444 Alaska Avenue
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
+1 424 999 9627
24/7 Customer Support
sales@markwideresearch.com
Email us at
Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at

Corporate User License
Unlimited User Access, Post-Sale Support, Free Updates, Reports in English & Major Languages, and more
$2150
The India epoxy resin industry market represents one of the most dynamic and rapidly expanding segments within the country’s chemical manufacturing sector. Epoxy resins have emerged as critical materials across diverse industrial applications, driving substantial growth in manufacturing, construction, automotive, and electronics sectors. The market demonstrates remarkable resilience and adaptability, with domestic production capacity expanding at an impressive 8.5% CAGR over recent years.
Industrial demand for epoxy resins continues to surge, particularly in infrastructure development projects and advanced manufacturing applications. The market benefits from India’s strategic position as a manufacturing hub, with government initiatives supporting chemical industry growth through favorable policies and investment incentives. Regional distribution shows concentrated activity in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu, accounting for approximately 70% of total production capacity.
Technology advancement plays a crucial role in market evolution, with manufacturers investing heavily in research and development to create specialized formulations. The industry showcases strong integration with downstream sectors, particularly in coatings and adhesives applications, which represent the largest consumption segments. Export potential remains significant, with Indian manufacturers increasingly targeting international markets through quality improvements and competitive pricing strategies.
The India epoxy resin industry market refers to the comprehensive ecosystem encompassing production, distribution, and consumption of epoxy resin products within the Indian subcontinent. Epoxy resins are thermosetting polymers formed through the reaction of epoxide compounds with curing agents, creating materials with exceptional adhesive, mechanical, and chemical resistance properties.
Market scope includes various epoxy resin types such as bisphenol-A based resins, bisphenol-F based resins, novolac resins, and specialty formulations designed for specific applications. The industry encompasses raw material suppliers, resin manufacturers, formulators, distributors, and end-user industries creating a complex value chain that supports diverse economic sectors.
Industrial significance extends beyond traditional applications, with epoxy resins serving critical roles in advanced composites, electronic encapsulation, marine coatings, and high-performance adhesives. The market definition includes both liquid and solid epoxy systems, water-based formulations, and solvent-free alternatives that address environmental concerns while maintaining performance standards.
Market dynamics in India’s epoxy resin industry reflect strong fundamentals driven by robust industrial growth and infrastructure development initiatives. The sector demonstrates exceptional resilience with consistent demand growth across multiple application segments, particularly in construction, automotive, and electronics industries. Manufacturing capabilities have expanded significantly, with domestic producers achieving 85% self-sufficiency in standard epoxy resin grades.
Competitive landscape features a mix of multinational corporations and domestic players, with increasing focus on product innovation and customer-specific solutions. Technology adoption remains a key differentiator, with leading manufacturers investing in advanced production processes and quality control systems. The market benefits from favorable regulatory environment and government support for chemical industry development.
Growth trajectory indicates sustained expansion opportunities, particularly in emerging applications such as wind energy, aerospace, and advanced electronics. Regional development shows balanced growth across major industrial clusters, with new capacity additions planned in strategic locations. Export performance continues to strengthen, with Indian manufacturers gaining recognition for quality and cost competitiveness in international markets.
Market penetration analysis reveals significant opportunities across various industrial segments, with construction and automotive sectors leading consumption patterns. Product innovation drives market differentiation, particularly in specialty formulations designed for high-performance applications. The industry demonstrates strong backward integration capabilities, with major players controlling raw material supply chains.
Technology trends indicate increasing adoption of water-based and solvent-free formulations, addressing environmental regulations and sustainability requirements. Supply chain optimization remains critical, with manufacturers focusing on raw material security and cost management strategies.
Infrastructure development serves as the primary catalyst for epoxy resin demand growth, with government initiatives in smart cities, highways, and industrial corridors creating substantial consumption opportunities. Construction industry expansion drives consistent demand for flooring systems, protective coatings, and structural adhesives, supported by urbanization trends and commercial development projects.
Automotive sector transformation creates significant growth opportunities through lightweighting initiatives and advanced coating requirements. Electric vehicle adoption generates new demand patterns for specialized epoxy formulations in battery systems, electronic components, and composite structures. Manufacturing sector growth across electronics, appliances, and industrial equipment supports steady consumption increases.
