toward premium and health-conscious rice varieties. The sector demonstrates remarkable resilience with consistent growth patterns, driven by increasing population, rising income levels, and expanding export opportunities across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
Production efficiency has improved significantly through the adoption of high-yielding varieties, mechanization, and sustainable farming practices. The market shows strong potential for continued expansion, with growth rates projected at 4.2% CAGR over the forecast period, supported by government initiatives promoting agricultural modernization and export facilitation programs.
The Indian rice market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing cultivation, processing, distribution, and consumption of rice varieties within India’s agricultural framework. This market includes all activities from seed production and farming operations to milling, packaging, branding, and final consumer sales across domestic and international channels.
Rice cultivation in India spans across diverse agro-climatic zones, producing various categories including long-grain basmati rice, medium and short-grain non-basmati varieties, aromatic rice, and specialty products like brown rice, red rice, and black rice. The market structure involves millions of smallholder farmers, thousands of rice millers, numerous traders, and established brands serving different market segments.
Market participants range from traditional farming communities and local processors to large-scale industrial mills and multinational food companies. The sector operates through complex supply chains connecting rural production centers with urban consumption markets and international trade networks, making it a critical component of India’s agricultural economy and food security infrastructure.
India’s rice market continues to demonstrate robust performance across production, processing, and export segments, establishing the country as a global leader in rice trade. The market benefits from favorable geographical conditions, extensive irrigation infrastructure, and government support through minimum support prices and export promotion schemes.
Key growth drivers include increasing domestic demand driven by population growth and changing dietary preferences, expanding export opportunities in emerging markets, and technological innovations in farming and processing techniques. The market shows strong adoption of sustainable farming practices, with organic rice production growing at 15% annually as consumers increasingly prefer chemical-free food options.
Regional distribution reveals that major producing states including Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh contribute approximately 65% of total production. The export segment demonstrates particular strength in basmati rice, where India maintains a 70% global market share, while non-basmati exports continue expanding into new geographical markets.
Market challenges include climate variability, water scarcity concerns, fragmented supply chains, and quality standardization requirements for international markets. However, ongoing government initiatives in agricultural modernization, infrastructure development, and farmer support programs position the market for sustained growth and enhanced competitiveness in global trade.
Production patterns in the Indian rice market reveal significant regional specialization and seasonal variations that drive market dynamics throughout the year. The following insights highlight critical market characteristics:
Population growth serves as the primary driver for India’s rice market, with increasing domestic consumption requirements supporting consistent demand expansion. The growing middle class demonstrates shifting preferences toward premium rice varieties, branded products, and convenient packaging options that drive market premiumization trends.
Export opportunities continue expanding as global demand for Indian rice increases, particularly in Middle Eastern, African, and Southeast Asian markets. Government initiatives including export promotion schemes, quality certification programs, and trade facilitation measures enhance India’s competitive position in international markets.
Technological advancement in agriculture drives productivity improvements through high-yielding varieties, precision farming techniques, and mechanization adoption. MarkWide Research indicates that technology-enabled farming practices have contributed to yield improvements of 18-22% in progressive farming regions.
Government support through minimum support prices, procurement programs, and agricultural subsidies provides stability and encourages production expansion. Infrastructure development including irrigation projects, rural roads, and storage facilities creates enabling conditions for market growth and efficiency improvements.
Health consciousness among consumers drives demand for specialty rice varieties including brown rice, red rice, and organic options. This trend supports market diversification and premium pricing opportunities for producers focusing on health-oriented product segments.
Climate variability poses significant challenges to rice production through irregular monsoon patterns, extreme weather events, and changing precipitation cycles. These factors create uncertainty in production planning and can lead to supply disruptions affecting market stability.
Water scarcity concerns increasingly impact rice cultivation, particularly in traditional growing regions where groundwater depletion and competing water demands from other sectors limit irrigation availability. This constraint necessitates adoption of water-efficient farming techniques and crop diversification strategies.
Fragmented supply chains result in inefficiencies, quality variations, and increased transaction costs throughout the value chain. The involvement of multiple intermediaries between farmers and end consumers often reduces farmer margins while increasing final product prices.
Quality standardization challenges affect export competitiveness, as international markets demand consistent quality parameters, proper grading, and certification compliance. Many small-scale producers struggle to meet these requirements without adequate infrastructure and technical support.
