444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2150
The India property and casualty insurance market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving segments within the country’s financial services landscape. This comprehensive sector encompasses various insurance products designed to protect individuals and businesses against property damage, liability claims, and unforeseen casualties. Market dynamics indicate robust growth driven by increasing awareness, regulatory reforms, and expanding economic activities across urban and rural regions.
Digital transformation has emerged as a key catalyst, with insurtech companies and traditional insurers leveraging technology to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. The market demonstrates significant potential with a penetration rate of approximately 1.2% compared to global averages, indicating substantial room for expansion. Regulatory frameworks established by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) continue to shape market development through progressive policies and consumer-centric reforms.
Economic growth and rising disposable incomes have contributed to increased demand for comprehensive insurance coverage. The sector benefits from growing awareness about risk management, particularly among the emerging middle class and small business owners. Infrastructure development and urbanization trends further support market expansion, creating new opportunities for property and casualty insurance products tailored to evolving customer needs.
The India property and casualty insurance market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem of insurance products and services that provide financial protection against property damage, theft, natural disasters, and various liability exposures within the Indian subcontinent. This market encompasses multiple insurance categories including motor insurance, health insurance, home insurance, commercial property coverage, and specialized casualty products designed to meet diverse risk management needs.
Property insurance components focus on protecting physical assets such as residential properties, commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and personal belongings against risks including fire, flood, earthquake, and theft. Casualty insurance elements provide coverage for liability exposures, personal accidents, travel-related risks, and other unforeseen circumstances that could result in financial losses for policyholders.
Market participants include public sector insurers, private insurance companies, foreign direct investment entities, and emerging insurtech platforms that collectively serve millions of customers across urban and rural markets. The sector operates under comprehensive regulatory oversight ensuring consumer protection, fair pricing practices, and sustainable business operations throughout the insurance value chain.
Strategic analysis reveals that the India property and casualty insurance market demonstrates exceptional growth potential driven by demographic advantages, economic expansion, and evolving consumer preferences. The sector benefits from a young population increasingly aware of insurance benefits and willing to invest in comprehensive risk protection solutions.
Technology adoption has accelerated significantly, with digital channels accounting for approximately 35% of new policy acquisitions across major insurance categories. This digital shift has improved accessibility, reduced processing times, and enhanced customer satisfaction levels throughout the insurance journey. Mobile-first strategies have proven particularly effective in reaching previously underserved market segments.
Regulatory support continues to foster market development through initiatives promoting insurance inclusion, product innovation, and competitive pricing structures. Recent policy reforms have simplified claim processes, enhanced transparency, and encouraged new market entrants to introduce innovative insurance solutions. Government initiatives supporting financial inclusion have created additional growth opportunities for property and casualty insurance providers.
Market consolidation trends indicate increasing collaboration between traditional insurers and technology companies, resulting in improved operational efficiency and expanded distribution networks. These partnerships have enabled insurers to leverage data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning capabilities to enhance risk assessment and pricing accuracy.
Consumer behavior analysis reveals significant shifts toward comprehensive insurance coverage, with customers increasingly seeking integrated solutions that address multiple risk exposures through single policy structures. This trend has prompted insurers to develop innovative product bundles combining property, casualty, and specialized coverage options.
Economic prosperity serves as a fundamental driver, with India’s expanding economy creating wealth that requires protection through comprehensive insurance coverage. Rising income levels enable more individuals and businesses to afford premium insurance products, driving market expansion across multiple segments.
Urbanization trends significantly impact market growth as urban populations demonstrate higher insurance awareness and purchasing power. City dwellers face increased property values and liability exposures, creating natural demand for comprehensive property and casualty insurance protection. Infrastructure development in urban areas further amplifies insurance needs for both residential and commercial properties.
Regulatory initiatives promoting financial inclusion have opened new market opportunities, particularly in previously underserved rural and semi-urban areas. Government policies encouraging insurance adoption through tax benefits and mandatory coverage requirements have expanded the customer base substantially. Digital India initiatives have facilitated online insurance transactions and improved accessibility.
Climate change awareness has heightened recognition of natural disaster risks, driving demand for comprehensive property insurance coverage. Increasing frequency of extreme weather events has made property owners more conscious of potential losses and the importance of adequate insurance protection. Business continuity concerns have similarly increased commercial insurance demand.
Technological advancement enables insurers to offer more sophisticated products and services while reducing operational costs. Advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning capabilities allow for better risk assessment, personalized pricing, and improved customer experience throughout the insurance lifecycle.