Government policy support through Make in India initiatives and chemical industry promotion schemes encourages domestic production expansion and technology upgrades. Environmental regulations paradoxically drive demand for high-performance epoxy systems that enable longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements. Export market opportunities provide additional growth avenues as Indian manufacturers gain international recognition for quality and competitiveness.
Technology advancement in application techniques and product formulations creates new market segments and improves performance characteristics. Raw material availability improvements through domestic production expansion and strategic partnerships enhance supply chain stability and cost competitiveness.
Raw material price volatility presents ongoing challenges for epoxy resin manufacturers, particularly regarding bisphenol-A and epichlorohydrin feedstock costs. Import dependency for specialized raw materials creates supply chain vulnerabilities and currency exchange risks that impact production planning and pricing strategies.
Environmental regulations impose increasing compliance costs and technical challenges, particularly regarding volatile organic compound emissions and waste management requirements. Health and safety concerns associated with epoxy resin handling and curing processes require substantial investments in worker protection and facility upgrades.
Competition from alternative materials such as polyurethanes, acrylics, and bio-based polymers creates pressure on traditional epoxy applications. Technical skill shortages in application and processing techniques limit market penetration in certain segments and geographic regions.
Economic cyclicality in key end-use industries creates demand fluctuations that impact production planning and capacity utilization. Quality consistency challenges in domestic production sometimes limit acceptance in high-performance applications, requiring continuous investment in process improvements and quality control systems.
Emerging applications in renewable energy, particularly wind turbine blade manufacturing and solar panel encapsulation, present substantial growth opportunities for specialized epoxy formulations. Infrastructure modernization projects create demand for high-performance protective coatings and structural repair systems with extended service life requirements.
Electronics industry expansion offers significant potential through semiconductor packaging, printed circuit board applications, and electronic component encapsulation. Aerospace sector development creates opportunities for advanced composite applications and specialized adhesive systems meeting stringent performance requirements.
Export market expansion provides growth avenues through competitive manufacturing costs and improving quality standards. Specialty formulation development enables premium pricing and market differentiation through customer-specific solutions and advanced performance characteristics.
Sustainability initiatives drive demand for bio-based epoxy resins and environmentally friendly formulations, creating new market segments and competitive advantages. Digital transformation in manufacturing processes enables improved efficiency, quality control, and customer service capabilities.
Regional market development in tier-2 and tier-3 cities offers expansion opportunities as industrial activity spreads beyond traditional manufacturing hubs. Technology partnerships with international companies provide access to advanced formulations and application techniques.
Supply-demand equilibrium in the India epoxy resin market reflects complex interactions between production capacity, raw material availability, and end-user consumption patterns. Market forces demonstrate increasing sophistication as manufacturers develop specialized products for niche applications while maintaining cost competitiveness in commodity segments.
Competitive intensity continues to escalate with new market entrants and capacity expansions by existing players. Price dynamics show correlation with raw material costs and international market trends, while quality differentiation becomes increasingly important for market positioning and customer retention.
Technology evolution drives continuous product development and process improvements, with manufacturers investing in research and development to maintain competitive advantages. Customer relationships evolve toward long-term partnerships and technical collaboration, particularly in specialized applications requiring customized solutions.
Regulatory environment influences market dynamics through environmental standards, safety requirements, and trade policies. Economic factors including GDP growth, industrial production, and infrastructure spending directly impact demand patterns and market expansion opportunities.
Comprehensive market analysis employs multiple research approaches combining primary and secondary data sources to ensure accuracy and reliability. Primary research includes extensive interviews with industry executives, technical experts, and end-user representatives across major consumption segments and geographic regions.
Secondary research encompasses analysis of industry publications, government statistics, trade association data, and company financial reports. Market sizing methodology utilizes bottom-up and top-down approaches, cross-validated through multiple data sources and expert consultations.
Data validation processes include triangulation of information from independent sources and verification through industry expert reviews. Quantitative analysis employs statistical modeling and trend analysis to project market developments and identify growth patterns.
Qualitative insights derive from in-depth discussions with market participants, technology providers, and regulatory authorities. Market segmentation analysis considers product types, applications, end-user industries, and geographic distribution patterns to provide comprehensive market understanding.
Western India dominates the epoxy resin market landscape, with Gujarat and Maharashtra accounting for approximately 55% of total production capacity. Gujarat’s chemical corridor provides strategic advantages through integrated petrochemical complexes, port connectivity, and established industrial infrastructure. Maharashtra’s industrial base supports strong demand from automotive, electronics, and construction sectors.