Price volatility in international markets creates uncertainty for exporters and can impact farmer income stability. Currency fluctuations, trade policy changes, and global supply-demand imbalances contribute to price unpredictability affecting long-term planning and investment decisions.
Export market expansion presents substantial opportunities as global rice consumption continues growing, particularly in developing countries across Africa and Asia. India’s competitive pricing, quality improvements, and established trade relationships position the country to capture increasing market share in emerging economies.
Value addition through processing and product diversification offers significant potential for revenue enhancement. Opportunities include ready-to-eat rice products, rice-based snacks, rice flour, and specialty products targeting health-conscious consumers and convenience-seeking urban populations.
Organic farming expansion represents a high-growth opportunity as global demand for organic food products increases rapidly. India’s traditional farming knowledge combined with certification programs can establish the country as a leading organic rice supplier to premium international markets.
Technology integration including precision agriculture, IoT-enabled monitoring, and blockchain-based traceability systems can enhance productivity, quality control, and market access. These innovations support premium positioning and meet evolving consumer demands for transparency and sustainability.
Direct marketing channels through e-commerce platforms, farmer producer organizations, and contract farming arrangements can improve farmer margins while ensuring quality control and traceability. These approaches reduce intermediary costs and create direct connections between producers and consumers.
Supply-side dynamics in the Indian rice market are characterized by seasonal production cycles, regional specialization, and varying productivity levels across different agro-climatic zones. The interplay between monsoon patterns, irrigation availability, and farming practices creates complex supply patterns that influence market pricing and availability throughout the year.
Demand patterns reflect diverse consumption preferences across rural and urban populations, with rural areas primarily consuming locally produced varieties while urban consumers increasingly prefer branded, premium, and specialty rice products. Export demand adds another dimension, with international markets showing strong preference for Indian basmati and specific non-basmati varieties.
Price mechanisms operate through multiple channels including government procurement at minimum support prices, open market transactions, and export pricing influenced by international market conditions. This multi-tiered pricing system creates opportunities for arbitrage while ensuring farmer income support and market stability.
Competitive dynamics involve traditional traders, modern retail chains, processing companies, and export houses competing across different market segments. The market shows increasing consolidation in processing and branding activities while production remains largely fragmented among smallholder farmers.
Regulatory environment significantly influences market operations through export policies, quality standards, procurement programs, and agricultural support schemes. Policy changes can rapidly alter market dynamics, affecting production decisions, trade flows, and investment patterns across the value chain.
Primary research methodologies employed in analyzing the Indian rice market include comprehensive field surveys across major producing states, in-depth interviews with farmers, millers, traders, and exporters, and structured questionnaires administered to key stakeholders throughout the value chain.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of government statistics, agricultural department reports, export-import data, and industry publications to establish market trends, production patterns, and trade dynamics. Historical data analysis provides insights into cyclical patterns and long-term growth trajectories.
Market segmentation analysis involves detailed examination of different rice varieties, regional markets, consumer segments, and distribution channels to understand specific dynamics within each category. This approach enables identification of growth opportunities and market gaps.
Stakeholder consultations with industry associations, government officials, research institutions, and international trade organizations provide expert perspectives on market developments, policy impacts, and future trends affecting the rice sector.
Data validation processes ensure accuracy and reliability through cross-verification of information sources, statistical analysis of data consistency, and expert review of findings to maintain research quality and credibility in market assessments.
Northern India dominates basmati rice production, with Punjab and Haryana contributing approximately 80% of total basmati output. This region benefits from favorable agro-climatic conditions, advanced irrigation infrastructure, and established export supply chains that support premium rice production and international market access.
Eastern India including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha represents the largest rice-producing region by volume, focusing primarily on non-basmati varieties for domestic consumption. The region shows potential for productivity improvements through technology adoption and infrastructure development initiatives.
Southern India encompasses major producing states like Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka, contributing significantly to both domestic supply and export volumes. The region demonstrates strong adoption of hybrid varieties and modern farming practices that enhance productivity and quality.
Western India including Maharashtra and Gujarat shows growing importance in rice production, particularly in specialty and organic segments. The region benefits from progressive farming practices and proximity to major consumption centers and export ports.