Low insurance awareness remains a significant challenge, particularly in rural areas where traditional risk management practices often take precedence over formal insurance coverage. Educational initiatives and awareness campaigns require substantial investment and time to change deeply rooted cultural attitudes toward insurance products.
Price sensitivity among consumers creates pressure on insurers to maintain competitive pricing while ensuring adequate coverage and profitability. Many potential customers view insurance as an unnecessary expense rather than essential financial protection, limiting market penetration in price-conscious segments. Economic uncertainties can further reduce discretionary spending on insurance products.
Complex regulatory environment sometimes creates operational challenges for insurers, particularly new market entrants seeking to introduce innovative products or distribution methods. Compliance requirements can increase operational costs and slow product development cycles. Regulatory changes may require significant system modifications and process adjustments.
Distribution challenges persist in reaching remote and rural areas where traditional insurance agents may be scarce and digital infrastructure remains limited. Building effective distribution networks requires substantial investment in training, technology, and local market development. Language barriers and cultural differences add complexity to market expansion efforts.
Claim settlement concerns among consumers can impact market growth, as negative experiences or perceptions about claim processing may discourage insurance adoption. Insurers must balance thorough claim investigation with customer satisfaction to maintain market confidence and growth momentum.
Digital transformation presents unprecedented opportunities for market expansion through innovative distribution channels, enhanced customer engagement, and improved operational efficiency. Insurtech partnerships enable traditional insurers to leverage cutting-edge technology while maintaining regulatory compliance and market expertise.
Rural market penetration offers substantial growth potential as agricultural modernization and rural economic development create new insurance needs. Customized products addressing rural-specific risks, combined with appropriate distribution strategies, can unlock significant market opportunities. Government initiatives supporting rural development provide additional growth catalysts.
Corporate sector expansion creates opportunities for specialized commercial property and casualty insurance products. Growing businesses require comprehensive risk management solutions, including cyber insurance, professional liability coverage, and business interruption protection. Startup ecosystem growth generates demand for innovative insurance solutions tailored to emerging business models.
Product innovation opportunities exist in developing coverage for emerging risks such as climate change, cyber threats, and new technology applications. Insurers can differentiate themselves through specialized products addressing evolving customer needs and market gaps. Parametric insurance and usage-based coverage models present additional innovation opportunities.
Partnership opportunities with banks, fintech companies, and e-commerce platforms can expand distribution reach and improve customer acquisition efficiency. Strategic alliances enable insurers to access new customer segments while leveraging partner expertise and established customer relationships.
Competitive intensity continues to increase as new market entrants challenge established players through innovative products, competitive pricing, and superior customer experience. This competition drives overall market improvement while creating pressure on profit margins and requiring continuous innovation investments.
Customer expectations have evolved significantly, with modern consumers demanding seamless digital experiences, transparent pricing, and rapid claim settlement. Insurers must adapt their operations and service delivery models to meet these heightened expectations while maintaining operational efficiency. Social media influence amplifies customer experiences, making reputation management increasingly critical.
Regulatory evolution shapes market dynamics through policy changes affecting product development, pricing strategies, and operational requirements. Insurers must remain agile to adapt to regulatory modifications while maintaining compliance and competitive positioning. Consumer protection measures continue to influence market practices and business models.
Technology disruption creates both opportunities and challenges as insurers invest in digital capabilities while managing legacy system integration and workforce transformation. Successful technology adoption can provide competitive advantages, while inadequate digital strategies may result in market share loss. Data security concerns require substantial cybersecurity investments.
Economic cycles influence market dynamics through their impact on consumer spending, business investment, and risk perception. Insurers must develop resilient business models capable of performing across various economic conditions while maintaining growth momentum and profitability targets.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research methodologies to ensure accurate and reliable insights into the India property and casualty insurance market. Primary research involves extensive surveys and interviews with industry stakeholders, including insurance executives, regulatory officials, distribution partners, and customers across diverse market segments.
Secondary research incorporates analysis of regulatory filings, industry reports, financial statements, and market data from authoritative sources. This approach provides historical context and trend analysis essential for understanding market evolution and future projections. Data triangulation methods ensure information accuracy and reliability across multiple sources.
Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical modeling and trend analysis to identify market patterns, growth drivers, and performance indicators. Advanced analytics techniques help extract meaningful insights from large datasets while ensuring statistical significance and reliability. Market sizing methodologies employ multiple approaches to validate findings and projections.
Qualitative research includes in-depth interviews with industry experts, focus group discussions with customers, and case study analysis of successful market initiatives. This approach provides contextual understanding of market dynamics, customer behavior, and competitive strategies. Expert opinions help validate quantitative findings and provide forward-looking insights.