Southern India represents a rapidly growing market segment, with Tamil Nadu and Karnataka leading consumption growth at 11% annually. Bangalore’s electronics hub creates substantial demand for specialized epoxy formulations, while Chennai’s automotive cluster drives consumption in coating and adhesive applications.
Northern India shows balanced growth across Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Punjab, supported by construction activity and industrial development. Delhi NCR region serves as a major consumption center for construction and infrastructure applications.
Eastern India demonstrates emerging potential with West Bengal and Odisha developing industrial capabilities and infrastructure projects. Regional distribution networks continue expanding to serve growing demand in tier-2 and tier-3 cities across all regions.
Market leadership reflects a diverse competitive environment with multinational corporations, domestic conglomerates, and specialized manufacturers competing across different segments. Strategic positioning varies from cost leadership in commodity grades to differentiation through specialty formulations and technical services.
Competitive strategies emphasize product innovation, customer service excellence, and supply chain optimization. Market consolidation trends indicate potential for strategic partnerships and acquisitions as companies seek scale advantages and technology access.
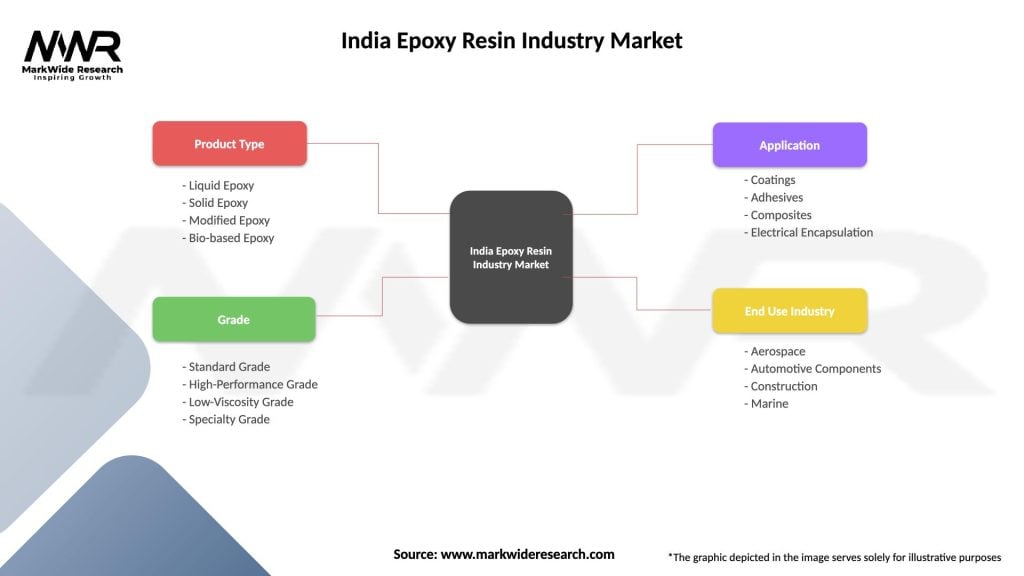
Product-based segmentation reveals distinct market characteristics across different epoxy resin types and formulations. Application segmentation demonstrates varying growth rates and profitability levels across end-use industries and specific use cases.
By Product Type:
By Application:
By End-User Industry:
Construction applications demonstrate steady growth driven by infrastructure development and building modernization projects. Flooring systems represent the largest sub-segment, with industrial and commercial applications showing particular strength. Protective coatings for concrete structures create substantial demand in infrastructure projects and industrial facilities.
Automotive segment shows dynamic evolution with increasing adoption of composite materials and advanced coating systems. Lightweighting initiatives drive demand for structural adhesives and composite applications, while electric vehicle development creates new opportunities in battery systems and electronic components.
Electronics applications require specialized formulations with precise properties for semiconductor packaging and circuit board applications. Miniaturization trends demand increasingly sophisticated epoxy systems with enhanced thermal and electrical properties. 5G technology deployment creates new requirements for high-frequency applications.
Industrial maintenance represents a stable demand segment for repair and refurbishment applications across various industries. Marine coatings show growth potential with expanding shipbuilding and offshore activities. Wind energy applications emerge as a significant growth driver for composite blade manufacturing.