Central India represents emerging production areas with potential for expansion through irrigation development and technology adoption. States like Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh show increasing contribution to national rice production with focus on sustainable farming practices.
Market leadership in the Indian rice sector is distributed across different segments, with various companies specializing in specific varieties, regions, or market channels. The competitive environment includes traditional players and emerging companies leveraging technology and branding strategies.
Competitive strategies focus on quality differentiation, brand building, supply chain efficiency, and market expansion through both domestic and international channels. Companies increasingly invest in technology, sustainability initiatives, and direct farmer engagement programs to secure supply and enhance competitiveness.
By Variety: The Indian rice market segments into distinct categories based on grain characteristics, cooking properties, and market positioning. Basmati rice commands premium pricing and export focus, while non-basmati varieties serve diverse domestic and international market requirements.
By Processing Level: Market segmentation based on processing sophistication and value addition reflects different consumer preferences and price points across various market channels.
By Distribution Channel: Market channels reflect diverse consumer access points and purchasing preferences across urban and rural markets with varying service requirements and price sensitivity.
Basmati Rice Category represents the premium segment of the Indian rice market, characterized by superior grain length, distinctive aroma, and exceptional cooking quality. This category demonstrates strong export performance with consistent demand from international markets, particularly in the Middle East, Europe, and North America.
Production concentration in northern states ensures quality consistency and supply reliability for basmati rice. The category benefits from geographical indication protection, premium pricing, and established brand recognition in global markets. MWR analysis indicates that basmati exports contribute approximately 60% of total rice export value despite representing smaller volume shares.
Non-Basmati Rice Category encompasses diverse varieties serving different market segments from basic consumption needs to specific culinary applications. This category shows strong domestic demand and growing export opportunities in price-sensitive international markets across Asia and Africa.
Organic Rice Category demonstrates rapid growth driven by health consciousness and environmental awareness among consumers. This segment commands premium pricing and shows strong potential for expansion as certification infrastructure improves and consumer awareness increases.
Specialty Rice Category includes nutritionally enhanced varieties like brown rice, red rice, and fortified rice products targeting health-conscious consumers and specific dietary requirements. This category shows strong growth potential in urban markets and export opportunities in developed countries.
Farmers benefit from stable income opportunities through government procurement programs, minimum support prices, and direct market access initiatives. Technology adoption and improved farming practices enhance productivity and reduce production costs, while contract farming arrangements provide assured markets and price stability.
Processors and millers gain from economies of scale, technology investments, and value addition opportunities that improve margins and market positioning. Modern processing facilities enable quality standardization, reduce wastage, and meet international market requirements for export competitiveness.
Exporters advantage from India’s competitive pricing, diverse variety portfolio, and established trade relationships with global markets. Government support through export promotion schemes, quality certification programs, and trade facilitation measures enhance export competitiveness and market access.
Retailers and distributors benefit from consistent supply availability, diverse product portfolio, and growing consumer demand across different market segments. Brand building opportunities and premium positioning enable margin enhancement and customer loyalty development.
Consumers gain from product diversity, quality improvements, competitive pricing, and enhanced availability through multiple distribution channels. Health-conscious consumers benefit from organic and specialty rice options, while convenience-seeking urban consumers access ready-to-cook and branded products.
Government stakeholders achieve food security objectives, export revenue generation, farmer income support, and rural employment creation through a thriving rice sector that contributes significantly to agricultural GDP and trade balance.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainability Focus emerges as a dominant trend with increasing adoption of organic farming practices, water-efficient cultivation techniques, and environmentally responsible processing methods. Consumers and international markets increasingly prefer sustainably produced rice, driving premium pricing and market differentiation opportunities.
Technology Integration transforms traditional farming and processing practices through precision agriculture, IoT-enabled monitoring systems, and automated processing equipment. These innovations enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve quality consistency while enabling traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain.
Premium Product Development shows strong momentum as consumers seek high-quality, branded, and specialty rice products. This trend supports market premiumization and enables processors to capture higher margins through value addition and brand building initiatives.
Direct Marketing Channels gain prominence through e-commerce platforms, farmer producer organizations, and contract farming arrangements that reduce intermediary costs and improve farmer margins. Digital platforms enable direct consumer connections and transparent pricing mechanisms.