Regional analysis incorporates state-level and city-level data collection to understand local market variations, regulatory differences, and demographic influences on insurance adoption. This granular approach enables more accurate market assessment and targeted strategy development for different geographic segments.
Western India dominates the property and casualty insurance market, accounting for approximately 42% of total premium collections due to high urbanization, industrial concentration, and superior economic development. States like Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan demonstrate strong insurance adoption rates driven by commercial activities and higher disposable incomes.
Northern India represents the second-largest market segment with Delhi and Punjab leading in per capita insurance penetration. The region benefits from government sector employment, agricultural prosperity, and growing awareness of insurance benefits. Infrastructure development projects in the region create additional demand for commercial property insurance.
Southern India shows remarkable growth potential with states like Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh demonstrating increasing insurance adoption rates. The region’s technology sector concentration drives demand for specialized commercial insurance products. Educational initiatives in southern states have improved insurance awareness significantly.
Eastern India presents emerging opportunities despite lower current penetration rates, with West Bengal and Odisha showing gradual improvement in insurance adoption. Industrial development and government initiatives supporting financial inclusion create growth prospects. Rural insurance programs show particular promise in this region.
Central India demonstrates steady growth driven by agricultural modernization and industrial development. States like Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh benefit from government policies promoting insurance inclusion. Mining and manufacturing activities in the region generate demand for specialized commercial insurance coverage.
Market leadership remains concentrated among established players who leverage extensive distribution networks, brand recognition, and regulatory expertise to maintain competitive advantages. These companies continue investing in digital transformation and customer experience enhancement to defend market positions.
Competitive strategies focus on digital transformation, customer experience enhancement, and product innovation to differentiate market offerings. Companies invest heavily in technology infrastructure, data analytics capabilities, and distribution network expansion to capture market opportunities.
Market consolidation trends indicate potential mergers and acquisitions as companies seek scale advantages and operational efficiencies. Strategic partnerships between insurers and technology companies create new competitive dynamics while improving service delivery capabilities.
By Product Type: The market encompasses diverse insurance categories serving different customer needs and risk exposures. Motor insurance represents the largest segment, followed by health insurance, property insurance, and specialized commercial products.
By Distribution Channel: Multi-channel distribution strategies combine traditional and digital approaches to maximize market reach and customer convenience.
By Customer Type: Market segmentation reflects diverse customer needs and purchasing behaviors across individual and commercial segments.
Motor Insurance Category continues dominating market share due to mandatory coverage requirements and growing vehicle ownership. This segment benefits from regulatory support and demonstrates consistent growth aligned with automotive industry expansion. Two-wheeler insurance represents a particularly large sub-segment given India’s transportation patterns.
Health Insurance Category shows exceptional growth potential driven by increasing healthcare costs, aging population, and growing health consciousness. The segment benefits from tax incentives and government initiatives promoting health insurance adoption. Family floater policies have gained significant popularity among middle-class families.
Property Insurance Category demonstrates steady growth supported by real estate development, urbanization, and increasing property values. Home insurance adoption remains relatively low but shows improvement with growing awareness and lender requirements. Commercial property insurance benefits from business expansion and regulatory compliance needs.
Liability Insurance Category represents an emerging opportunity as businesses become more aware of litigation risks and regulatory requirements. Professional liability, directors’ and officers’ insurance, and general liability coverage show increasing demand. Cyber insurance emerges as a specialized growth area.
Specialty Insurance Category includes niche products addressing specific risks such as marine insurance, aviation insurance, and agricultural insurance. These segments require specialized expertise but offer higher margins and growth potential. Crop insurance benefits from government support and agricultural modernization.
Insurance Companies benefit from expanding market opportunities, improved operational efficiency through technology adoption, and enhanced customer engagement capabilities. Digital transformation enables cost reduction while improving service quality and market reach.
Customers gain access to comprehensive risk protection, improved service quality, and competitive pricing through increased market competition. Digital platforms enhance convenience and transparency in insurance transactions.
Regulatory Authorities benefit from improved market stability, enhanced consumer protection, and increased financial inclusion through expanded insurance coverage. Market growth contributes to overall economic stability and risk management.
Economic Stakeholders including banks, businesses, and government entities benefit from improved risk management, financial stability, and economic growth facilitated by comprehensive insurance coverage throughout the economy.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Digital-First Strategies have become essential for market success as customers increasingly prefer online insurance transactions and digital customer service. Insurers invest heavily in mobile applications, web platforms, and digital payment systems to meet evolving customer expectations. Artificial intelligence and chatbot integration improve customer interaction efficiency.