Manufacturers benefit from expanding market opportunities across diverse application segments and geographic regions. Product diversification enables risk mitigation and revenue optimization through balanced portfolio management. Technology advancement provides competitive advantages and premium pricing opportunities in specialized segments.
Raw material suppliers gain from stable demand growth and long-term supply relationships with epoxy resin manufacturers. Backward integration opportunities create value addition potential and supply chain security benefits.
End-users benefit from improved product performance, technical support, and customized solutions addressing specific application requirements. Cost optimization through advanced formulations and application techniques enhances overall project economics and operational efficiency.
Distributors and traders capitalize on expanding market reach and product portfolio diversification opportunities. Technical service capabilities create differentiation and customer loyalty advantages in competitive markets.
Government stakeholders benefit from industrial development, employment generation, and export revenue contributions. Environmental benefits accrue from advanced formulations enabling longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Opportunities:
Threats:
Sustainability transformation drives development of bio-based epoxy resins and environmentally friendly formulations addressing regulatory requirements and customer preferences. Circular economy principles influence product design and manufacturing processes, with emphasis on recyclability and reduced environmental impact.
Digitalization adoption enhances manufacturing efficiency, quality control, and customer service capabilities through advanced process monitoring and data analytics. Industry 4.0 integration enables predictive maintenance, automated quality control, and optimized production scheduling.
Customization demand increases as end-users seek specialized formulations tailored to specific application requirements and performance criteria. Technical service expansion becomes crucial for market differentiation and customer retention in competitive segments.
Supply chain localization gains importance as companies seek to reduce dependency on imports and enhance supply security. Strategic partnerships between manufacturers and raw material suppliers create integrated value chains and cost optimization opportunities.
Application innovation drives market expansion into new segments such as 3D printing, flexible electronics, and advanced composites. Performance enhancement through nanotechnology integration and hybrid formulations creates premium market opportunities.
Capacity expansion initiatives by major manufacturers indicate strong confidence in market growth prospects and long-term demand sustainability. Technology upgrades focus on process efficiency, product quality, and environmental compliance improvements.
Strategic acquisitions and partnerships reshape competitive landscape as companies seek scale advantages and technology access. International collaborations enable knowledge transfer and market expansion opportunities for domestic players.
Product launches emphasize specialty formulations for emerging applications and enhanced performance characteristics. Research and development investments increase as companies recognize the importance of innovation for competitive positioning.
Regulatory compliance initiatives drive industry-wide improvements in safety standards, environmental protection, and product quality. Certification programs enhance market credibility and enable access to premium applications and export markets.
Infrastructure development includes new production facilities, research centers, and distribution networks supporting market expansion and customer service enhancement. Sustainability initiatives focus on energy efficiency, waste reduction, and alternative raw material development.
MarkWide Research analysis indicates that companies should prioritize specialty product development and technical service capabilities to differentiate in competitive markets. Investment focus should emphasize research and development, quality systems, and customer application support to capture premium market opportunities.
Strategic recommendations include developing partnerships with raw material suppliers to ensure supply security and cost competitiveness. Market expansion strategies should target emerging applications in renewable energy, electronics, and advanced manufacturing sectors.
Technology adoption priorities should include digitalization of manufacturing processes, advanced quality control systems, and customer relationship management platforms. Sustainability initiatives become increasingly important for regulatory compliance and market positioning.
Export market development requires investment in quality certifications, brand building, and distribution network establishment in target regions. Talent development programs should focus on technical expertise, application knowledge, and customer service capabilities.
Risk management strategies should address raw material price volatility, regulatory changes, and competitive pressures through diversification and operational flexibility. Long-term planning should consider emerging technologies, changing customer requirements, and evolving market dynamics.
Market trajectory indicates sustained growth opportunities driven by infrastructure development, industrial expansion, and emerging application segments. Technology evolution will continue shaping product development and manufacturing processes, with emphasis on performance enhancement and environmental compatibility.
Demand patterns suggest increasing sophistication as end-users seek specialized solutions and technical support. Supply chain evolution will emphasize localization, sustainability, and digital integration to enhance efficiency and responsiveness.
Competitive dynamics will intensify as market participants invest in differentiation strategies and customer relationship development. Innovation cycles will accelerate with focus on bio-based materials, advanced formulations, and application-specific solutions.