Health-Conscious Consumption drives demand for nutritionally enhanced rice varieties including brown rice, fortified rice, and organic options. This trend creates opportunities for product diversification and premium positioning in health-focused market segments.
Export Market Diversification reflects efforts to reduce dependency on traditional markets and explore new geographical opportunities. Emerging economies in Africa and Latin America present significant potential for Indian rice exports with appropriate market development strategies.
Government Policy Initiatives include the launch of comprehensive agricultural modernization programs, export promotion schemes, and farmer income support measures that strengthen the rice sector’s competitiveness and sustainability. Recent policy changes focus on quality improvement, infrastructure development, and market access facilitation.
Technology Adoption Programs demonstrate significant progress in mechanization, precision farming, and digital agriculture initiatives across major rice-producing states. These developments enhance productivity, reduce labor dependency, and improve quality consistency in rice production and processing.
Infrastructure Investments in storage facilities, processing plants, and transportation networks create enabling conditions for market expansion and efficiency improvements. Modern infrastructure reduces post-harvest losses and enables quality maintenance throughout the supply chain.
International Market Expansion efforts result in new trade agreements, quality certifications, and market access approvals that enhance India’s rice export potential. Recent developments include entry into new geographical markets and premium product category approvals.
Sustainability Certifications gain momentum as producers and processors obtain organic, fair trade, and environmental certifications that enable premium market access and support sustainable development objectives. These certifications enhance brand value and consumer trust.
Research and Development initiatives focus on developing climate-resilient varieties, improving nutritional content, and enhancing processing technologies. Collaborative efforts between research institutions and industry players accelerate innovation and technology transfer.
Production Optimization requires focused efforts on improving productivity through technology adoption, better seed varieties, and efficient farming practices. Analysts recommend increased investment in mechanization, precision agriculture, and farmer training programs to enhance competitiveness and sustainability.
Quality Standardization emerges as a critical priority for maintaining and expanding market share in premium segments. Industry experts suggest implementing comprehensive quality control systems, certification programs, and traceability mechanisms to meet international market requirements.
Value Chain Integration presents opportunities for margin enhancement and market positioning improvement. MarkWide Research analysts recommend strategic partnerships between farmers, processors, and marketers to create efficient supply chains and reduce transaction costs.
Export Market Diversification should focus on emerging economies with growing rice consumption and favorable trade conditions. Analysts suggest developing market-specific strategies, establishing distribution networks, and building brand recognition in target markets.
Sustainability Initiatives require immediate attention to address environmental concerns and meet evolving consumer preferences. Experts recommend investing in organic farming, water-efficient technologies, and renewable energy adoption throughout the value chain.
Technology Investment in digital platforms, automation, and data analytics can significantly enhance operational efficiency and market responsiveness. Analysts emphasize the importance of technology adoption for long-term competitiveness and growth sustainability.
Market expansion prospects remain robust with projected growth rates of 4.2% CAGR driven by increasing domestic consumption, export market opportunities, and value addition initiatives. The sector shows strong potential for sustained growth supported by government policies, infrastructure development, and technology adoption.
Production growth is expected to continue through productivity improvements, area expansion in suitable regions, and adoption of high-yielding varieties. Climate-resilient farming practices and water-efficient technologies will become increasingly important for sustainable production growth.
Export performance shows promising outlook with expanding market opportunities in emerging economies and growing demand for premium Indian rice varieties. Strategic market development and quality enhancement initiatives will support export growth and revenue expansion.
Technology integration will accelerate across the value chain, from precision farming and automated processing to digital marketing and supply chain management. These developments will enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve market responsiveness.
Sustainability focus will intensify as environmental concerns and consumer preferences drive adoption of organic farming, renewable energy, and circular economy principles. Companies investing in sustainability initiatives will gain competitive advantages and premium market access.
Market consolidation trends may emerge in processing and marketing segments as companies seek economies of scale and competitive positioning. However, production will likely remain fragmented among smallholder farmers requiring continued support and integration efforts.
The Indian rice market stands at a pivotal juncture with substantial opportunities for growth, modernization, and global market expansion. The sector’s fundamental strengths including diverse production capabilities, competitive cost structure, and established export networks provide a solid foundation for future development and market leadership maintenance.