Personalization Trends drive development of customized insurance products based on individual risk profiles, lifestyle factors, and specific coverage needs. Advanced data analytics enable insurers to offer tailored solutions while maintaining competitive pricing. Usage-based insurance models gain popularity particularly in motor insurance segments.
Ecosystem Integration involves partnerships between insurers and various service providers to create comprehensive customer solutions. Integration with healthcare providers, automotive companies, and financial services creates value-added propositions. Platform business models emerge as insurers seek to become central hubs for customer risk management needs.
Sustainability Focus influences product development as insurers introduce coverage for climate-related risks and promote environmentally responsible practices. Green insurance products and sustainable business practices become competitive differentiators. ESG considerations increasingly influence investment and underwriting decisions.
Regulatory Technology adoption helps insurers manage compliance requirements more efficiently while reducing operational costs. RegTech solutions automate reporting, monitoring, and compliance processes. Data privacy and cybersecurity measures become increasingly critical for maintaining customer trust and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Reforms continue shaping market evolution through initiatives promoting competition, consumer protection, and market development. Recent policy changes have simplified product approval processes and encouraged innovation while maintaining prudential oversight. Sandbox regulations enable testing of innovative insurance solutions.
Technology Partnerships between traditional insurers and fintech companies accelerate digital transformation and market expansion. These collaborations combine insurance expertise with technological innovation to create superior customer experiences. Insurtech investments have increased significantly as companies seek competitive advantages.
Product Launches focus on addressing emerging risks and underserved market segments through innovative coverage options. Recent introductions include cyber insurance, parametric weather insurance, and specialized small business coverage. Microinsurance products target low-income segments with affordable protection options.
Distribution Evolution involves expansion of digital channels while maintaining traditional agent networks for comprehensive market coverage. Companies invest in omnichannel strategies that provide consistent customer experience across all touchpoints. Bancassurance partnerships continue expanding to leverage existing customer relationships.
Merger and Acquisition Activity reflects industry consolidation trends as companies seek scale advantages and operational synergies. Strategic acquisitions focus on technology capabilities, distribution networks, and specialized market expertise. Foreign investment brings additional capital and international best practices to the market.
MarkWide Research analysis indicates that successful market participants should prioritize digital transformation initiatives while maintaining strong traditional distribution capabilities. Companies must balance technology investment with customer service quality to achieve sustainable competitive advantages in the evolving market landscape.
Customer-Centric Strategies should focus on improving claim settlement processes, enhancing transparency, and providing personalized insurance solutions. Insurers must invest in customer education and awareness programs to expand market penetration, particularly in underserved rural areas. Trust building remains essential for long-term market success.
Product Innovation opportunities exist in developing coverage for emerging risks such as cyber threats, climate change, and new business models. Companies should leverage data analytics and customer insights to create relevant and competitively priced insurance solutions. Parametric insurance models offer potential for addressing specific market needs.
Partnership Development with technology companies, financial institutions, and service providers can accelerate market expansion and capability enhancement. Strategic alliances enable access to new customer segments while sharing development costs and risks. Ecosystem approaches create additional value for customers and competitive differentiation.
Regulatory Engagement remains crucial as policy changes continue shaping market dynamics. Companies should actively participate in regulatory discussions and ensure compliance while advocating for policies that promote market development and innovation. Proactive compliance strategies help avoid regulatory issues and maintain market reputation.
Market expansion is expected to accelerate over the next decade driven by economic growth, increasing awareness, and supportive regulatory policies. The sector anticipates achieving significantly higher penetration rates as insurance becomes more accessible and affordable for diverse customer segments. Digital adoption will continue transforming market dynamics and customer expectations.
Technology integration will deepen with artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technologies becoming standard components of insurance operations. These technologies will enable more accurate risk assessment, automated claim processing, and personalized customer experiences. IoT integration will create new opportunities for usage-based insurance models.
Product evolution will focus on addressing emerging risks and changing customer needs through innovative coverage options and flexible policy structures. Climate-related insurance products, cyber coverage, and specialized commercial insurance will experience substantial growth. Microinsurance will expand to serve previously excluded market segments.
Distribution transformation will continue with digital channels gaining market share while traditional agents adapt to provide value-added services. Omnichannel strategies will become essential for comprehensive market coverage and customer satisfaction. Direct-to-consumer models will grow particularly among younger demographics.
Regulatory evolution will support market development through policies promoting innovation, competition, and consumer protection. Expected reforms include simplified product approval processes, enhanced digital transaction frameworks, and expanded foreign investment opportunities. MWR projections indicate the market will achieve approximately 12-15% annual growth over the medium term, driven by these favorable conditions and expanding economic opportunities.