Regulatory environment will continue evolving toward stricter environmental and safety standards, driving industry adaptation and innovation. Market consolidation may occur as companies seek scale advantages and technology access through strategic partnerships and acquisitions.
Export potential remains significant with Indian manufacturers expected to gain 25% international market share in cost-sensitive segments over the next five years. MWR projections indicate continued expansion in specialty applications and emerging markets, supported by improving quality standards and competitive positioning.
The India epoxy resin industry market demonstrates exceptional growth potential and strategic importance within the country’s chemical manufacturing sector. Market fundamentals remain strong, supported by robust domestic demand, expanding industrial base, and improving manufacturing capabilities. The industry’s evolution toward specialty applications and technical service excellence positions it well for sustained growth and international competitiveness.
Strategic opportunities abound across emerging applications, export markets, and technology advancement initiatives. Industry participants who invest in innovation, quality systems, and customer relationships will be best positioned to capitalize on market expansion and achieve sustainable competitive advantages. The sector’s contribution to India’s manufacturing economy and export potential continues to strengthen, making it an attractive investment destination for both domestic and international players.
Future success will depend on the industry’s ability to adapt to changing market requirements, environmental regulations, and technological developments while maintaining cost competitiveness and operational excellence. The India epoxy resin industry market stands poised for continued growth and increasing global significance in the years ahead.
What is Epoxy Resin?
Epoxy resin is a type of synthetic polymer that is widely used in various applications due to its excellent adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and durability. It is commonly utilized in coatings, adhesives, and composite materials across industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics.
What are the key players in the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market?
Key players in the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market include companies like Aditya Birla Chemicals, Hexion Inc., and BASF SE, which are known for their innovative products and strong market presence. These companies focus on developing advanced epoxy formulations for diverse applications, among others.
What are the growth factors driving the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market?
The growth of the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market is driven by increasing demand from the automotive and construction sectors, where epoxy resins are used for coatings and adhesives. Additionally, the rise in infrastructure development and the trend towards lightweight materials in manufacturing contribute to market expansion.
What challenges does the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market face?
The India Epoxy Resin Industry Market faces challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and environmental regulations regarding the use of certain chemicals. These factors can impact production costs and limit the availability of specific epoxy formulations.
What opportunities exist in the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market?
Opportunities in the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market include the growing demand for bio-based epoxy resins and advancements in technology that enhance the performance of epoxy products. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable materials presents new avenues for innovation and market growth.
What trends are shaping the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market?
Trends shaping the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market include the shift towards eco-friendly formulations and the integration of smart technologies in epoxy applications. Furthermore, the expansion of the electric vehicle market is driving the need for advanced epoxy materials in battery and component manufacturing.
India Epoxy Resin Industry Market
| Segmentation Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Liquid Epoxy, Solid Epoxy, Modified Epoxy, Bio-based Epoxy |
| Grade | Standard Grade, High-Performance Grade, Low-Viscosity Grade, Specialty Grade |
| Application | Coatings, Adhesives, Composites, Electrical Encapsulation |
| End Use Industry | Aerospace, Automotive Components, Construction, Marine |
Please note: The segmentation can be entirely customized to align with our client’s needs.
Leading companies in the India Epoxy Resin Industry Market
Please note: This is a preliminary list; the final study will feature 18–20 leading companies in this market. The selection of companies in the final report can be customized based on our client’s specific requirements.
Trusted by Global Leaders
Fortune 500 companies, SMEs, and top institutions rely on MWR’s insights to make informed decisions and drive growth.
ISO & IAF Certified
Our certifications reflect a commitment to accuracy, reliability, and high-quality market intelligence trusted worldwide.
Customized Insights
Every report is tailored to your business, offering actionable recommendations to boost growth and competitiveness.
Multi-Language Support
Final reports are delivered in English and major global languages including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Russian, and more.
Unlimited User Access
Corporate License offers unrestricted access for your entire organization at no extra cost.
Free Company Inclusion
We add 3–4 extra companies of your choice for more relevant competitive analysis — free of charge.
Post-Sale Assistance
Dedicated account managers provide unlimited support, handling queries and customization even after delivery.
GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


GET A FREE SAMPLE REPORT
This free sample study provides a complete overview of the report, including executive summary, market segments, competitive analysis, country level analysis and more.
ISO AND IAF CERTIFIED


Suite #BAA205 Torrance, CA 90503 USA
24/7 Customer Support
Email us at