Strategic priorities for market participants include quality enhancement, technology adoption, sustainability initiatives, and value chain optimization to capture emerging opportunities and address evolving challenges. The focus on premium product development, export market diversification, and direct marketing channels will drive revenue growth and margin improvement across the sector.
Government support through policy initiatives, infrastructure development, and farmer welfare programs creates enabling conditions for sustained market growth and competitiveness enhancement. Continued investment in research and development, quality certification, and market promotion will strengthen India’s position in global rice markets and support long-term sector sustainability.
What is Rice?
Rice is a staple food grain that is cultivated and consumed widely across the world, particularly in Asia. It serves as a primary source of carbohydrates and is integral to various cuisines and dietary practices.
What are the key players in the Indian Rice Market?
Key players in the Indian Rice Market include companies like KRBL Limited, LT Foods, and Tilda, which are known for their extensive rice production and distribution networks. These companies contribute significantly to the market through various rice varieties and brands, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the Indian Rice Market?
The Indian Rice Market is driven by factors such as increasing population, rising demand for processed and packaged rice products, and the growing trend of rice consumption in urban areas. Additionally, government initiatives to support rice farmers also play a crucial role.
What challenges does the Indian Rice Market face?
The Indian Rice Market faces challenges such as fluctuating weather conditions affecting crop yields, competition from other staple foods, and issues related to storage and supply chain logistics. These factors can impact the overall availability and pricing of rice.
What opportunities exist in the Indian Rice Market?
Opportunities in the Indian Rice Market include the potential for export growth, the introduction of organic and specialty rice varieties, and advancements in agricultural technology that can enhance productivity. These factors can help meet the evolving consumer preferences.
What trends are shaping the Indian Rice Market?
Trends in the Indian Rice Market include the increasing popularity of basmati rice, the rise of health-conscious consumers opting for fortified rice, and the growing use of e-commerce platforms for rice distribution. These trends reflect changing consumer behaviors and preferences.
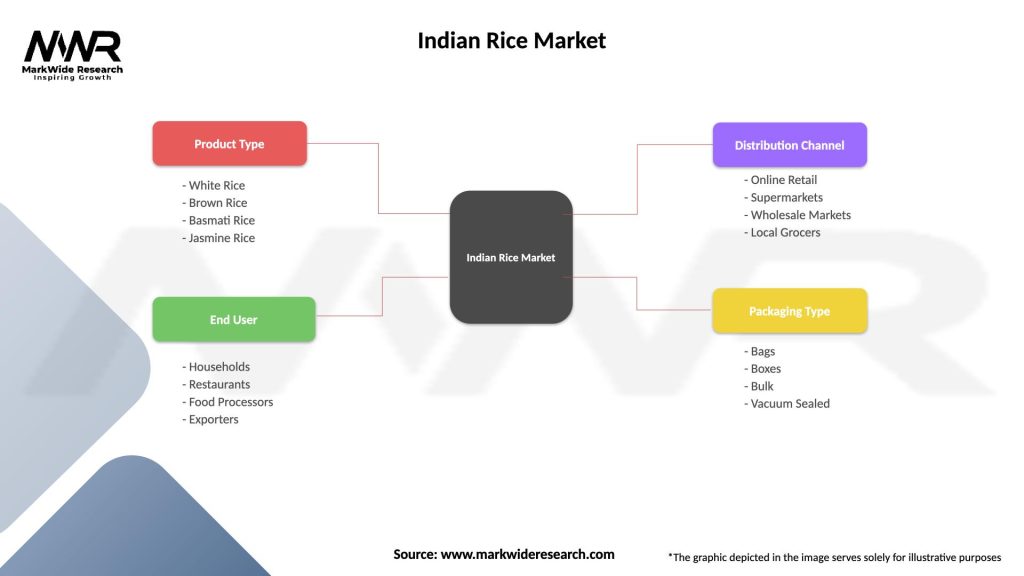
Indian Rice Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | White Rice, Brown Rice, Basmati Rice, Jasmine Rice |
| End User | Households, Restaurants, Food Processors, Exporters |
| Distribution Channel | Online Retail, Supermarkets, Wholesale Markets, Local Grocers |
| Packaging Type | Bags, Boxes, Bulk, Vacuum Sealed |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the Indian Rice Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at