The India property and casualty insurance market presents exceptional growth opportunities driven by favorable demographics, economic expansion, and supportive regulatory frameworks. Digital transformation initiatives, increasing insurance awareness, and evolving customer expectations create a dynamic environment for market participants to achieve sustainable growth and competitive success.
Strategic success will require balanced approaches combining technology investment with customer service excellence, product innovation with operational efficiency, and market expansion with regulatory compliance. Companies that effectively navigate these requirements while building strong customer relationships will capture the substantial opportunities available in this rapidly evolving market.
Future market leaders will be those organizations that successfully integrate digital capabilities with traditional insurance expertise, develop innovative products addressing emerging risks, and build comprehensive distribution networks serving diverse customer segments across India’s vast and varied market landscape. The sector’s continued evolution promises significant value creation for all stakeholders participating in this dynamic and growing market.
What is Property & Casualty Insurance?
Property & Casualty Insurance refers to a type of insurance that provides coverage for property loss and liability for damages to others. It encompasses various policies, including homeowners, auto, and commercial insurance, protecting individuals and businesses from financial losses due to unforeseen events.
What are the key players in the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market?
Key players in the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market include ICICI Lombard, HDFC ERGO, and Bajaj Allianz. These companies offer a range of insurance products catering to both individual and commercial clients, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market?
The growth of the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market is driven by increasing awareness of insurance products, rising disposable incomes, and the expansion of the middle class. Additionally, the growth of the real estate sector and increasing vehicle ownership contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market face?
The India Property & Casualty Insurance Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, intense competition among insurers, and the need for technological advancements. Additionally, low penetration rates in rural areas pose a significant challenge for market growth.
What opportunities exist in the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market?
Opportunities in the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market include the potential for digital transformation, the introduction of innovative insurance products, and the growing demand for customized coverage solutions. The increasing focus on risk management among businesses also presents new avenues for growth.
What trends are shaping the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market?
Trends shaping the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market include the rise of insurtech companies, the adoption of data analytics for risk assessment, and the growing emphasis on customer-centric services. Additionally, sustainability initiatives are becoming increasingly important in shaping insurance offerings.
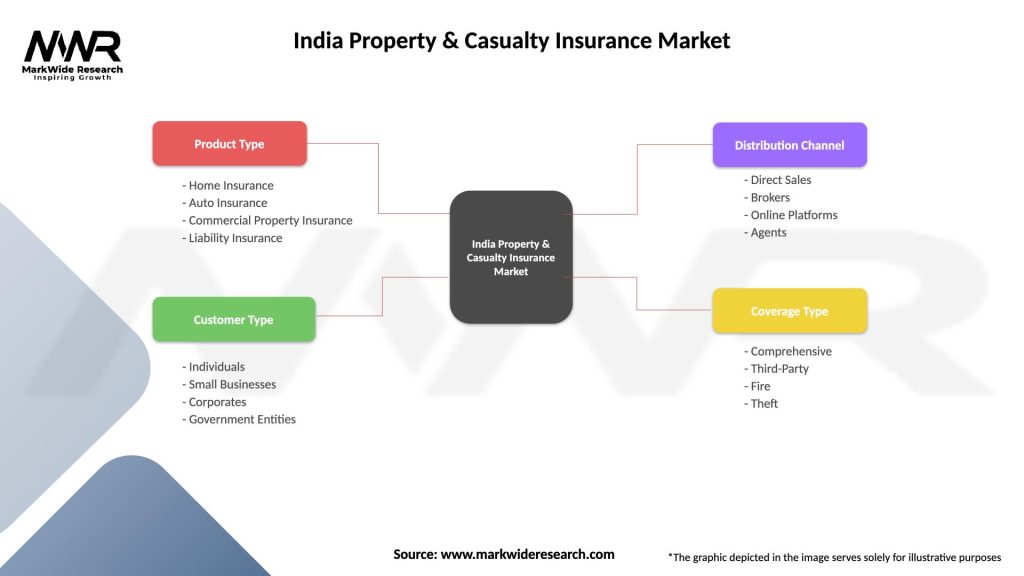
India Property & Casualty Insurance Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Home Insurance, Auto Insurance, Commercial Property Insurance, Liability Insurance |
| Customer Type | Individuals, Small Businesses, Corporates, Government Entities |
| Distribution Channel | Direct Sales, Brokers, Online Platforms, Agents |
| Coverage Type | Comprehensive, Third-Party, Fire, Theft |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the India Property & Casualty Insurance Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at