444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at
Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2450
The power market in India plays a crucial role in the country’s overall economic development. It encompasses the generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption of electricity across various sectors. With a population of over 1.3 billion people and rapid industrialization, India’s power market is dynamic and constantly evolving. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the India power market, including its meaning, executive summary, key market insights, market drivers, market restraints, market opportunities, market dynamics, regional analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation, category-wise insights, key benefits for industry participants and stakeholders, SWOT analysis, market key trends, Covid-19 impact, key industry developments, analyst suggestions, future outlook, and conclusion.
The India power market refers to the entire ecosystem involved in the production, transmission, distribution, and consumption of electrical power within the country. It includes power generation plants, transmission and distribution networks, electricity distribution companies, consumers, and regulatory bodies. The power market encompasses various sources of energy, such as thermal power, hydroelectric power, nuclear power, renewable energy sources like solar and wind, and emerging technologies like energy storage.
Executive Summary
The India power market is a significant sector contributing to the country’s economic growth. It has witnessed substantial investments in power generation capacity, transmission infrastructure, and renewable energy projects. The government’s initiatives, such as the “Power for All” program and the promotion of renewable energy, have driven the growth of the power market. However, challenges related to grid reliability, transmission losses, and financial viability of distribution companies persist. The power market presents opportunities for innovation, technology adoption, and sustainable energy solutions.

Important Note: The companies listed in the image above are for reference only. The final study will cover 18–20 key players in this market, and the list can be adjusted based on our client’s requirements.
Key Market Insights
Market Drivers
Market Restraints
Market Opportunities
Market Dynamics
The India power market is driven by a combination of factors, including government policies, economic growth, technological advancements, environmental concerns, and consumer demand. The market dynamics are influenced by the interplay of supply and demand, regulatory frameworks, pricing mechanisms, investment climate, and technological innovations. Balancing the need for reliable and affordable power supply with sustainability and environmental goals remains a key challenge for market stakeholders.
Regional Analysis
The power market in India varies across different regions due to variations in energy resources, demand patterns, infrastructure development, and policy frameworks. Different states have diverse energy mixes, with some having a higher reliance on thermal power, while others emphasize renewable energy sources. Regional disparities in power infrastructure and electricity access also exist, with urban areas typically having better power supply than rural and remote areas. Government initiatives, such as state-level renewable energy policies, influence the regional dynamics of the power market.
Competitive Landscape
Leading Companies in the India Power Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.

Segmentation
The India power market can be segmented based on various factors:
Category-wise Insights
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders
SWOT Analysis
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Market Key Trends
Covid-19 Impact
The Covid-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the India power market. The lockdown measures and disruptions in economic activities led to a temporary decline in power demand, particularly in commercial and industrial sectors. However, the power sector demonstrated resilience by ensuring the continued supply of electricity to essential services and households. The pandemic highlighted the importance of a robust and reliable power infrastructure to support healthcare facilities, remote work, and online education. The crisis also emphasized the need to accelerate the transition to cleaner and sustainable energy sources.
Key Industry Developments
Analyst Suggestions
Future Outlook
The future of the India power market is expected to be shaped by ongoing energy transitions, technological advancements, and policy interventions. The focus will continue to shift towards renewable energy, with solar and wind power playing a dominant role. Investments in grid modernization, smart grid technologies, and energy storage will facilitate the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources. The power market will witness increased consumer engagement, energy efficiency measures, and digital solutions for better power management. Government initiatives, regulatory reforms, and collaborations between public and private stakeholders will be crucial for a sustainable and resilient power sector.
Conclusion
The India power market is undergoing significant transformations driven by renewable energy adoption, grid modernization, and consumer-centric approaches. Despite challenges related to grid reliability, financial viability of distribution companies, and environmental concerns, the power market presents immense opportunities for stakeholders. The industry must focus on sustainable and clean energy solutions, technological innovations, and efficient power infrastructure to meet the growing demand for electricity while ensuring environmental sustainability. The India power market is poised for growth, and with the right policies and investments, it can contribute to the country’s sustainable development goals and economic progress.
What is Power?
Power refers to the rate at which energy is transferred or converted. In the context of the India Power Market, it encompasses various forms of energy generation, distribution, and consumption, including electricity from renewable and non-renewable sources.
What are the key players in the India Power Market?
Key players in the India Power Market include Tata Power, Adani Power, and NTPC Limited, which are involved in electricity generation and distribution. These companies play a significant role in shaping the energy landscape in India, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the India Power Market?
The India Power Market is driven by increasing energy demand due to urbanization, government initiatives promoting renewable energy, and investments in infrastructure. Additionally, the push for energy efficiency and sustainability is also contributing to market growth.
What challenges does the India Power Market face?
The India Power Market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles, inadequate infrastructure, and financial issues among power distribution companies. These factors can hinder the efficient delivery of electricity and affect overall market stability.
What opportunities exist in the India Power Market?
Opportunities in the India Power Market include the expansion of renewable energy projects, advancements in smart grid technology, and increased investment in energy storage solutions. These developments can enhance energy security and sustainability.
What trends are shaping the India Power Market?
Trends in the India Power Market include a shift towards renewable energy sources, the adoption of smart grid technologies, and a focus on energy efficiency. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on decentralized energy generation and electric mobility.
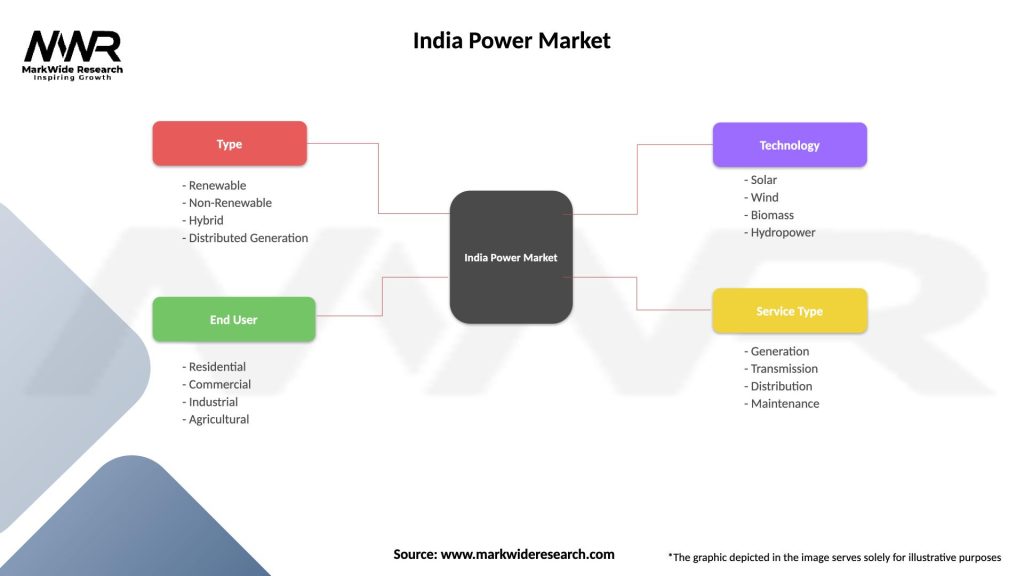
India Power Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Renewable, Non-Renewable, Hybrid, Distributed Generation |
| End User | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural |
| Technology | Solar, Wind, Biomass, Hydropower |
| Service Type | Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Maintenance |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading Companies in the India Power Market:
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at